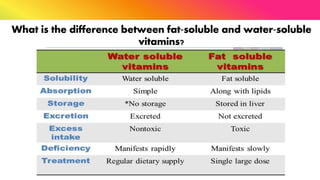
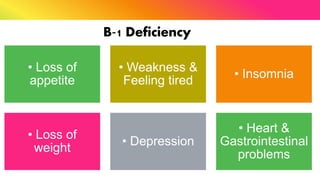
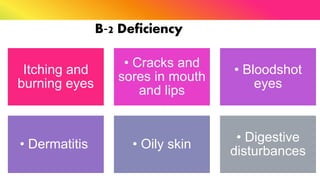
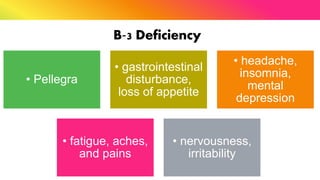
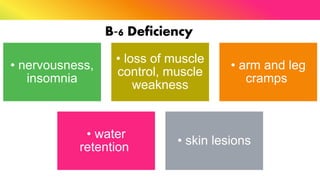
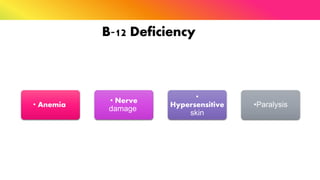
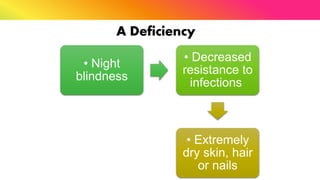
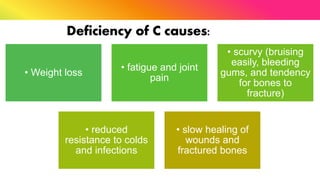
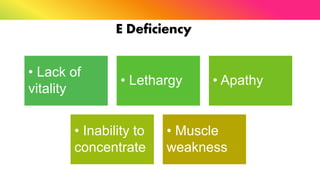
The document provides a comprehensive overview of vitamins, categorizing them into fat-soluble and water-soluble groups, detailing their functions, sources, and symptoms associated with deficiencies. It discusses specific vitamins, such as A, D, E, K, and the B vitamins, explaining their importance for bodily functions and health. The text also addresses the potential toxicity of excessive intake of certain vitamins and offers suggestions for preventing vitamin deficiencies.