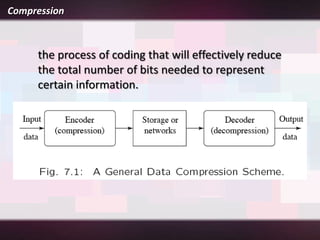
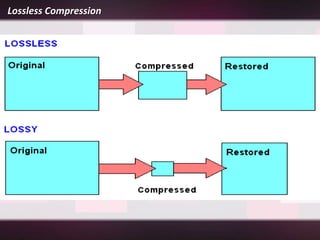
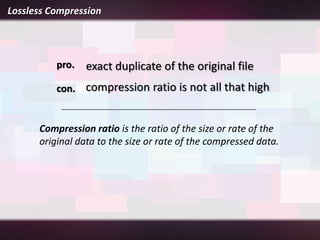
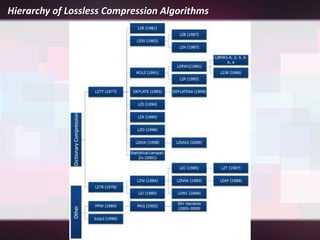
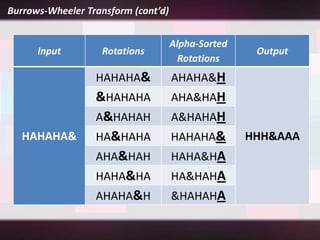
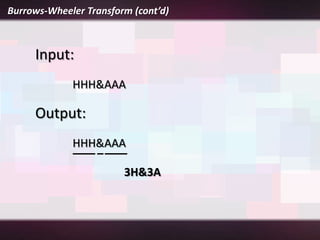
Lossless compression is a data compression technique that reduces the size of a file without sacrificing any original data. It allows for an exact duplicate of the original file to be recreated. Common lossless compression techniques include run-length encoding and the Burrows-Wheeler transform. Run-length encoding replaces runs of identical characters with the character and number of repeats. The Burrows-Wheeler transform rearranges data to group similar characters together in order to compress more efficiently with run-length encoding.