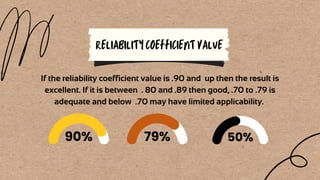
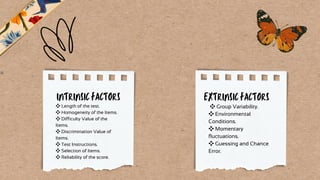
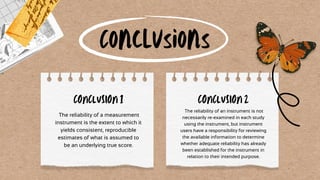
Reliability refers to the consistency and repeatability of measurements or test results. There are several types of reliability: test-retest, parallel forms, split-half, and internal consistency. Factors that can affect reliability include test length and homogeneity, item difficulty and discrimination, instructions, selection of items, and environmental conditions during testing. Reliability is important and can be improved by creating clear measurement directions and expanding the sample of test items.