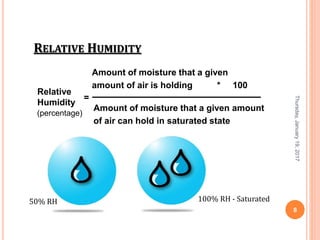
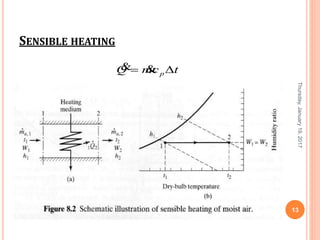
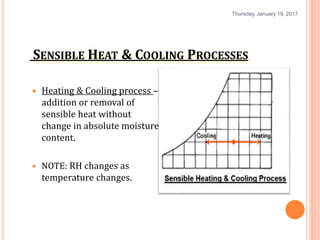
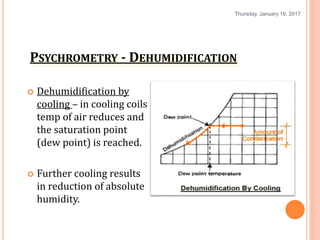
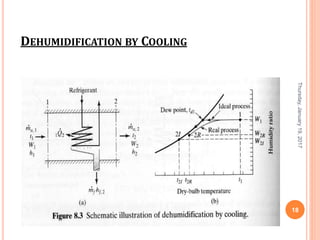
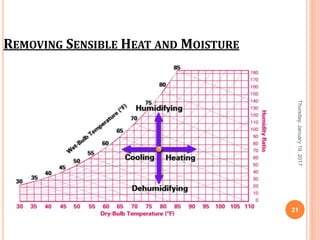
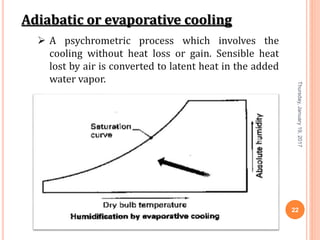
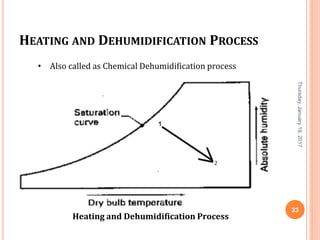
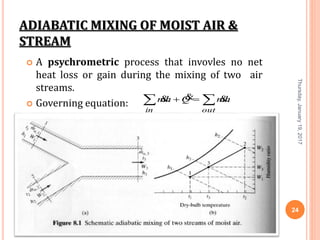
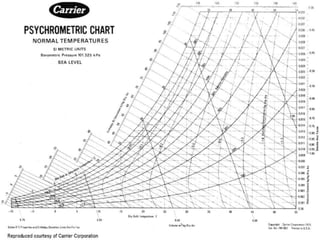
Gourav Tiwari's presentation introduces psychrometry, the science of air-water vapor mixtures. It discusses key psychrometric properties like dry bulb temperature, wet bulb temperature, and dew point. It also covers psychrometric processes such as sensible heating and cooling, which change temperature along constant humidity lines; and dehumidification and humidification, which change moisture content. The presentation aims to explain these concepts using a psychrometric chart to illustrate different psychrometric processes and how they affect air temperature and moisture levels.