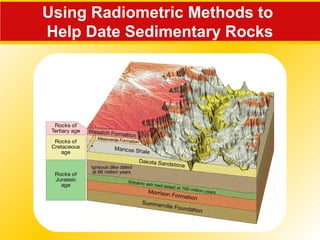
This document discusses methods that geologists use to determine the age of rocks and events in Earth's history. It introduces the concepts of relative dating, which determines the sequence of events but not their absolute age. Radiometric dating allows determining absolute ages by measuring the decay of radioactive isotopes. The geologic time scale divides Earth's history into standardized units like eons, eras, periods and epochs based on changes in life forms and rock formations. Radiometric dating has supported the immense timescale of geologic history.