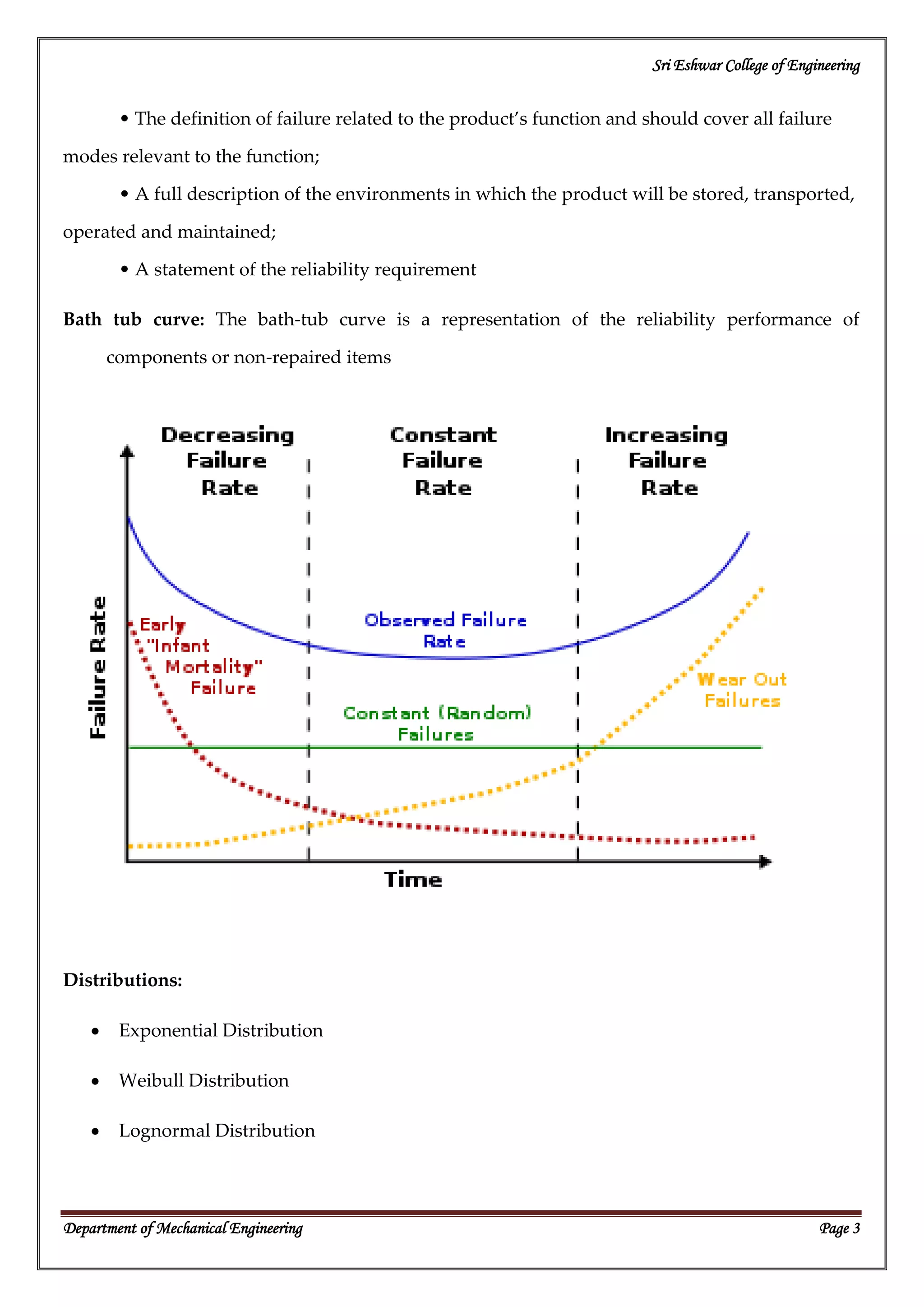
Reliability is associated with unexpected failures and understanding why failures occur helps improve reliability. Failures can be caused by design flaws, overstressing, wear-out, variation, wrong specifications, misuse, or operating outside intended environments. Measuring reliability is important for safety, competitiveness, profits, costs, reputation, and involves defining failure modes, operating environments, and reliability requirements. The bath tub curve represents reliability over time with high failure rates early on, low steady rates later, and increasing rates again over the lifetime. Common distributions used to model reliability include exponential, Weibull, and lognormal distributions.