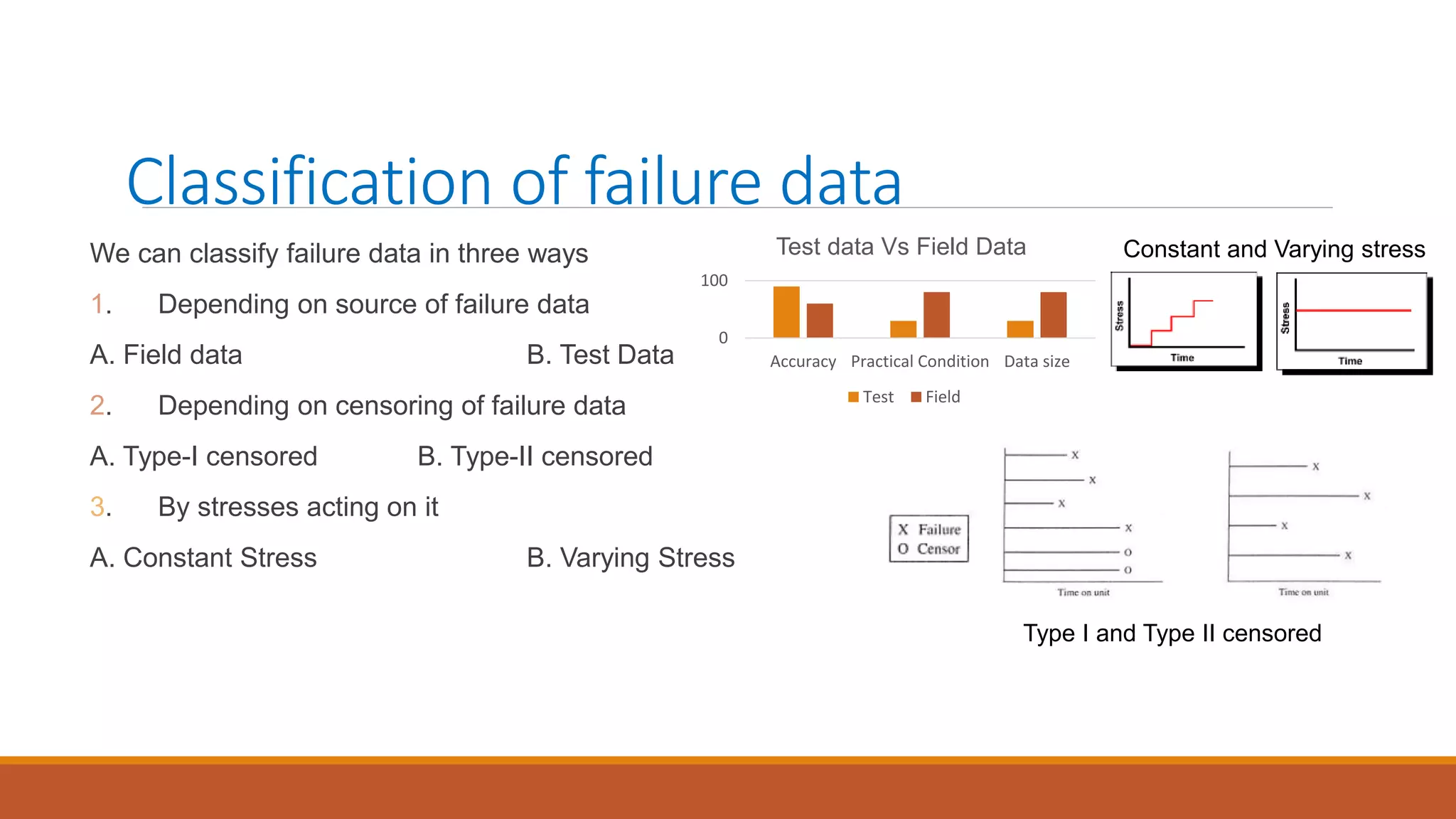
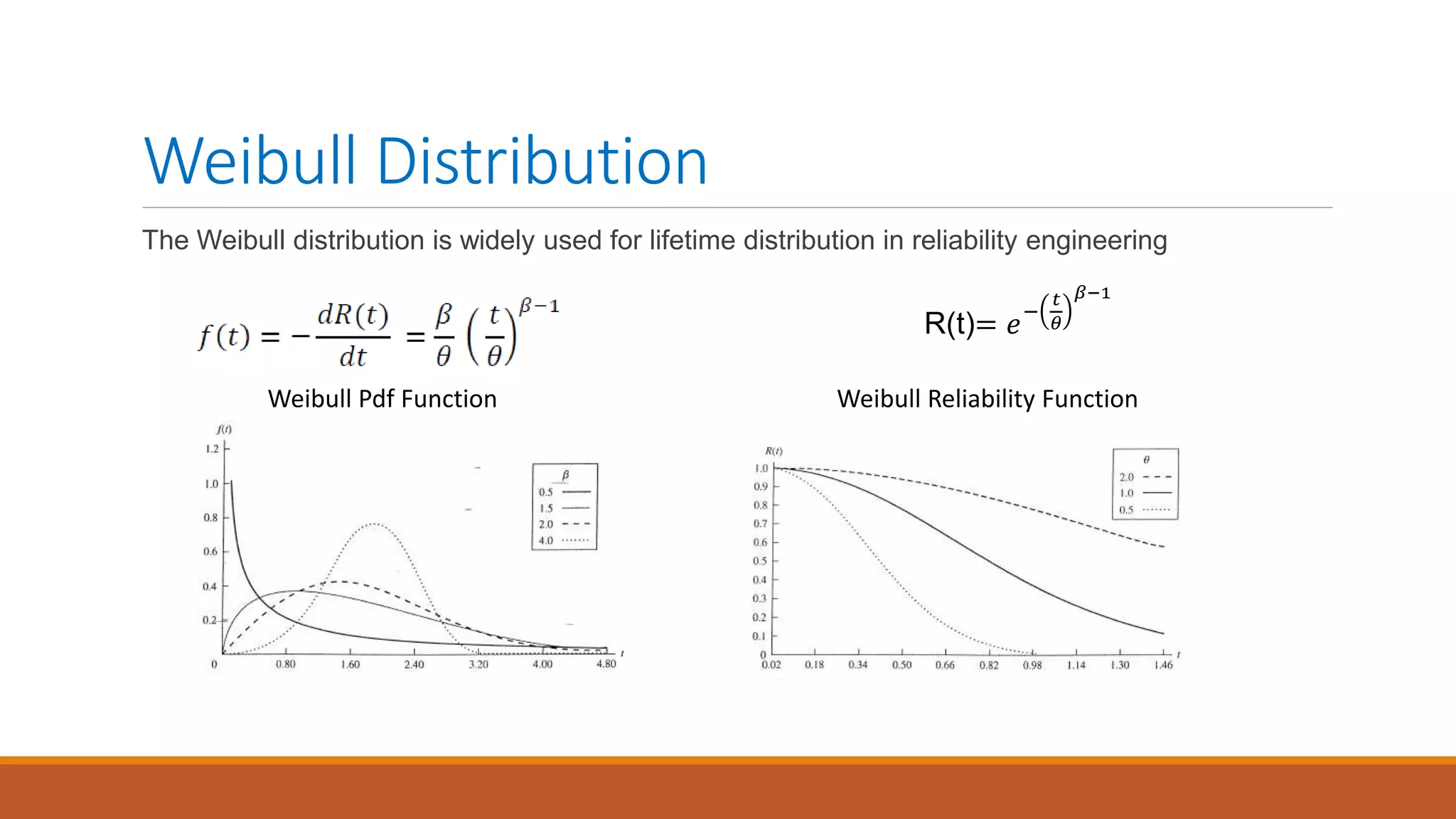
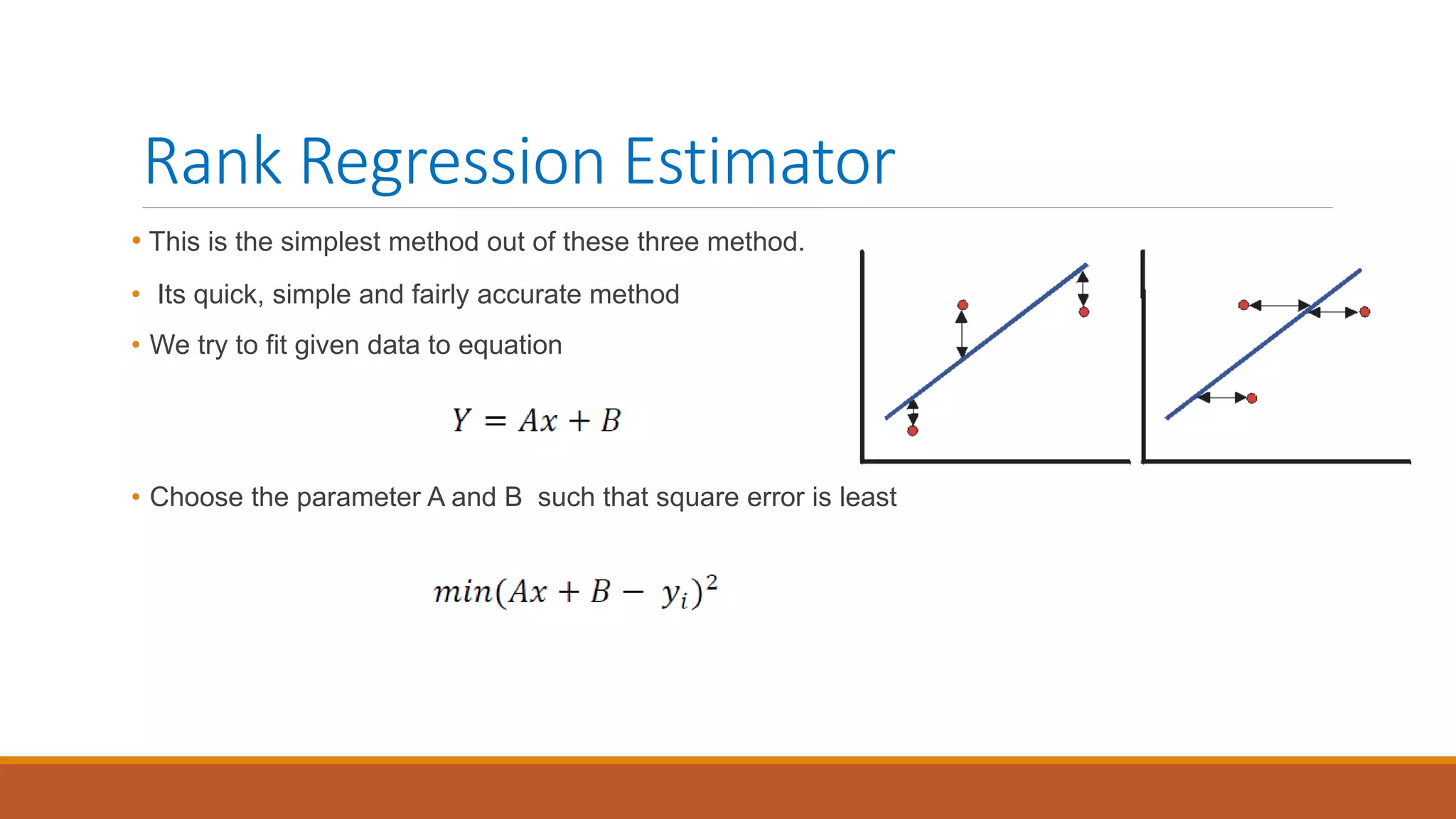
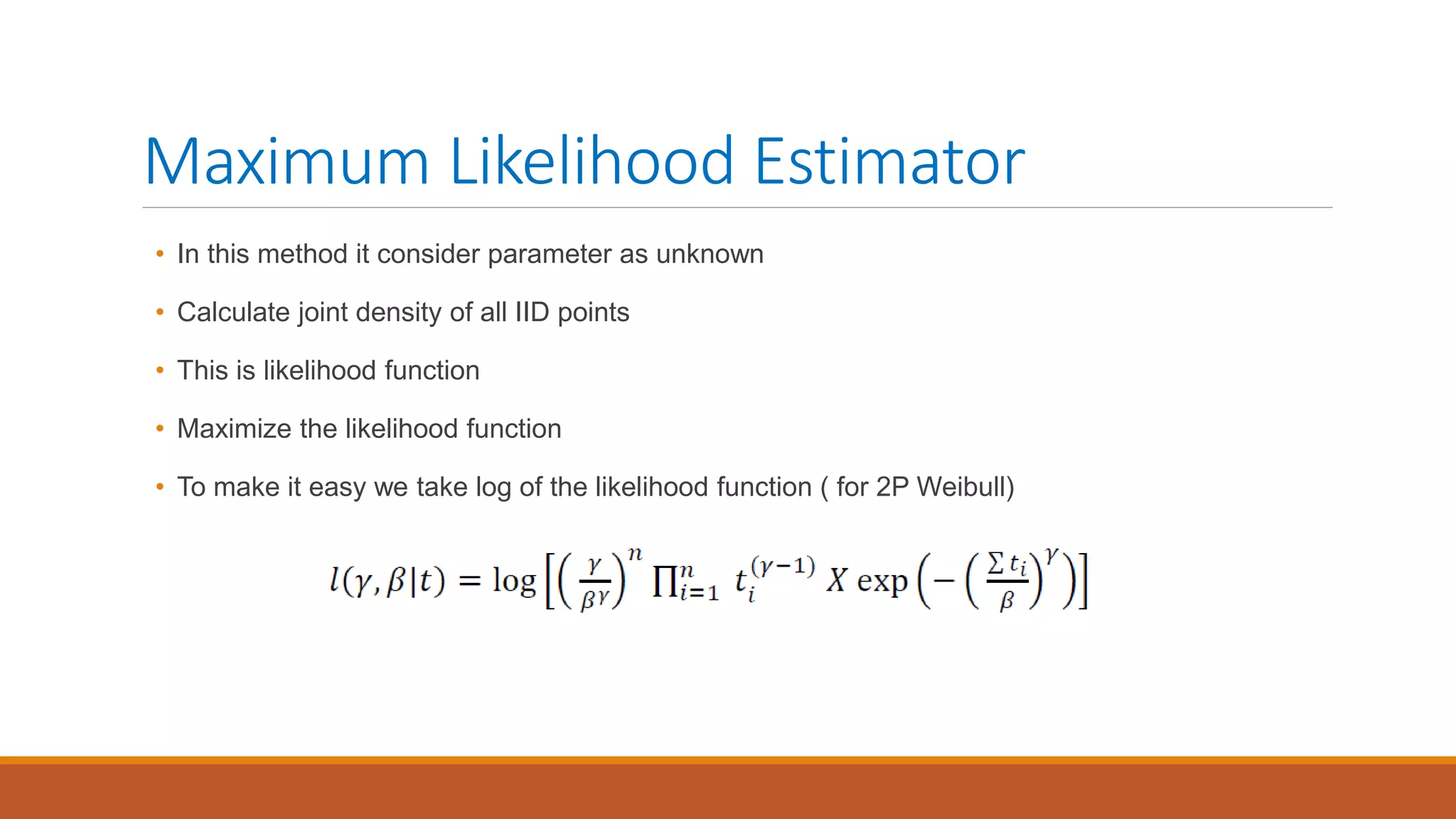
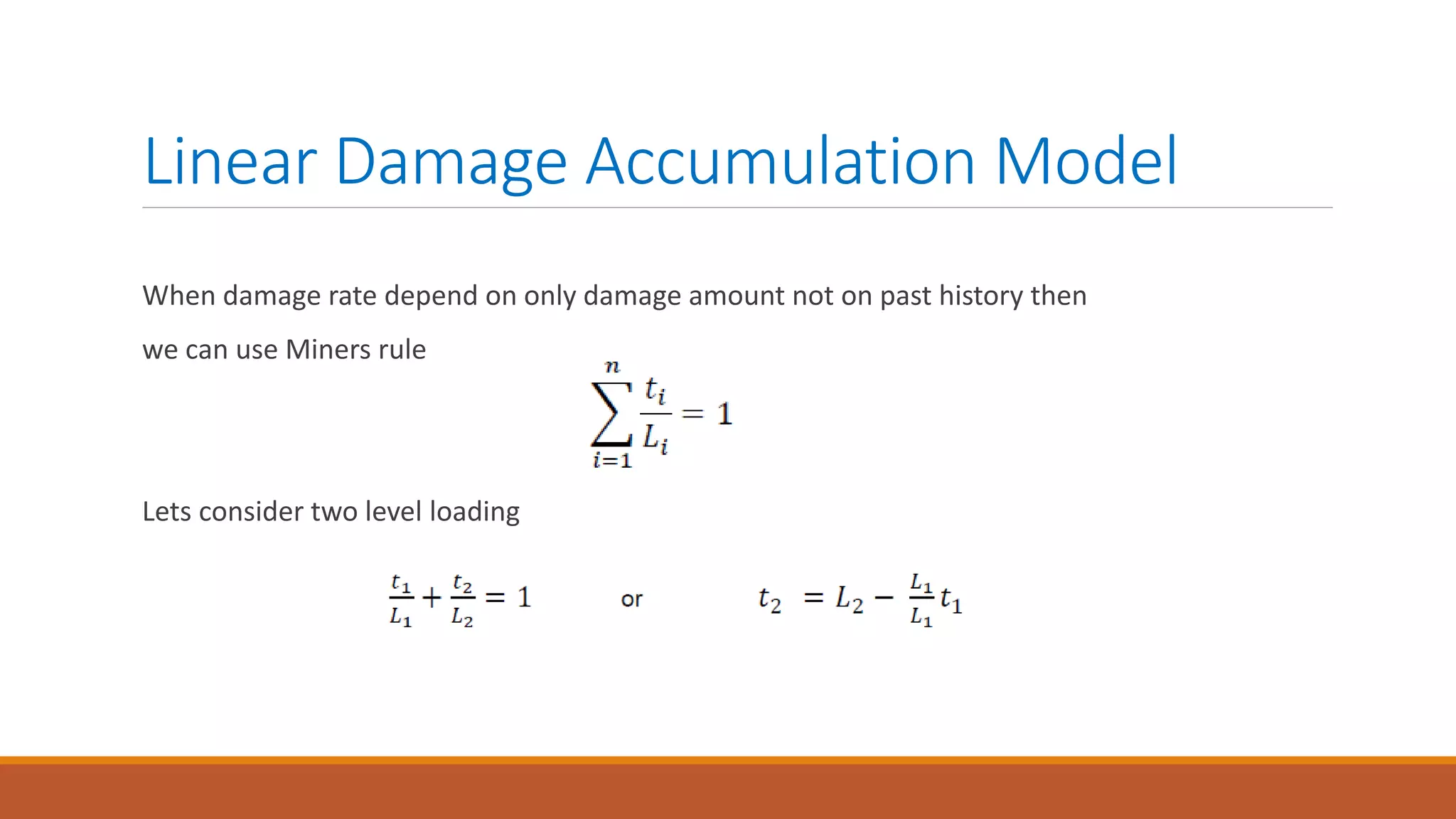
This document introduces nonlinear damage accumulation models. It discusses different types of failure data and prognostic approaches. Common life distributions like Weibull, exponential, and normal distributions are presented. Parameter estimation methods like maximum likelihood estimation and method of moments are described. Finally, linear and nonlinear damage accumulation models are covered, including the Manson-Halford and Huiying-Hong models which account for load interaction effects.