This document discusses reliability engineering and methods for estimating reliability. It covers:
1. Key principles of reliability design including component selection, safety factors, and redundancy.
2. The design process involving requirements, specifications, basic and detailed design, and development.
3. Four methods for estimating reliability - test-retest, parallel forms, split-half, and internal consistency.
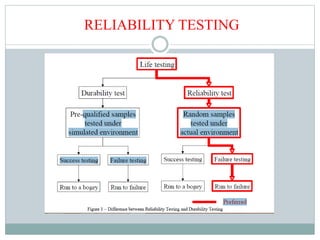
4. The purposes of reliability testing to evaluate feasibility and optimize performance and reliability under varying conditions.