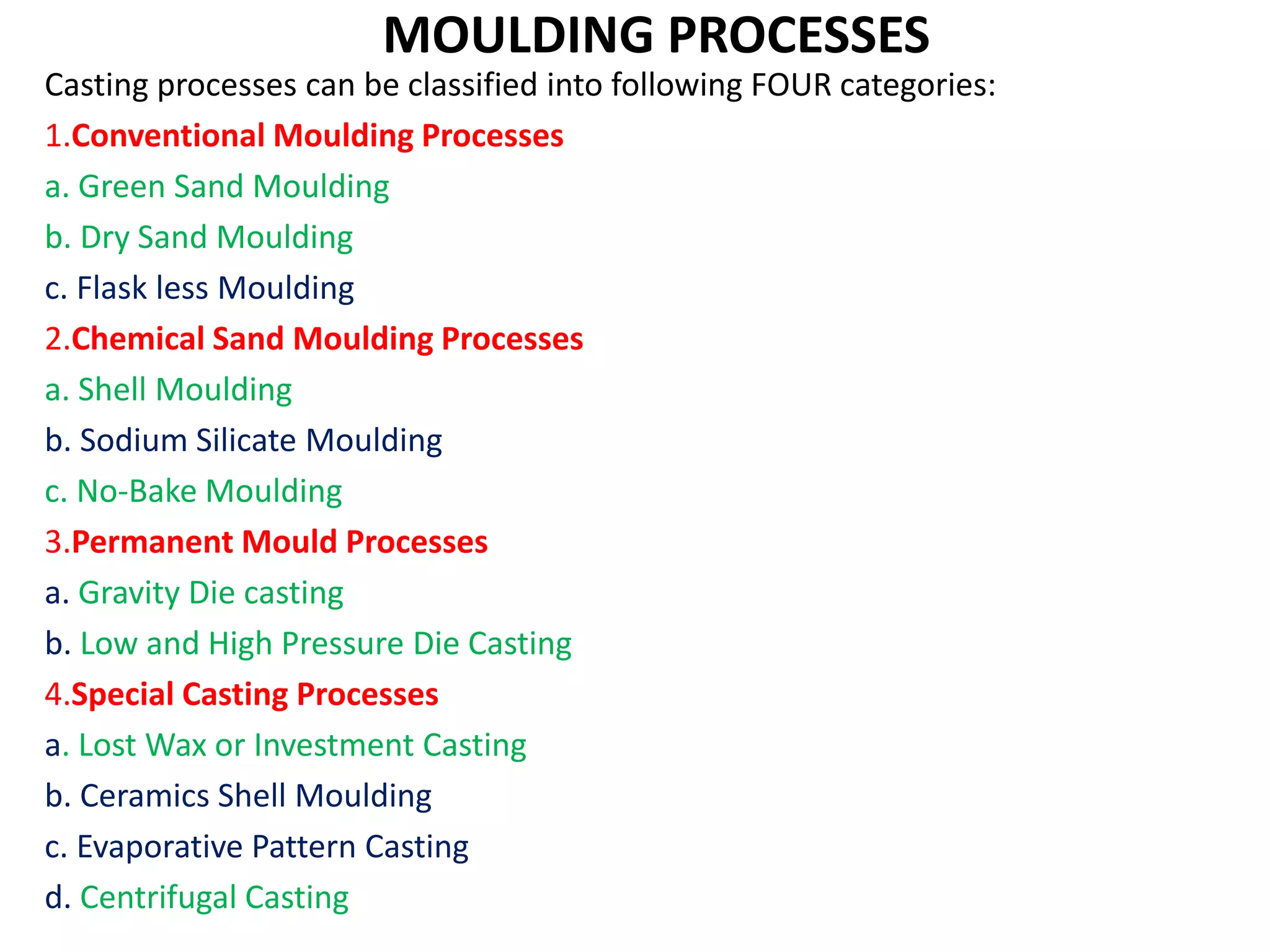
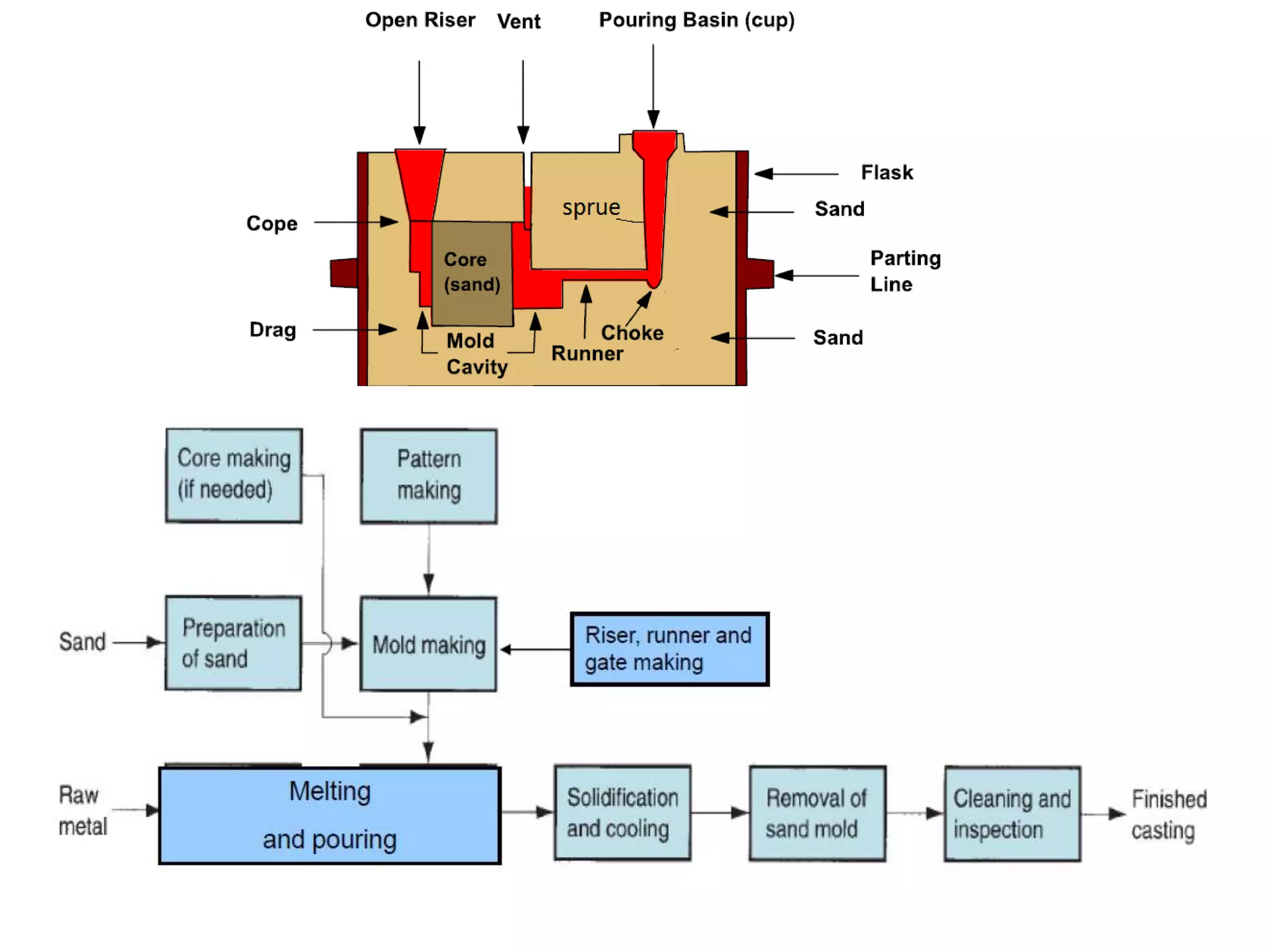
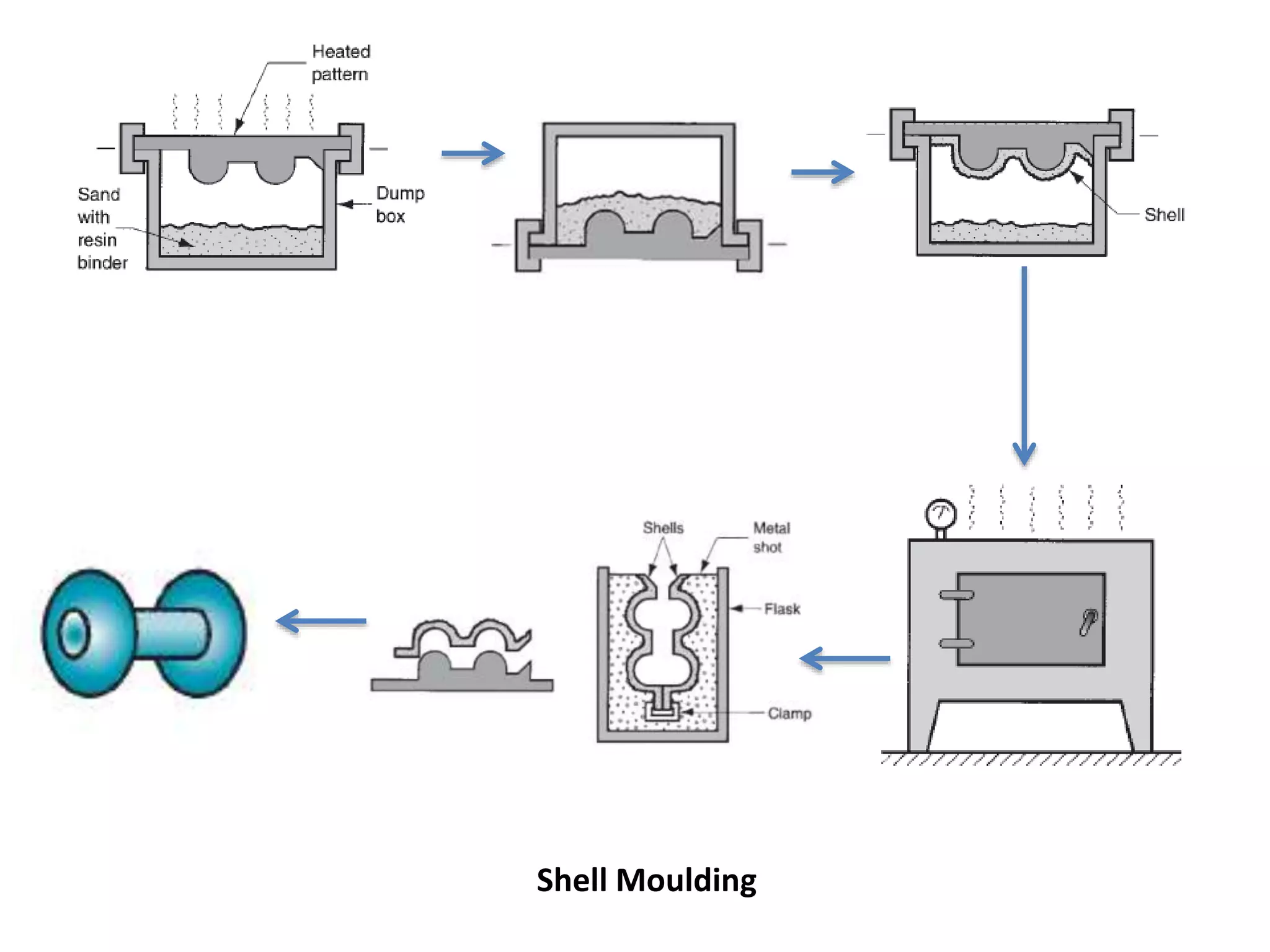
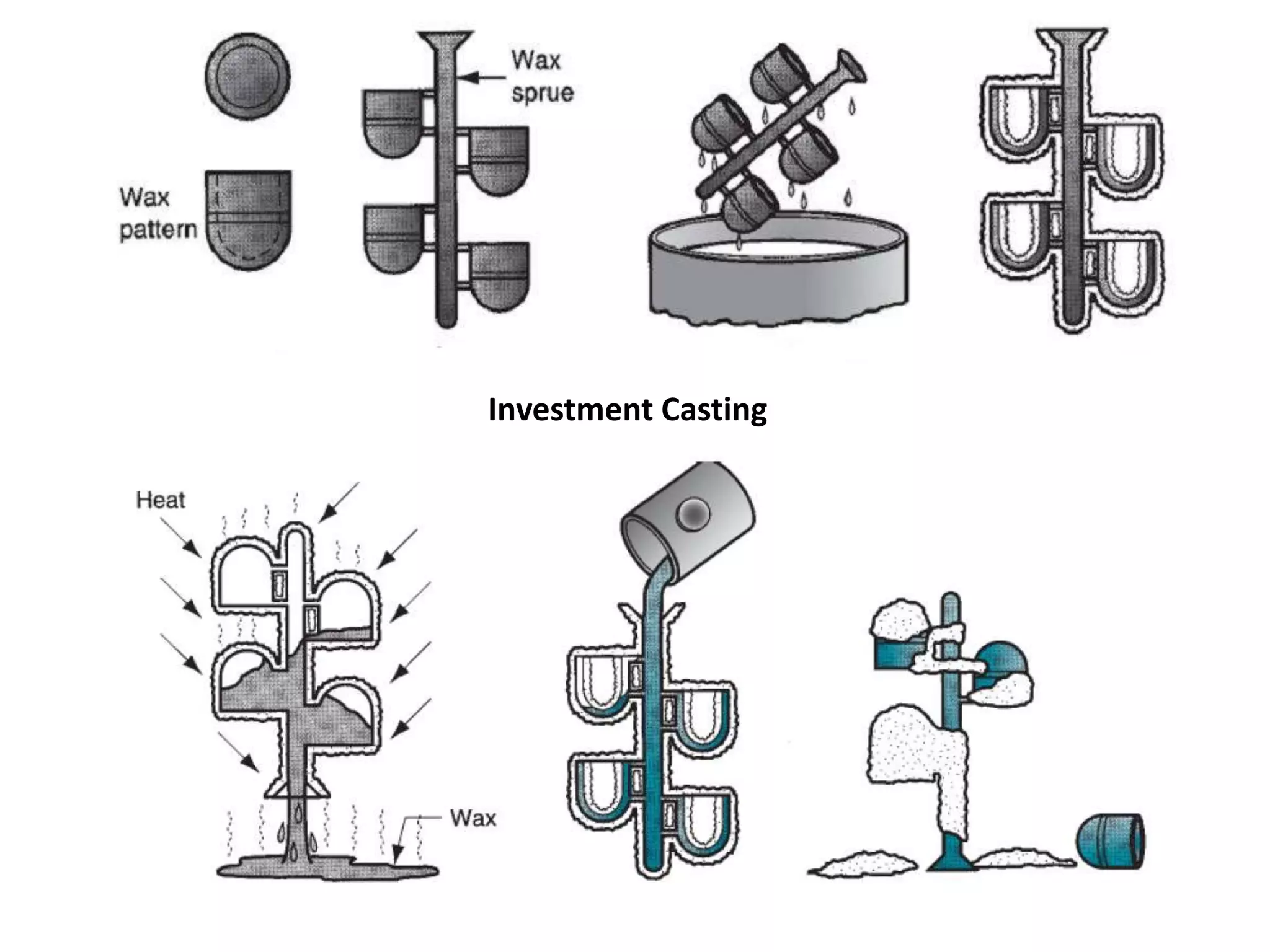
This document discusses various metal casting processes and their characteristics. It describes four main categories of casting processes: conventional moulding, chemical sand moulding, permanent mould processes, and special casting processes. Green sand moulding is the most common conventional process and uses sand mixed with clay as the mould material. Dry sand moulding bakes the mould to increase strength. Shell moulding uses a resin-bound sand mould only a few millimeters thick to provide a smooth surface finish. Investment casting allows for intricate parts by coating a wax pattern in refractory material before melting away the wax.