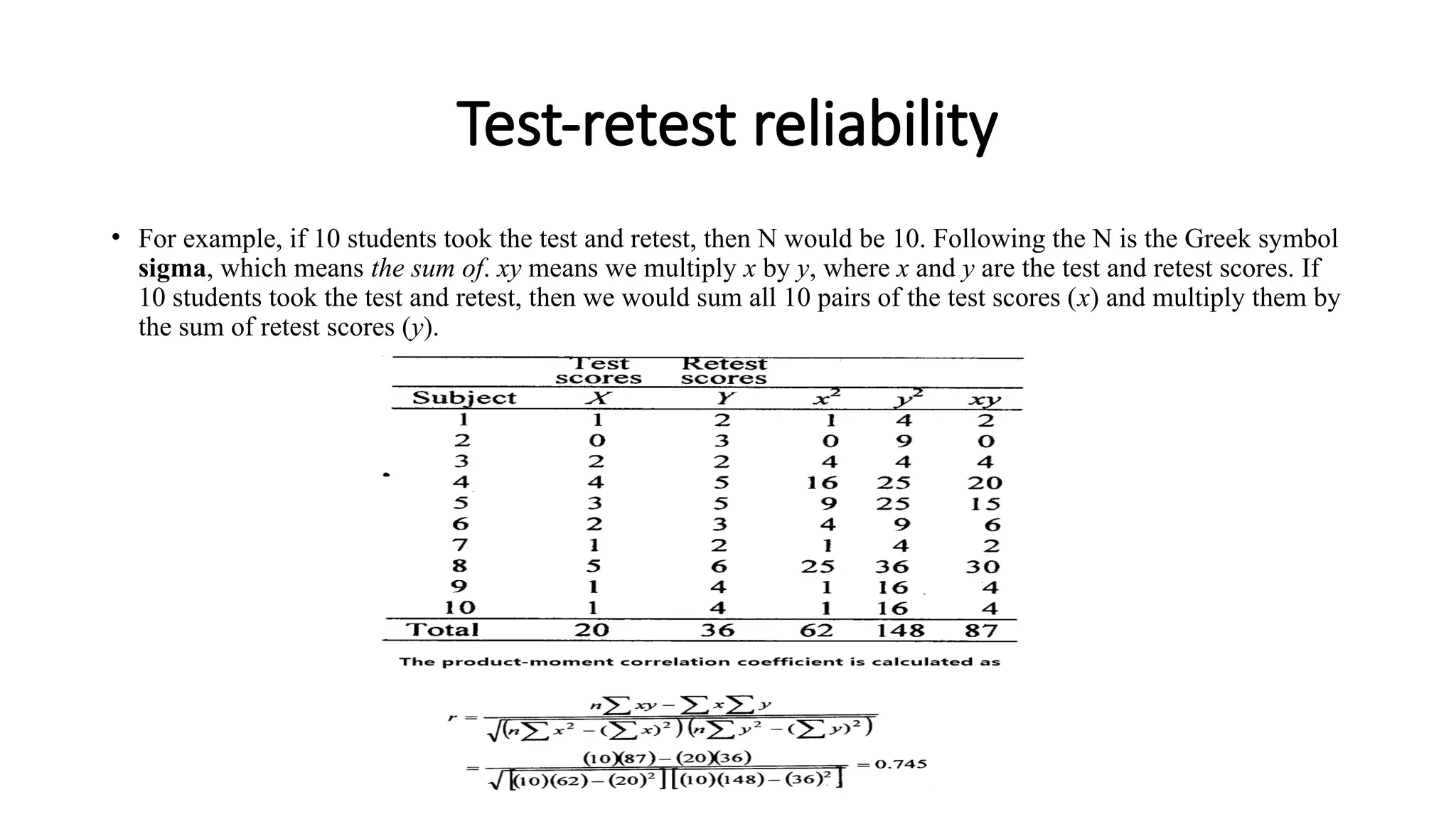
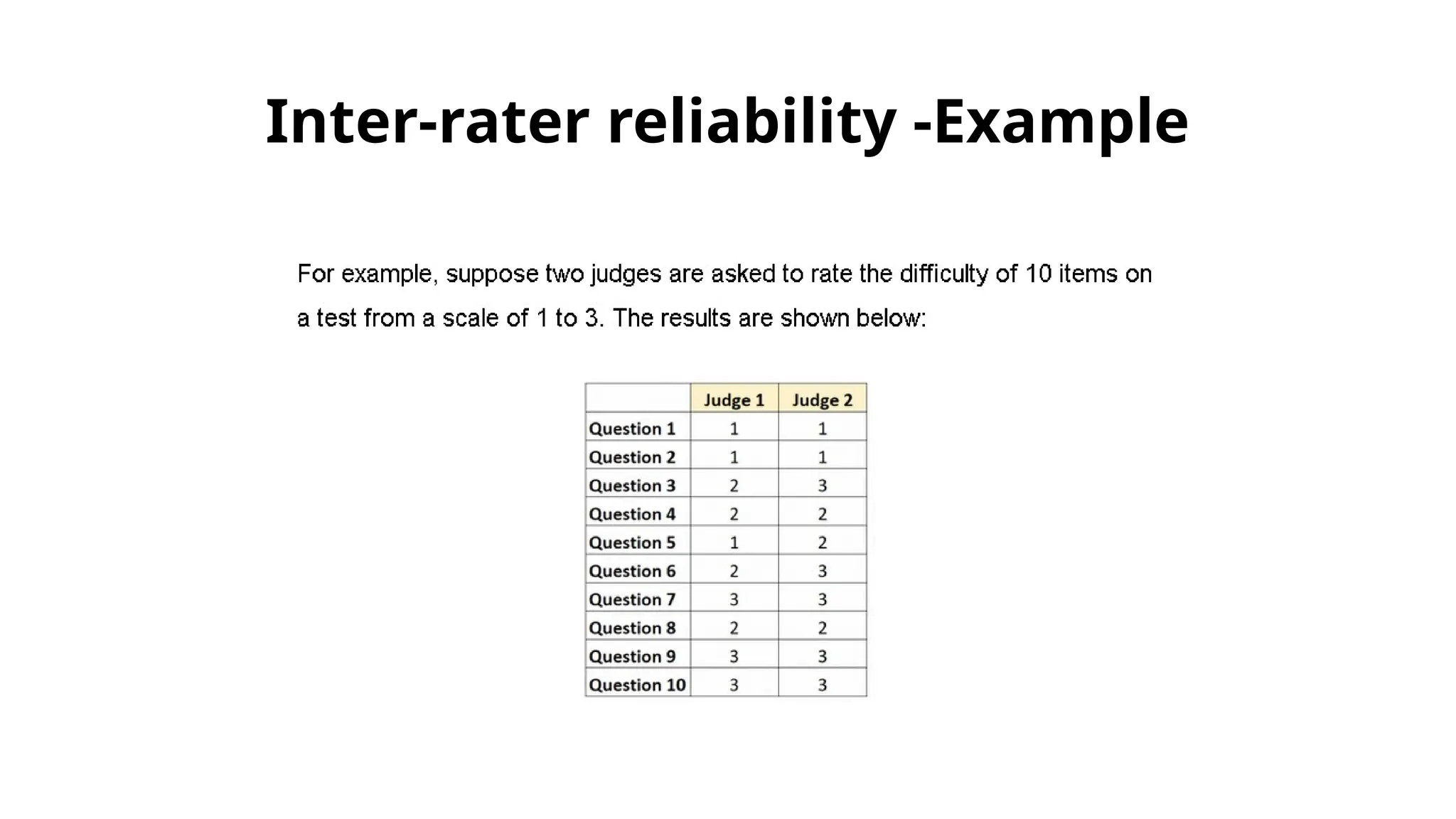
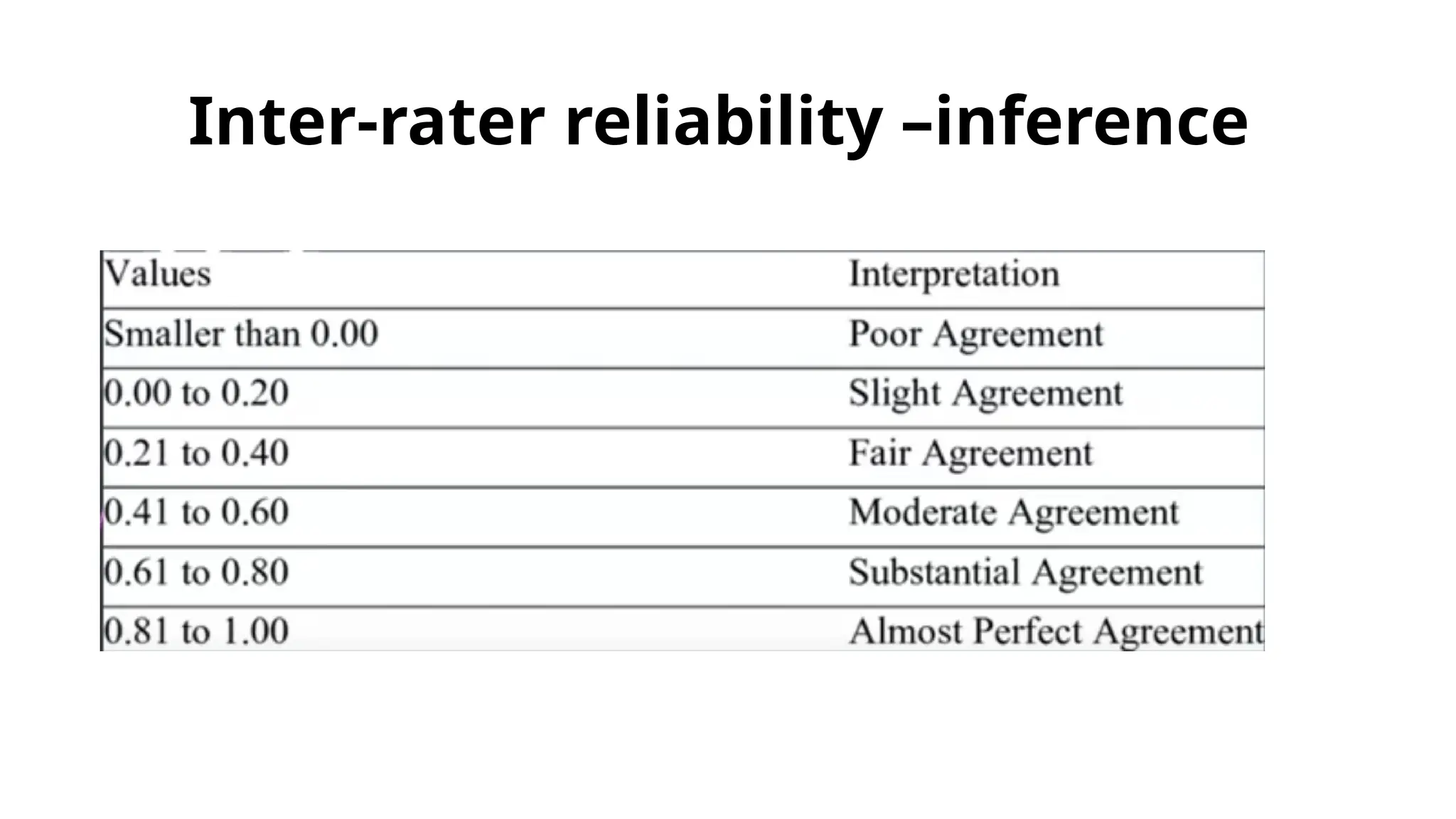
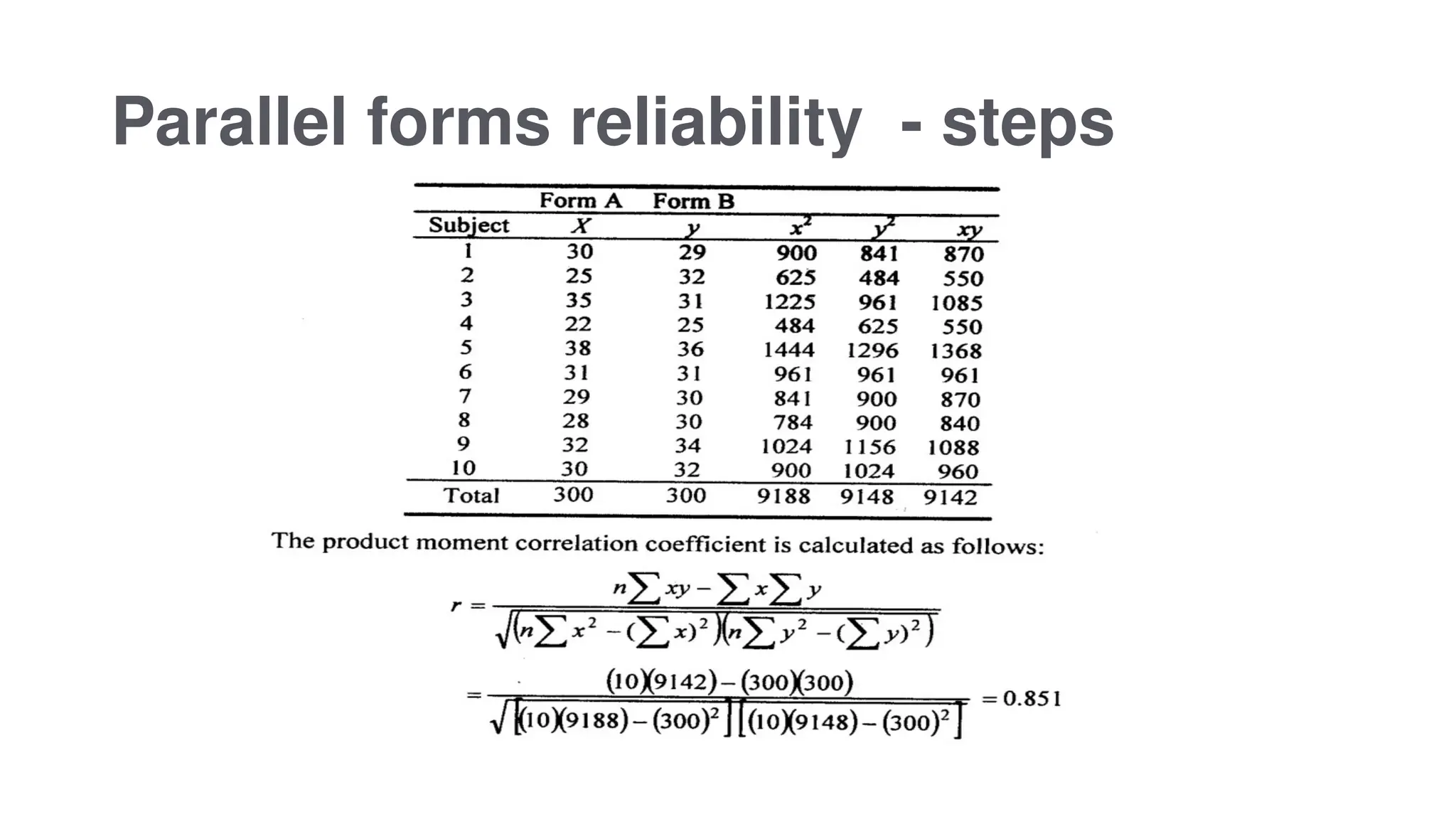
The document outlines various types of reliability in research, focusing on test-retest reliability, inter-rater reliability, and parallel forms reliability. Test-retest reliability assesses score stability over time, while inter-rater reliability evaluates agreement among different raters. Parallel forms reliability compares two equivalent sets of questions measuring the same construct to determine reliability, as illustrated by an example involving a sound recognition test.