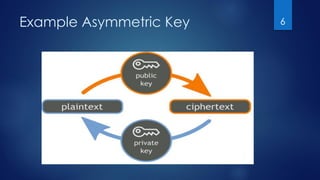
This document outlines types of cryptography based on key usage: symmetric, which relies on a single, shared key for both encryption and decryption, and asymmetric, which uses a public and a private key. It describes the principles of cryptographic techniques like substitution and transposition ciphers, emphasizing that encryption strength is influenced by key length. The text details the process of text encryption and the mathematical functions involved, ensuring user privacy against potential intrusions.