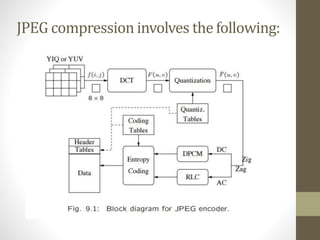
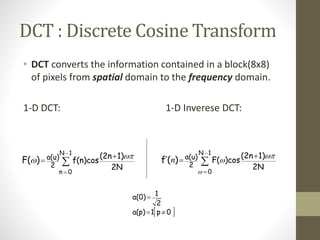
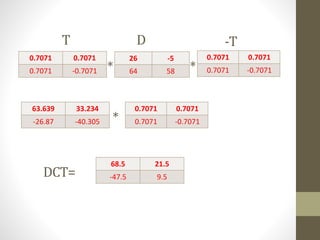
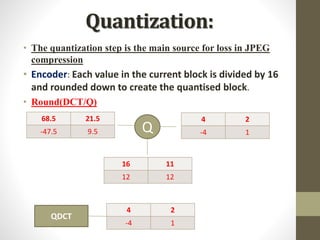
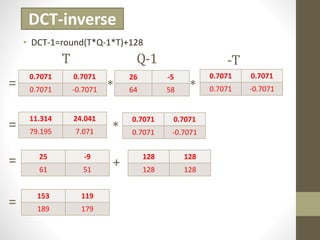
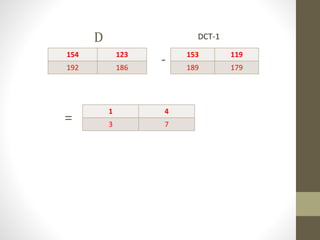
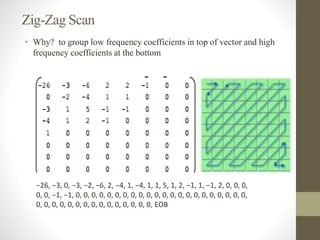
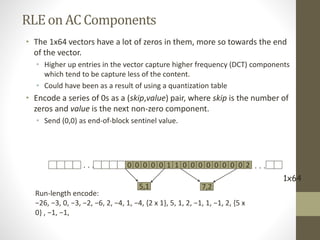
The document discusses JPEG image compression, which involves lossy compression. It describes the major steps in JPEG coding as: transforming RGB to YIQ/YUV color space and subsampling color; applying discrete cosine transformation (DCT); quantization; zig-zag ordering; DPCM on DC component; run-length encoding; and entropy coding like Huffman coding. Quantization is the main source of loss in JPEG compression, where each DCT value is divided by a quantization value and rounded down.