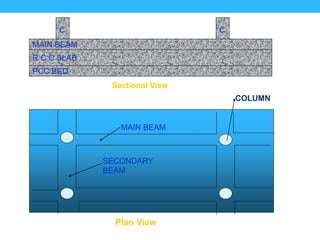
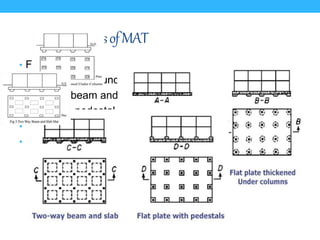
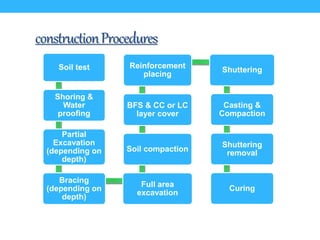
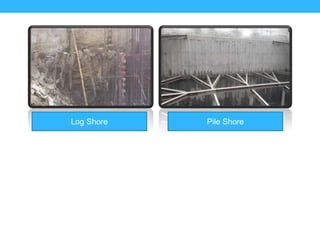
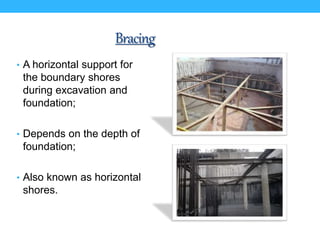
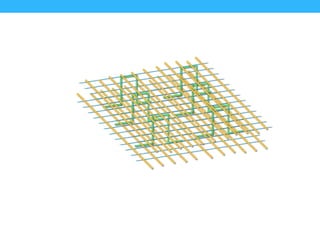
This presentation summarizes the key aspects of a mat foundation. It was presented by 10 civil engineering students with their IDs listed. The presentation covered what a mat foundation is, when they are used, different types, construction procedures including soil testing, reinforcement placement, shuttering, casting, and curing. Construction steps like shoring, waterproofing and bracing were also explained depending on the depth of the foundation.