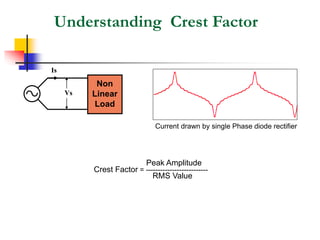
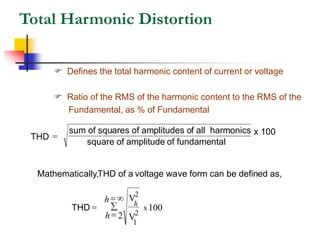
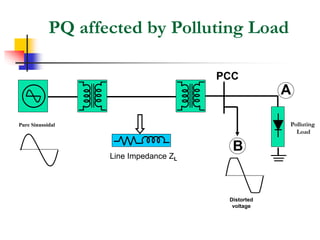
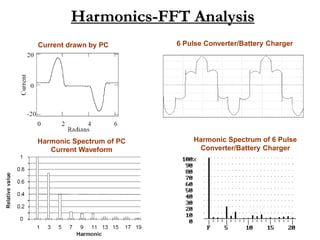
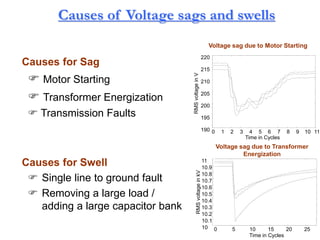
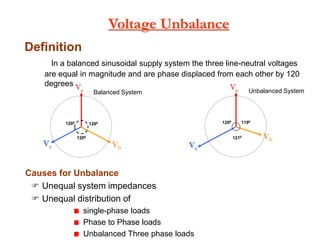
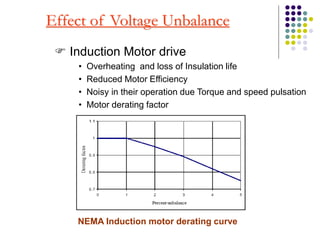
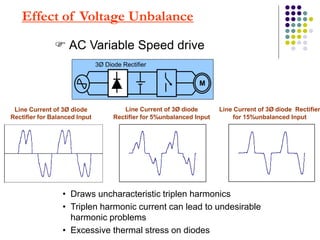
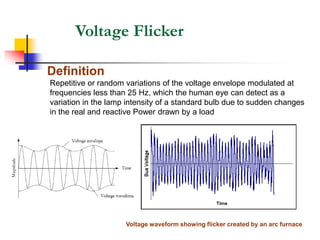
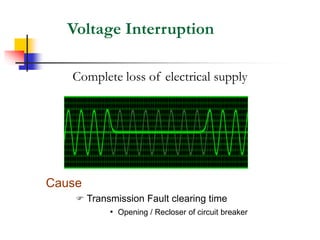
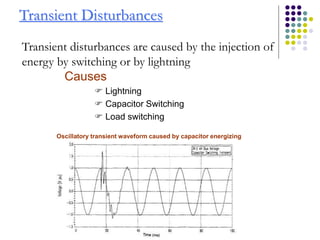
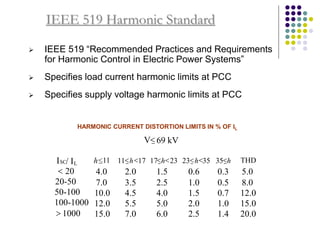
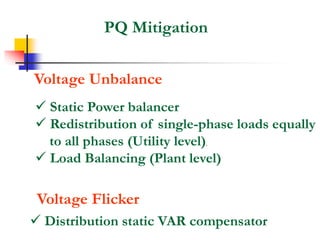
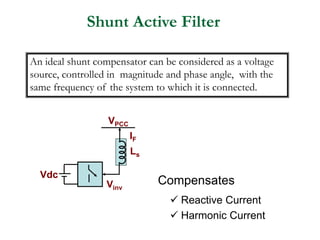
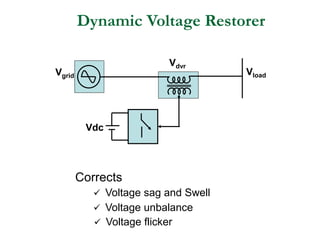
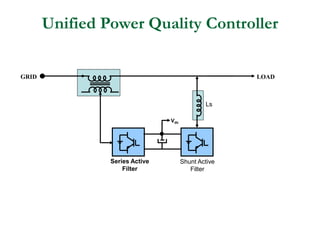
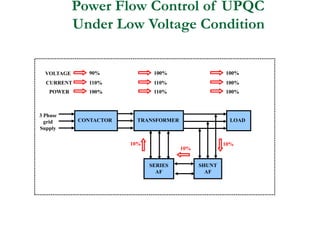
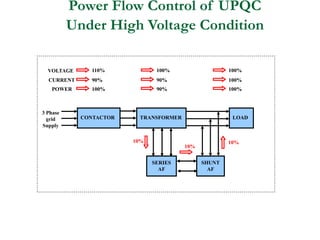
This document discusses power quality issues and solutions. It begins with an introduction to concepts like reactive power, power factor, harmonics, and crest factor. It then discusses common power quality disturbances such as voltage sags, swells, harmonics, and unbalance. Standards like IEEE 519 are mentioned. The document concludes with an overview of power quality mitigation techniques including active and passive filters, DVRs, and UPQC devices. Case studies are provided on how these solutions can compensate for reactive power, harmonics, voltage issues, and control power flow.