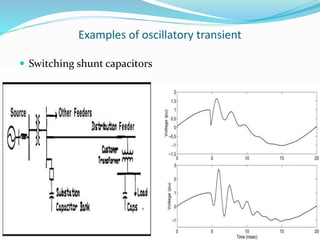
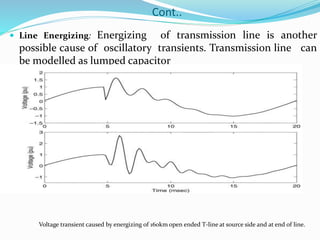
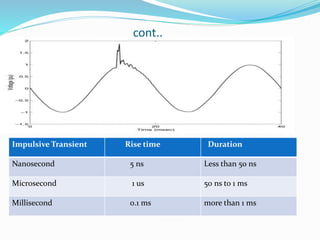
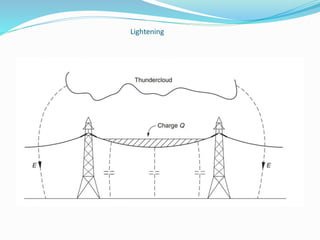
Transient disturbances in power systems refer to abrupt changes in voltage and current for short durations, often caused by events like switching operations, faults, and lightning. These can be categorized into oscillatory and impulsive transients, each with distinct characteristics and causes. Improved assessment of power quality requires new indices based on signal processing techniques as existing indices have limitations.