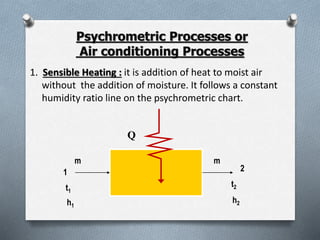
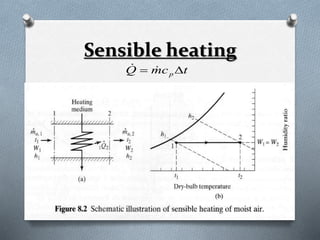
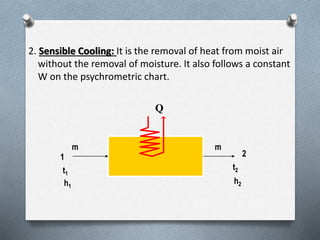
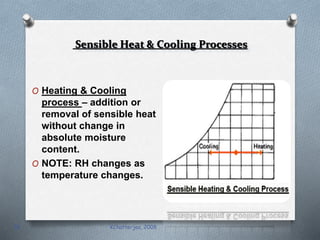
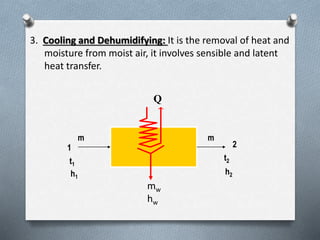
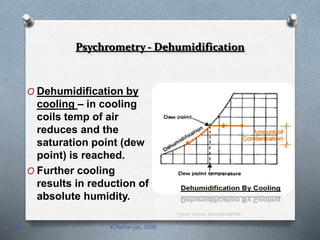
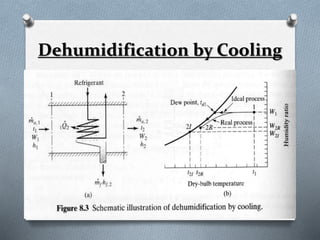
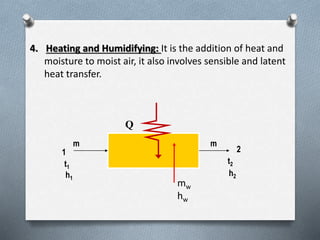
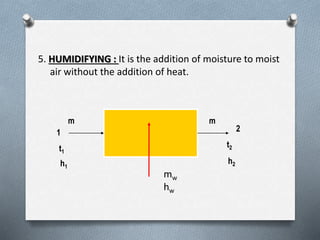
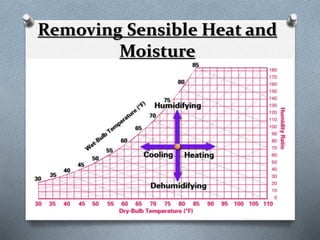
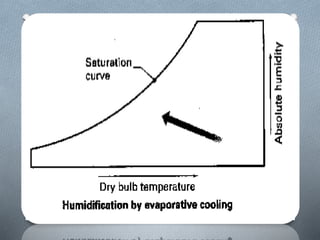
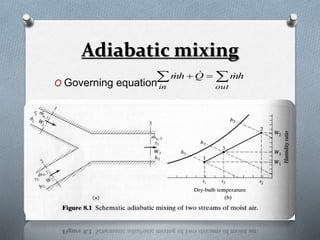
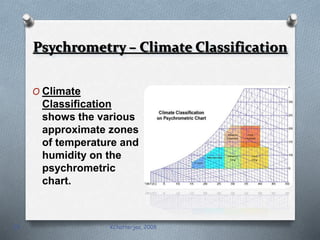
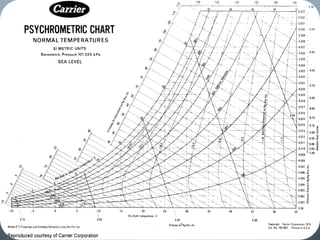
Psychrometry is the science dealing with air-water vapor mixtures. It studies moist air and its properties like dew point temperature, relative humidity, and dry/wet bulb temperatures. Psychrometric processes involve changes to moist air through sensible heating/cooling, humidifying, dehumidifying, and adiabatic mixing/cooling. The psychrometric chart is used to analyze these processes by plotting air properties and showing lines for temperature, humidity, and enthalpy. It is a useful tool for understanding air conditioning systems and classifying climates.