1. The document discusses methods for dating rocks, including relative dating techniques based on stratigraphy and principles like superposition, as well as absolute dating using radiometric methods like radiocarbon, potassium-argon, and uranium-lead dating.
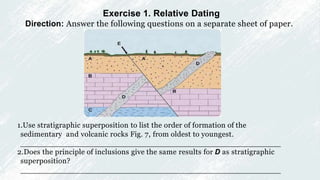
2. It explains key concepts in stratigraphy like how stratified rocks are formed through deposition of sediments in horizontal layers. The principles of superposition, original horizontality, cross-cutting relationships, inclusions, and fossil succession allow geologists to determine the relative ages of stratified rocks.
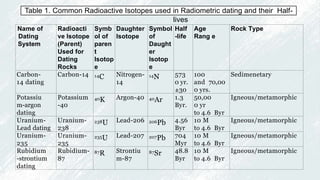
3. Absolute dating methods like radiocarbon, potassium-argon, uranium-lead, and rubidium-strontium dating determine the numerical ages of rocks by measuring the decay of