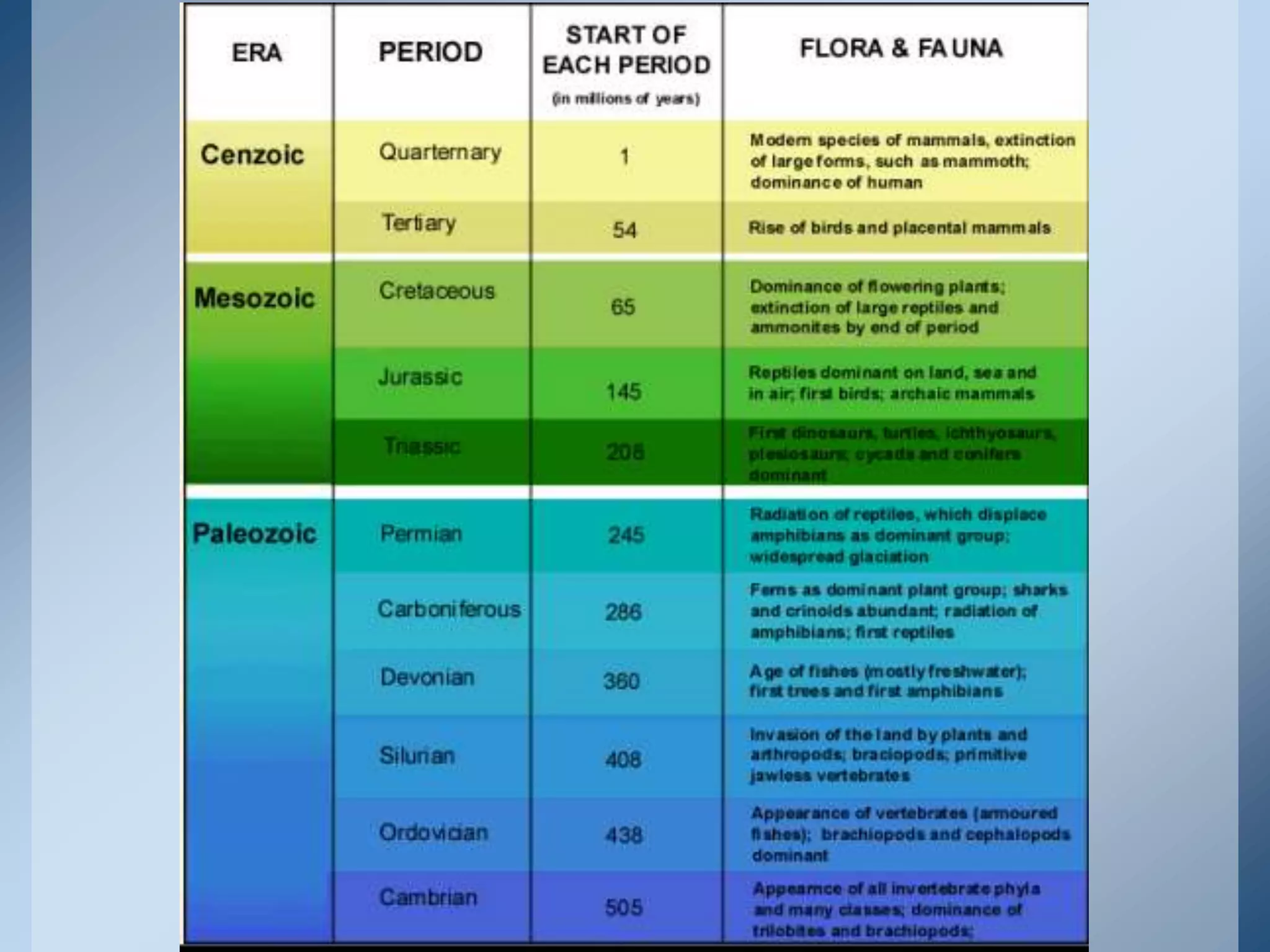
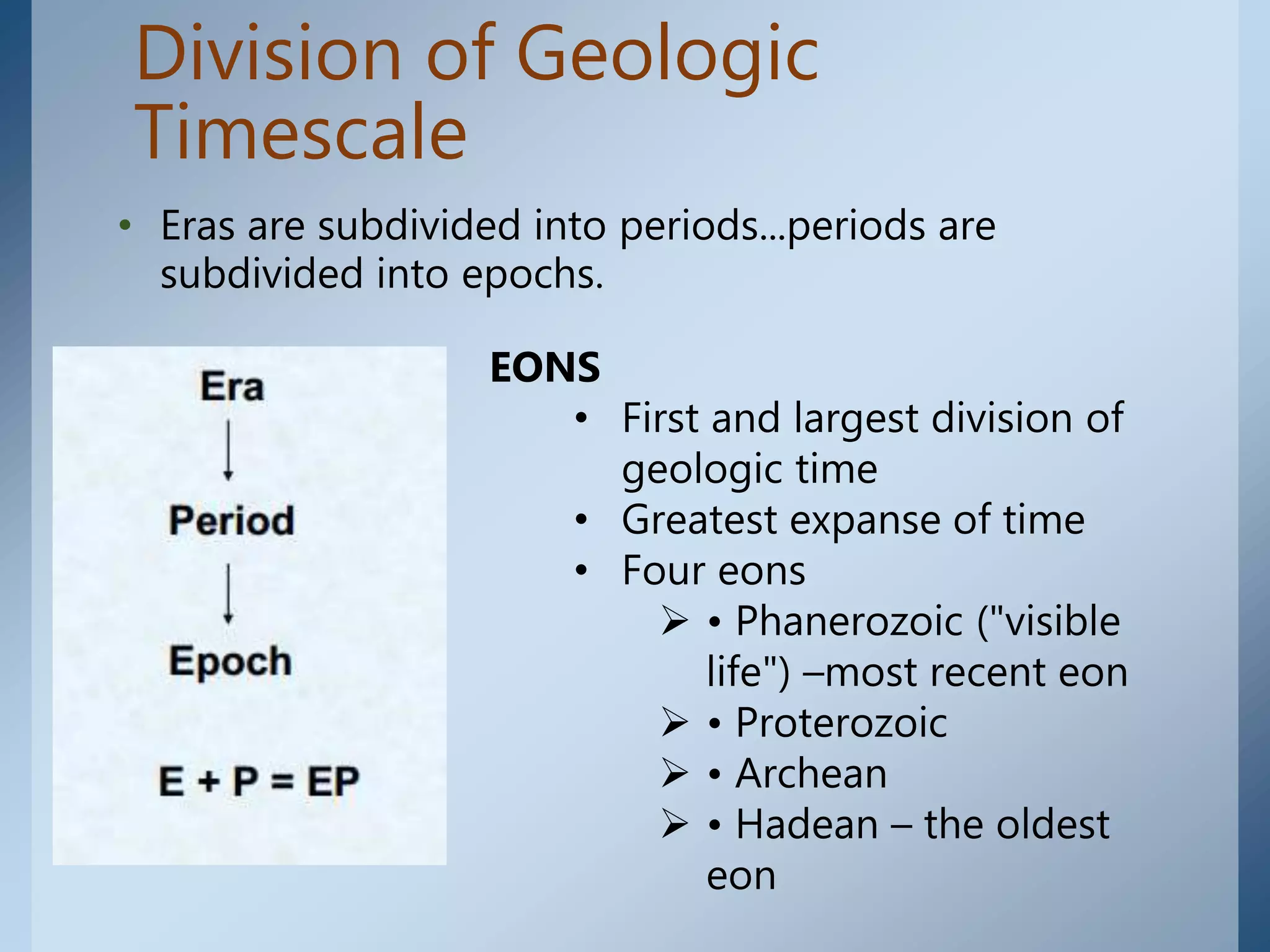
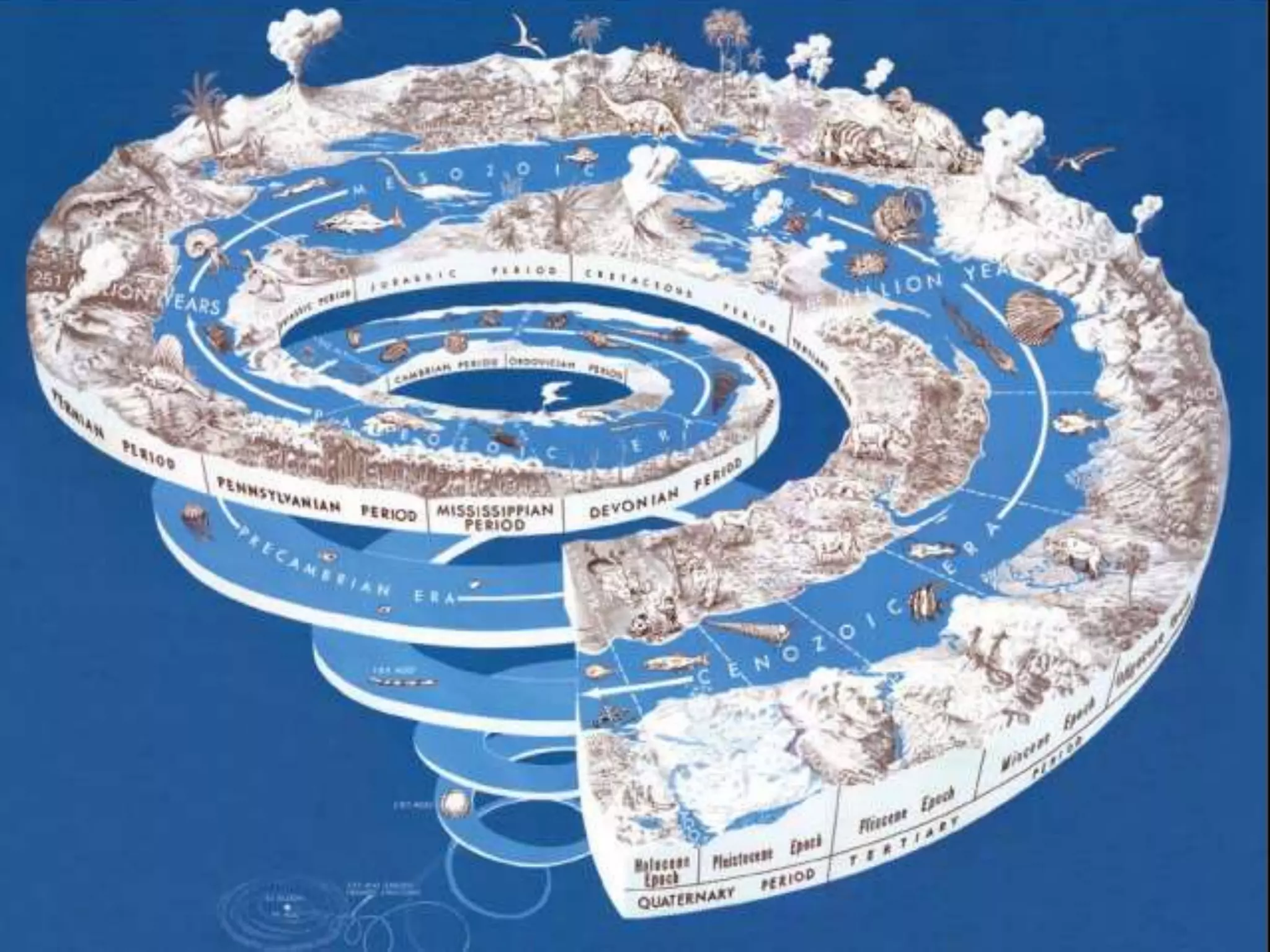
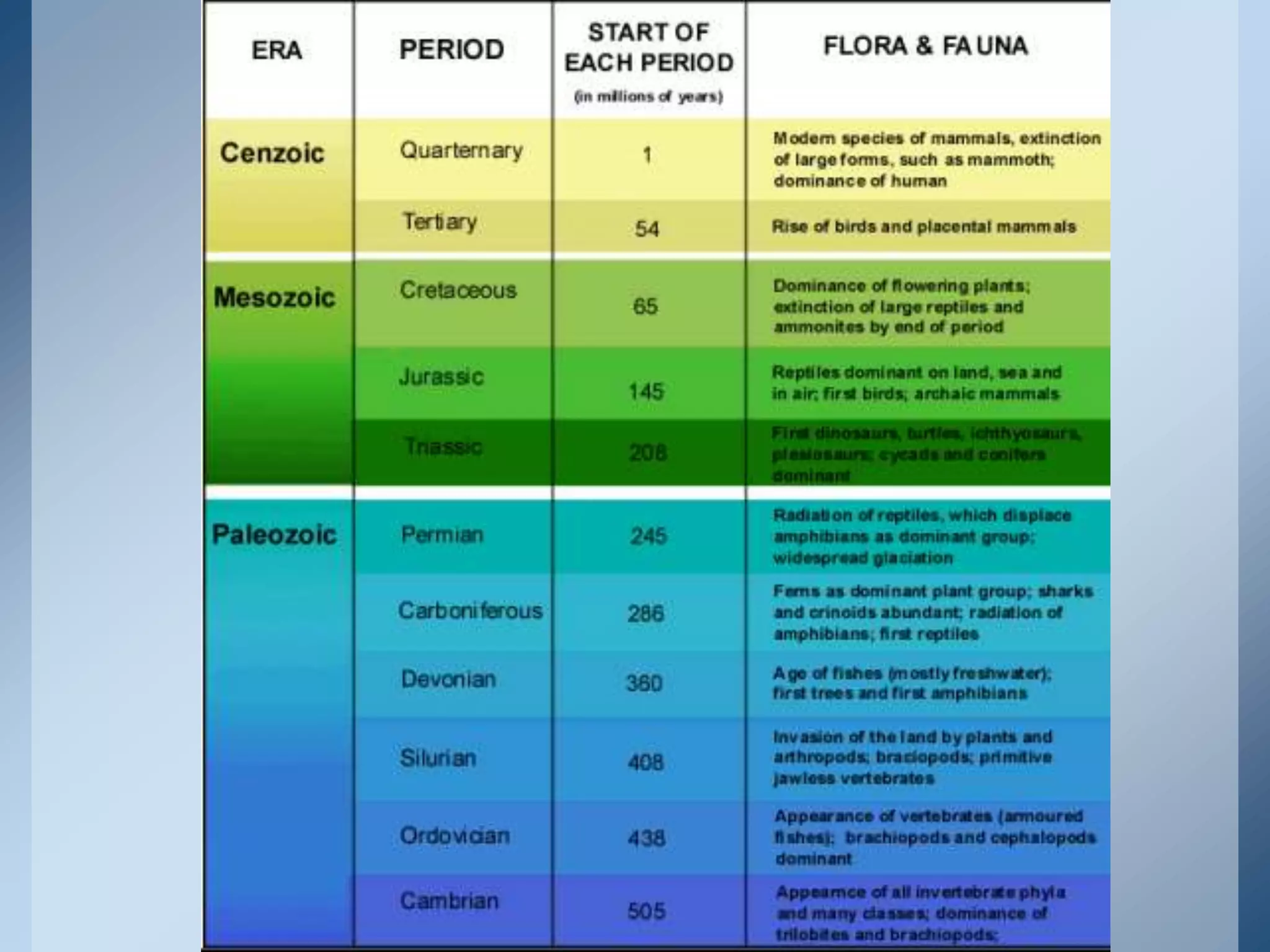
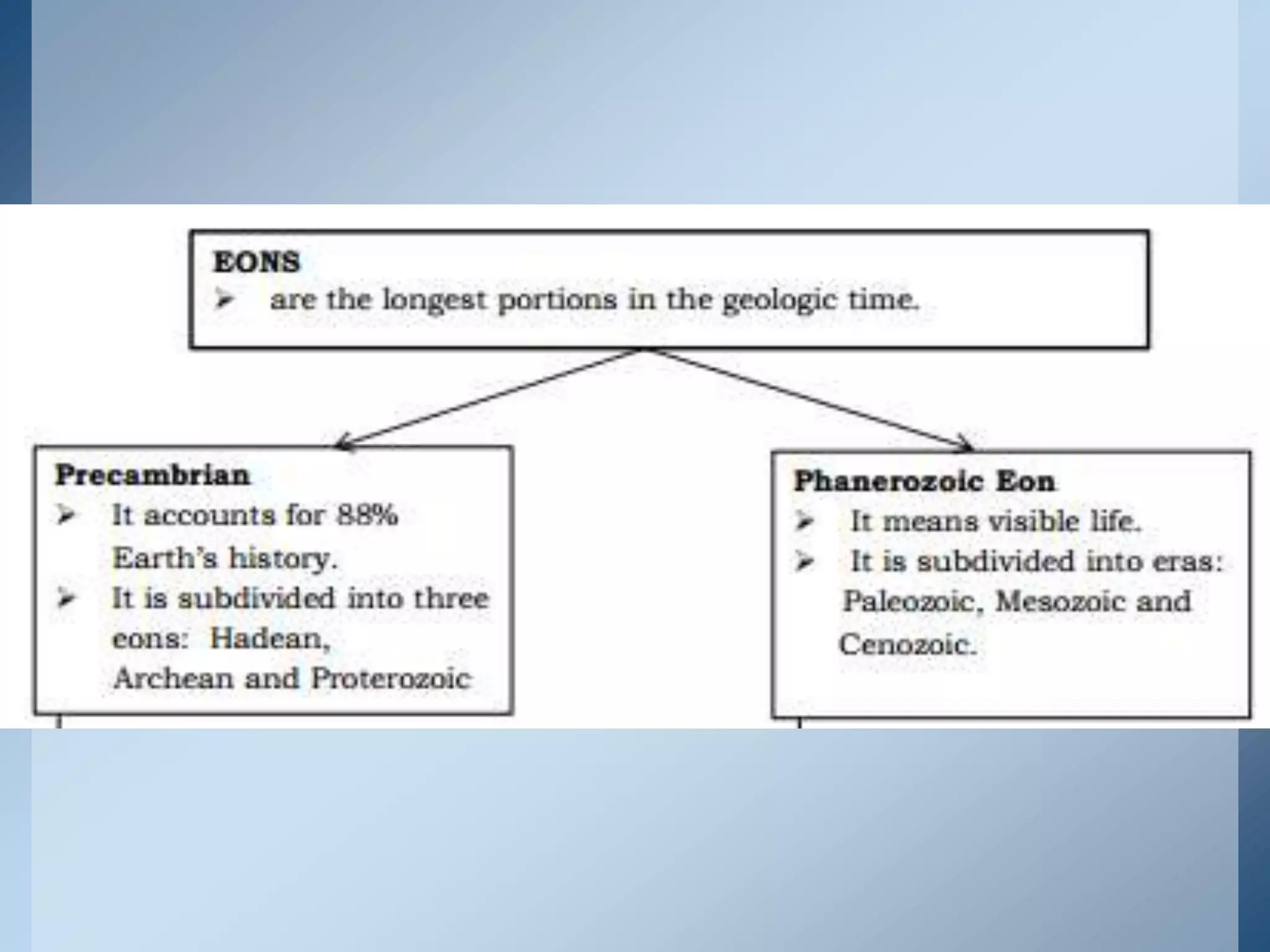
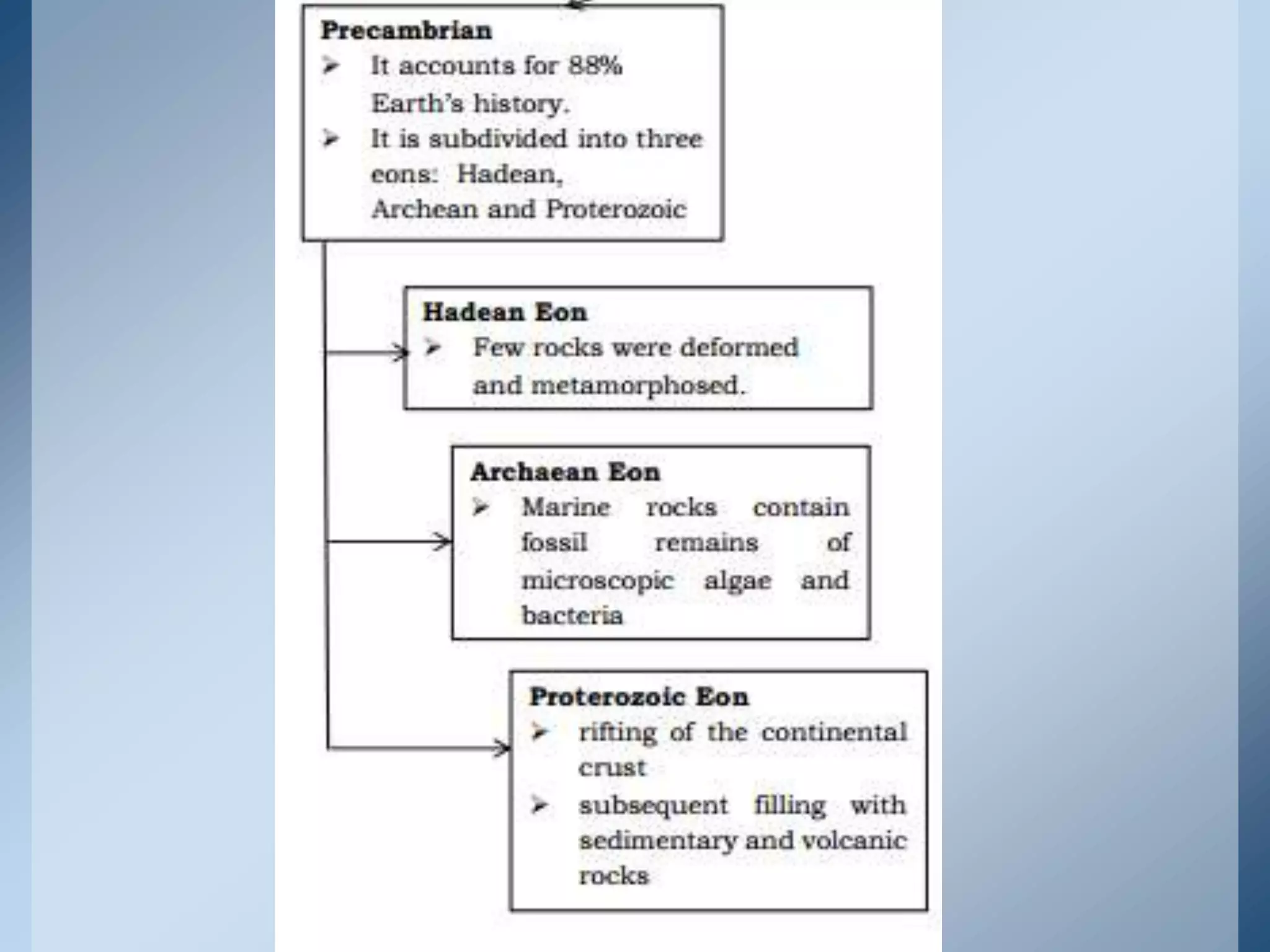
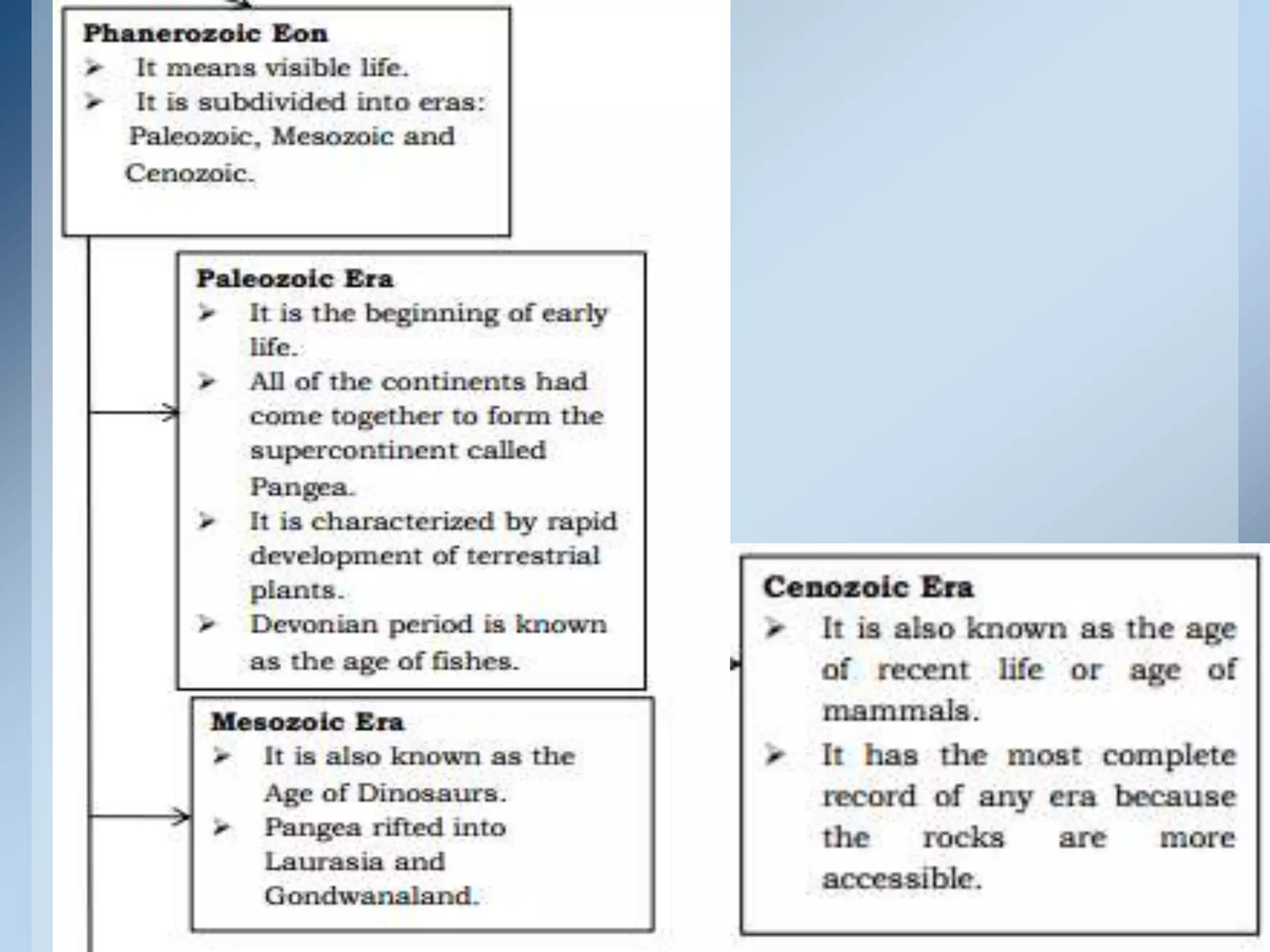
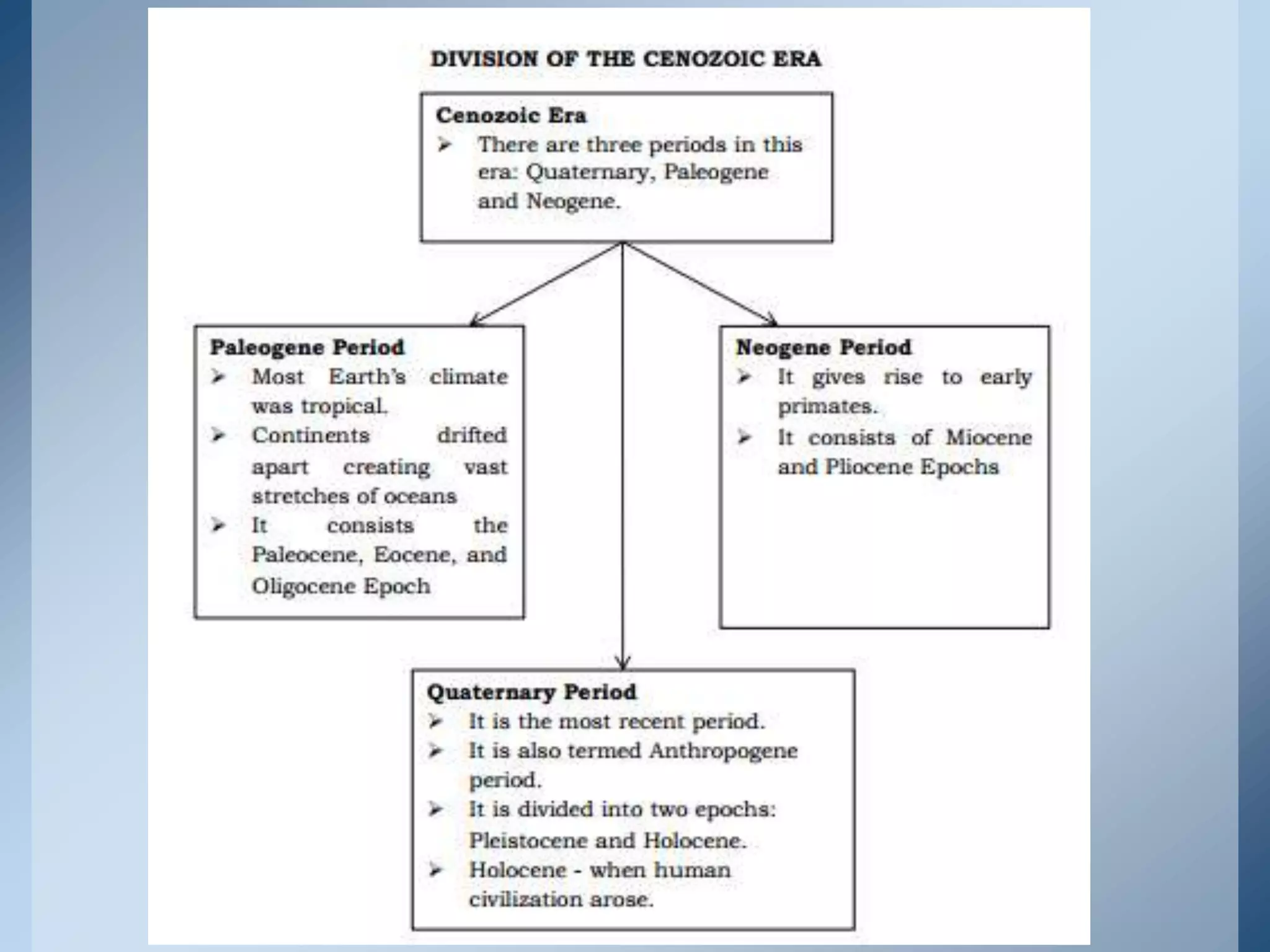
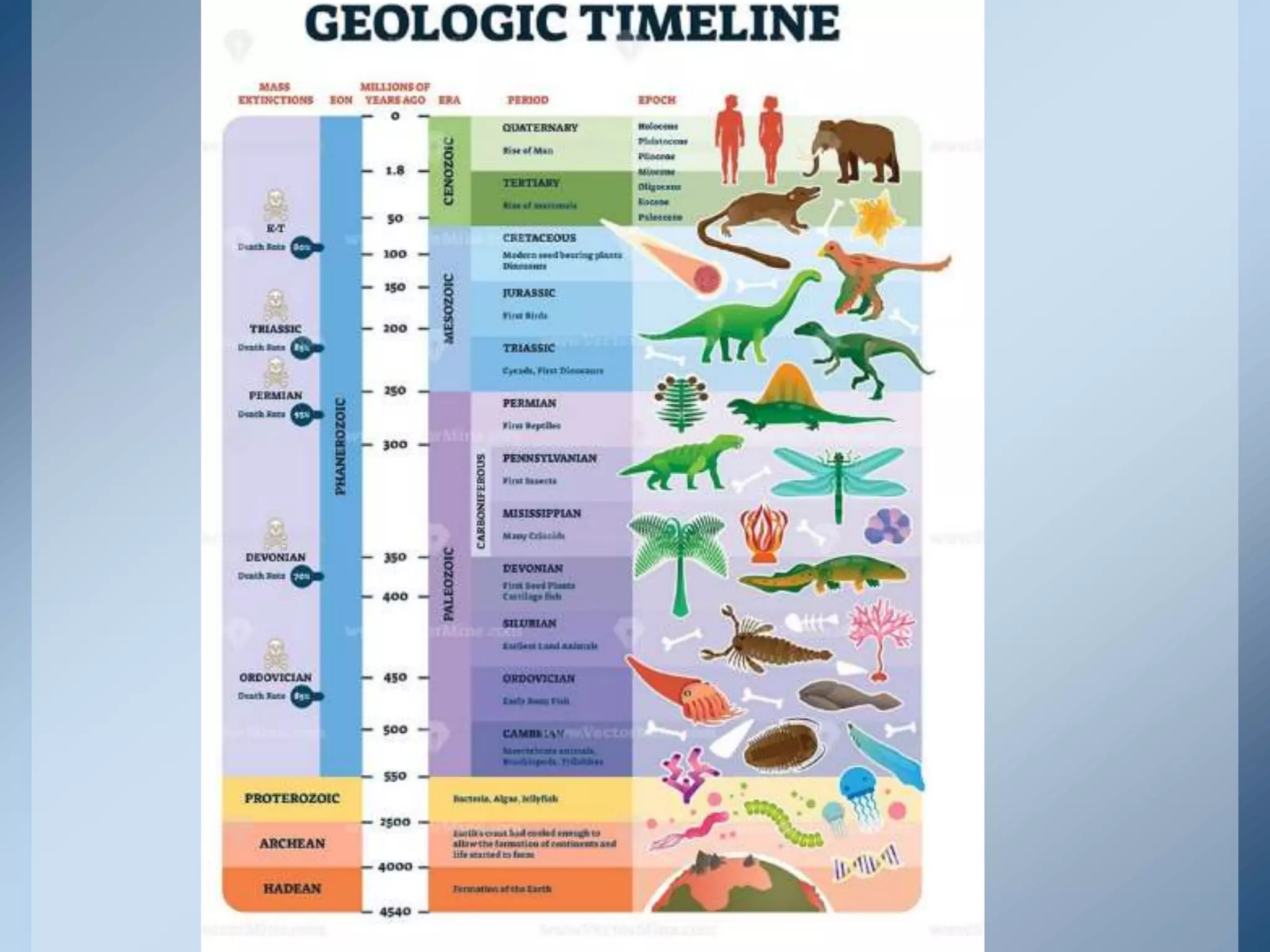
This document provides an overview of the geologic timeline and its divisions. It explains that the geologic timeline serves as a standard chronology for describing the age of rocks, fossils, and Earth's history. The timeline is divided into eons, eras, periods, and epochs. Key events and lifeforms that characterized the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras are summarized, including the formation of Pangea, rise of reptiles and dinosaurs, mass extinctions, and evolution of mammals. The document stresses the importance of understanding Earth's history for comprehending present-day conditions and future changes.