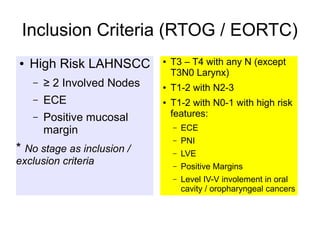
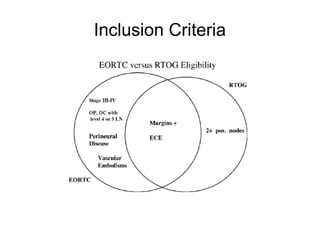
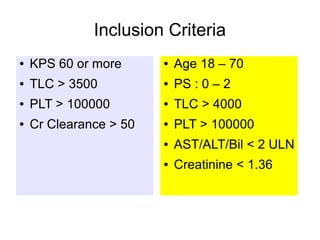
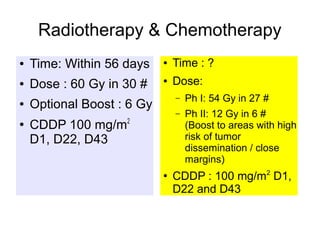
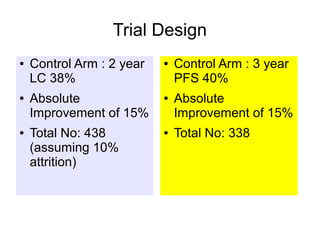
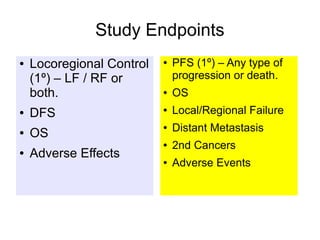
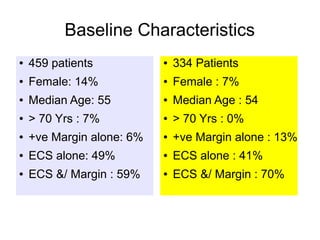
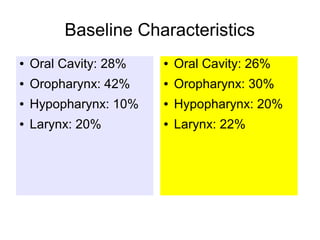
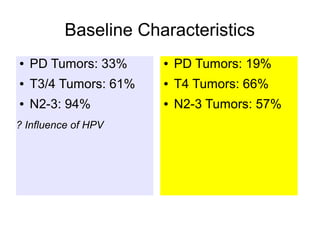
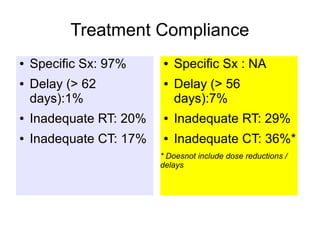
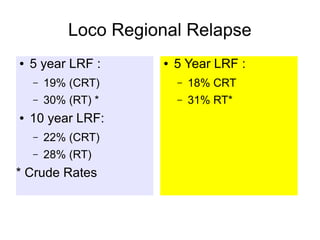
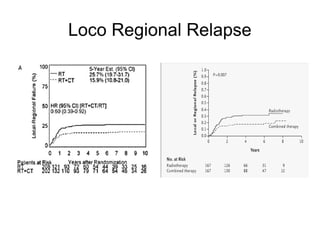
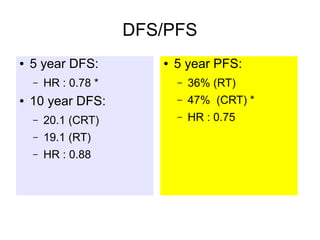
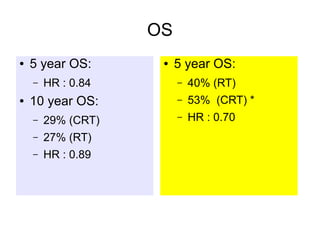
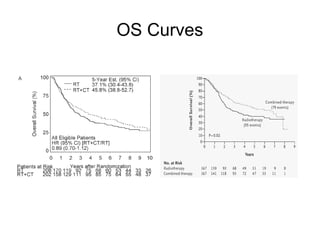
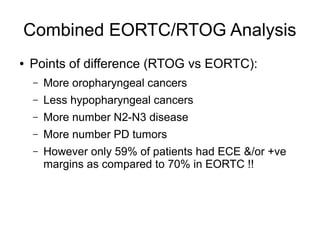
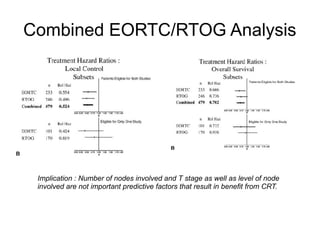
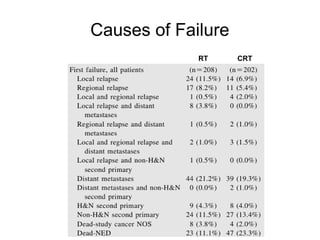
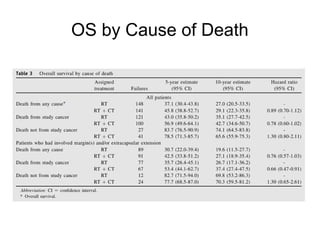
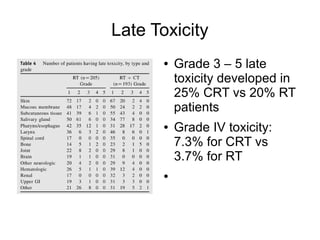
The document discusses the long-term follow-up results of the RTOG 9501/Intergroup Phase III trial, which evaluated postoperative concurrent radiation therapy and chemotherapy for high-risk squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. It highlights inclusion criteria, trial design, treatment compliance, and outcomes such as locoregional control, disease-free survival, and overall survival. Although concurrent treatment showed some benefits in specific circumstances, longer-term follow-up suggested diminishing advantages compared to radiation therapy alone, with an increase in late toxicities observed.