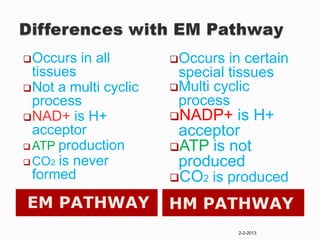
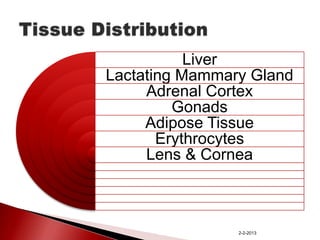
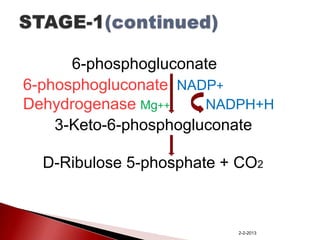
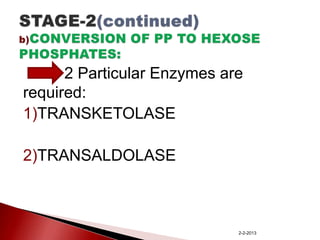
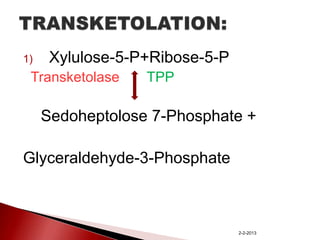
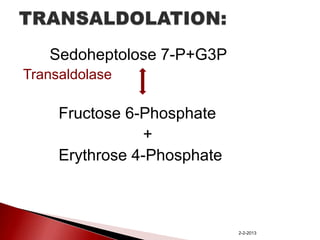
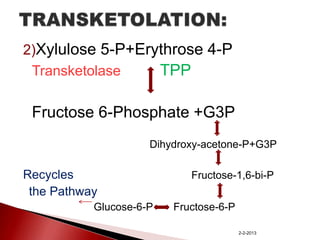
The document summarizes the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), also known as the phosphogluconate pathway or hexose monophosphate shunt. It has two main functions: providing NADPH and producing pentoses. The PPP occurs mainly in the liver, lactating mammary glands, and other tissues. It has an oxidative and non-oxidative phase and involves enzymes that oxidize glucose-6-phosphate to produce NADPH and pentose phosphates through a series of reactions. Deficiencies in enzymes in this pathway can cause hemolytic anemia, neurological disorders, and other conditions.













![Occurs in 3 ways:
a) Ratio of [NADP+][NADPH]
_1st Step is Rate-limiting step catalysed by
G6PD.
b) Increased
HMP Shunt on feeding
high CHO diet & decreased in
Diabetes Mellitus
c)HORMONES:
Insulin & Thyroid hormones
2-2-2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hmpshunt1-131230081415-phpapp01/85/Hmp-shunt-21-320.jpg)