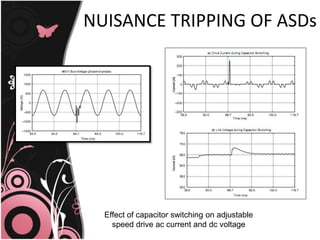
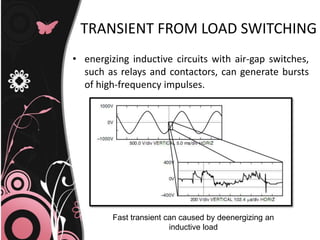
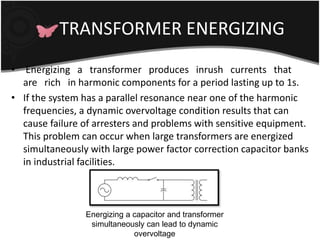
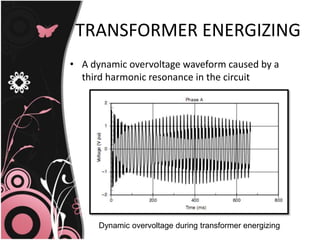
This document discusses transient problems related to load switching that can cause nuisance tripping of adjustable speed drives (ASDs). It notes that ASDs use voltage source inverters with capacitors in the DC link, making them sensitive to overvoltage transients from utility capacitor switching or load switching. Such transients from load switching can generate high frequency impulses when energizing inductive loads like relays or contactors. Simultaneously energizing large transformers and capacitor banks can also cause dynamic overvoltage problems if system resonances occur. Protection methods include electrical separation of sensitive equipment, as well as using filters, isolation transformers, and shielding.