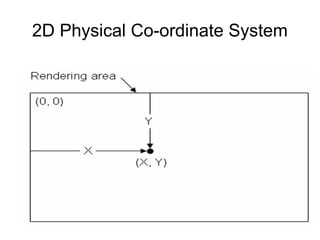
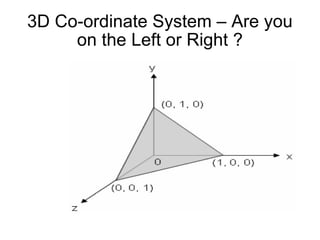
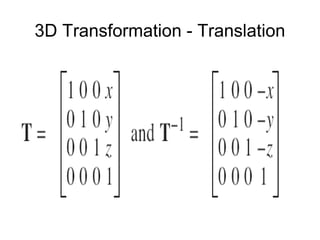
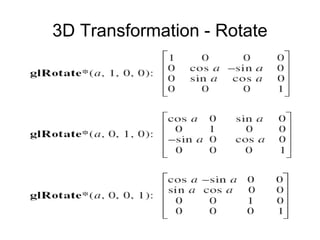
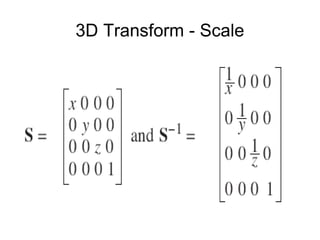
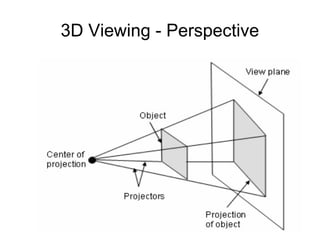
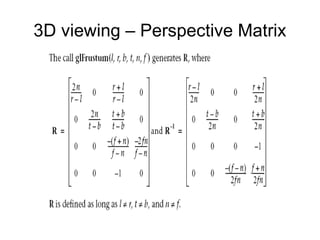
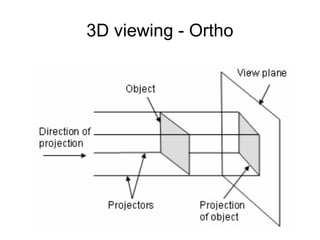
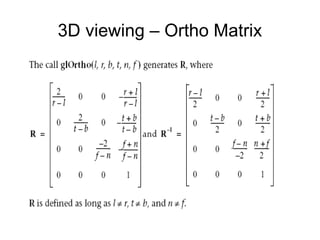
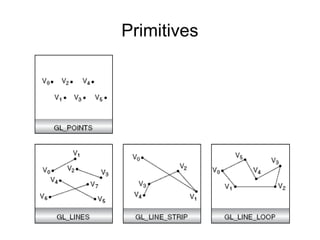
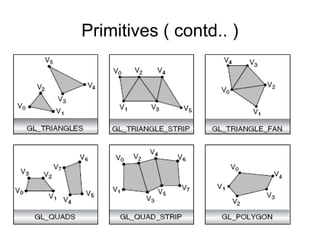
1. The document provides an introduction to 3D computer graphics and graphics programming, covering fundamental concepts like pixels, 2D and 3D coordinate systems, and transformations.
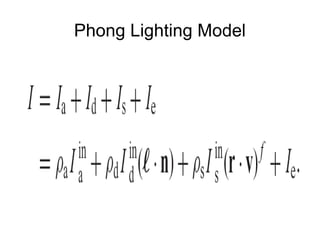
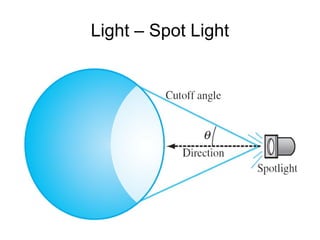
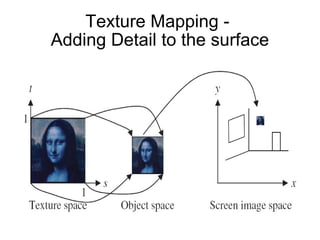
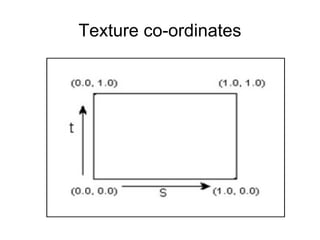
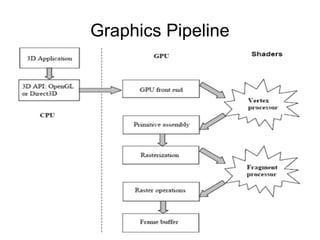
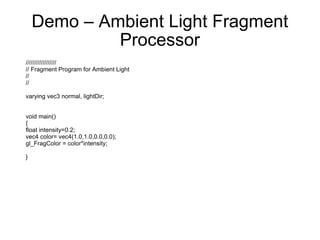
2. It discusses rendering concepts such as lighting models, texture mapping, and shaders. Modern GPUs allow for programmable shading through languages like Cg, GLSL, and HLSL.
3. Advanced techniques like ray tracing are also introduced, which trace the path of light in a scene to realistically render 3D graphics.
![3D Computer Graphics - a Technical Introduction AKA 3D Graphics Programming ! By Praseed Pai K.T. http://praseedp.blogspot.com [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/praseedpai-091220224535-phpapp01/85/Praseed-Pai-1-320.jpg)