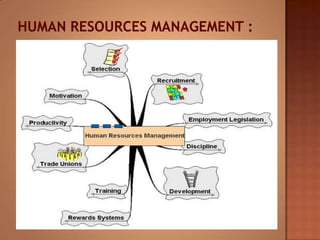
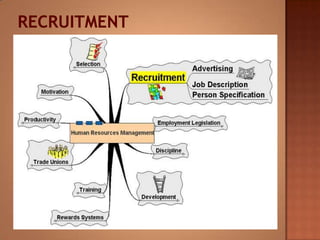
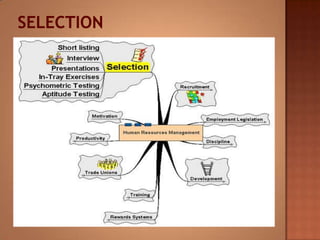
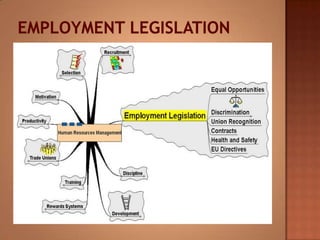
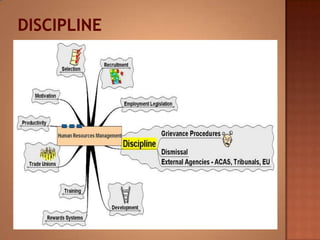
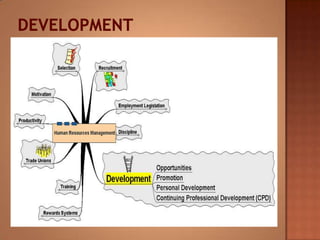
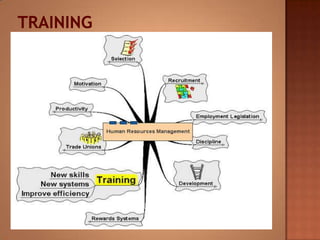
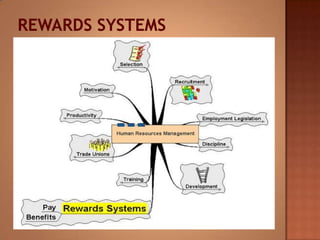
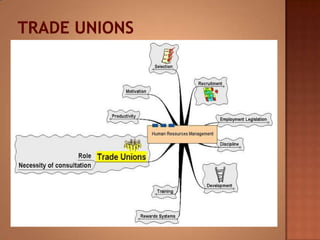
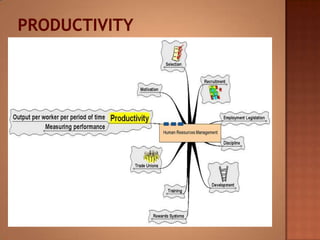
This document discusses human resource management. It covers recruitment, selection, employment legislation, development, trade unions, and productivity. Recruitment involves identifying job vacancies and notifying potential employees. Selection assesses candidates and appoints a post holder, often through interviews, testing, and exercises. Employment legislation regulates areas like race, gender, and disability to protect employees. Development adds to employees' skills through training. Trade unions are important for building relationships and negotiating change. Productivity measures workers' contributions through appraisal and performance reviews. Overall, effective HRM engages employees to build a competitive advantage through strategic leadership and two-way communication.