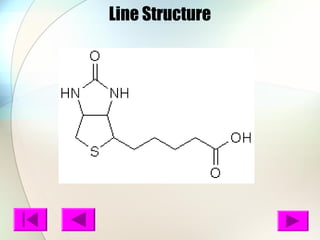
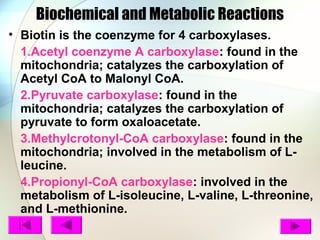
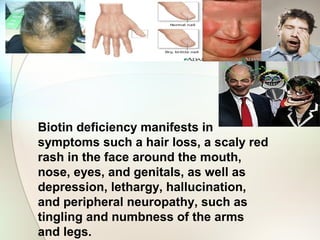
Biotin is a B vitamin that acts as a coenzyme in carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism. It is essential for cell growth and DNA/RNA replication. Biotin deficiency can cause dermatitis, hair loss, and neuromuscular dysfunction with symptoms like scaly skin, rash, hypotonia, and depression. Good dietary sources of biotin include eggs, organ meats, nuts, dairy, and whole grains.