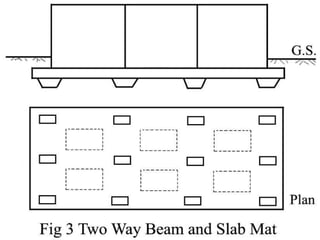
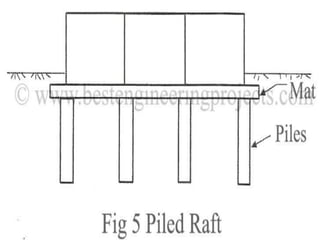
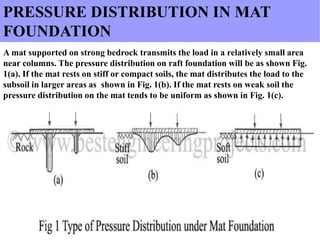
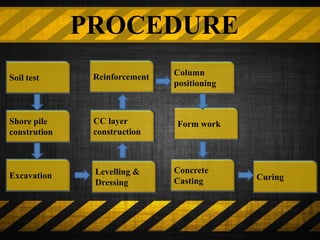
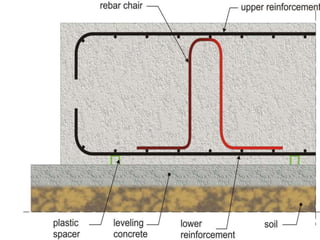
The document details mat foundations, describing them as thick reinforced concrete slabs that support structures by transmitting loads to the soil. It outlines when and why they are used, various types of mat foundations, and the construction process including soil testing, reinforcement placement, and formwork types. Additionally, it highlights the advantages and disadvantages of mat foundations, emphasizing economic benefits and potential challenges.