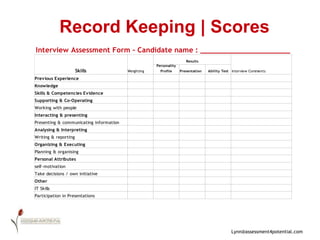
The document outlines the processes involved in selection and recruitment, emphasizing the importance of attracting qualified candidates and employing techniques to appoint suitable individuals. It defines key components such as job analysis, job descriptions, and person specifications, while highlighting the use of various recruitment sources and assessment methods including psychometric testing. Additionally, it provides a detailed guide on structuring interviews and the importance of record-keeping throughout the selection process.














![Attract Candidates Internal Notice-boards etc External Job Centres Employment Agencies Local Newspapers Trade Journals Job fairs CV or Application Form? External [cont] Engage networks of friends and colleagues Business/society meetings Internet [inc craigslist, job boards, etc] Local colleges and trade schools](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonselectionforuploading-110708111045-phpapp02/85/Presentation-on-selection-for-uploading-15-320.jpg)
![Advertisement Check-list Salary or salary guide Whether the role is full-time or permanent or a short-term contract (if not implicitly clear from elsewhere in the advert) Oher package details or guide (pension, car etc) Explanation of recruitment process Response and application instructions [include dates] Contact details as necessary, for example, address, phone, fax, email, etc. Job and or advert reference (advert references help you analyse results from different adverts for the same job) Website address | corporate branding Quality accreditations, for example in the UK, Investor in People Equal opportunities statement Job title, Job base location Employer or recruitment agency/consultancy Succinct description of business/organization/division activity and market position and aims To whom the position reports - or other indication of where the role is in the structure Outline of job role and purpose - expressed in the 'second-person' (you, your, etc) Indication of scale, size, responsibility, time-scale, and territory of role Outline of ideal candidate profile - expressed in 'second-person' Indicate qualifications and experience required (which could be incorporated within candidate profile)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonselectionforuploading-110708111045-phpapp02/85/Presentation-on-selection-for-uploading-16-320.jpg)