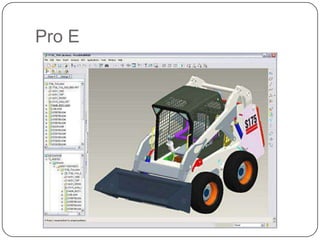
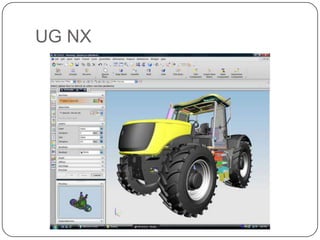
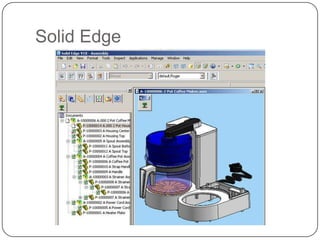
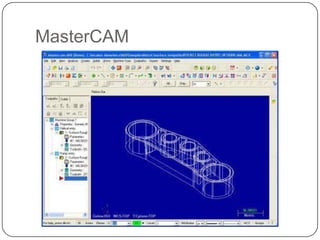
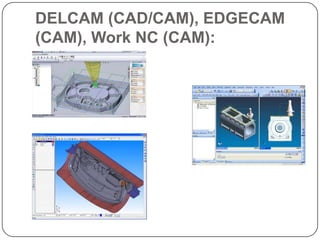
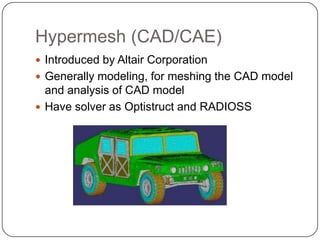
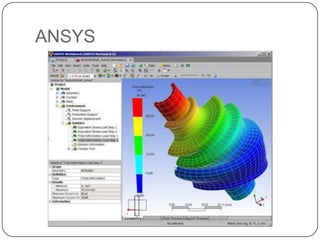
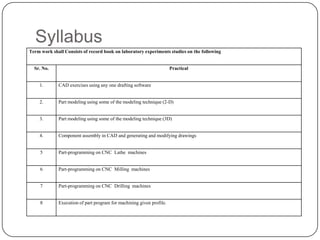
This document provides an overview of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) tools and software. It defines design and discusses popular design approaches. CAD is defined as using computers to assist in product design, while CAM uses computers to control manufacturing operations. The need for CAD/CAM is explained in terms of increasing productivity, quality, and optimization. Popular CAD software like AutoCAD, CATIA, Pro/ENGINEER, Siemens NX, Solid Edge, and SolidWorks are described. CAM and CAE software such as MasterCAM, DELCAM, EdgeCAM, Work NC, HyperMesh, ANSYS, and SIMULIA are also summarized. The document concludes with the syllabus for