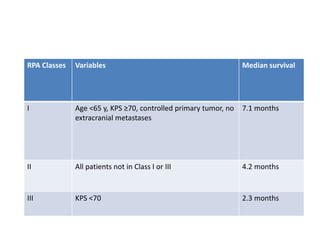
This document discusses recursive partitioning analysis (RPA), a statistical tool used to identify significant prognostic factors and classify patients into groups with similar outcomes. RPA has been used to analyze data from clinical trials in high-grade glioma (HGG) and brain metastasis patients. Key factors like age, performance status, extent of surgery, and molecular alterations help divide patients into prognostic classes. More recent studies have refined RPA models by incorporating additional molecular data to better stratify patients and guide treatment decisions.