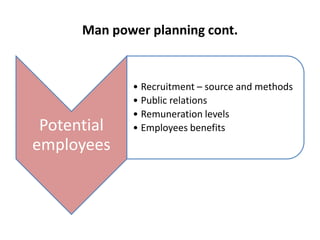
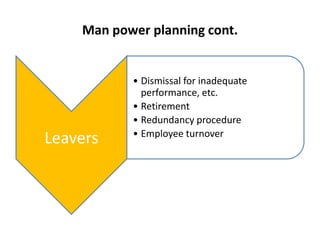
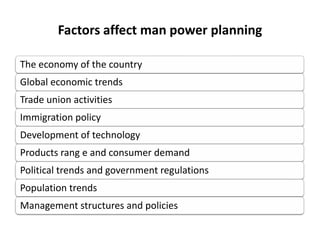
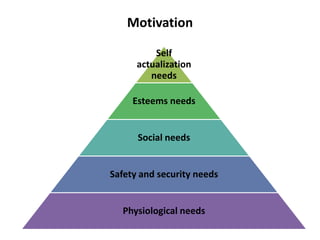
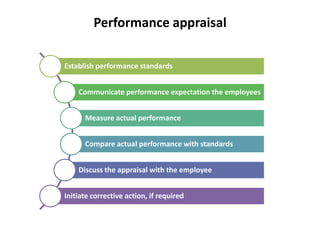
This document provides an overview of human resource management functions including: HR planning, recruitment and selection, induction, training and development, motivation, health and safety, performance appraisal, discipline, employment legislation, and remuneration. It describes the purpose of HR planning to meet organizational goals through forecasting workforce needs. Key HR functions like recruitment, selection, training and performance appraisal are summarized. Factors influencing motivation and components of an effective remuneration system are also highlighted at a high level.