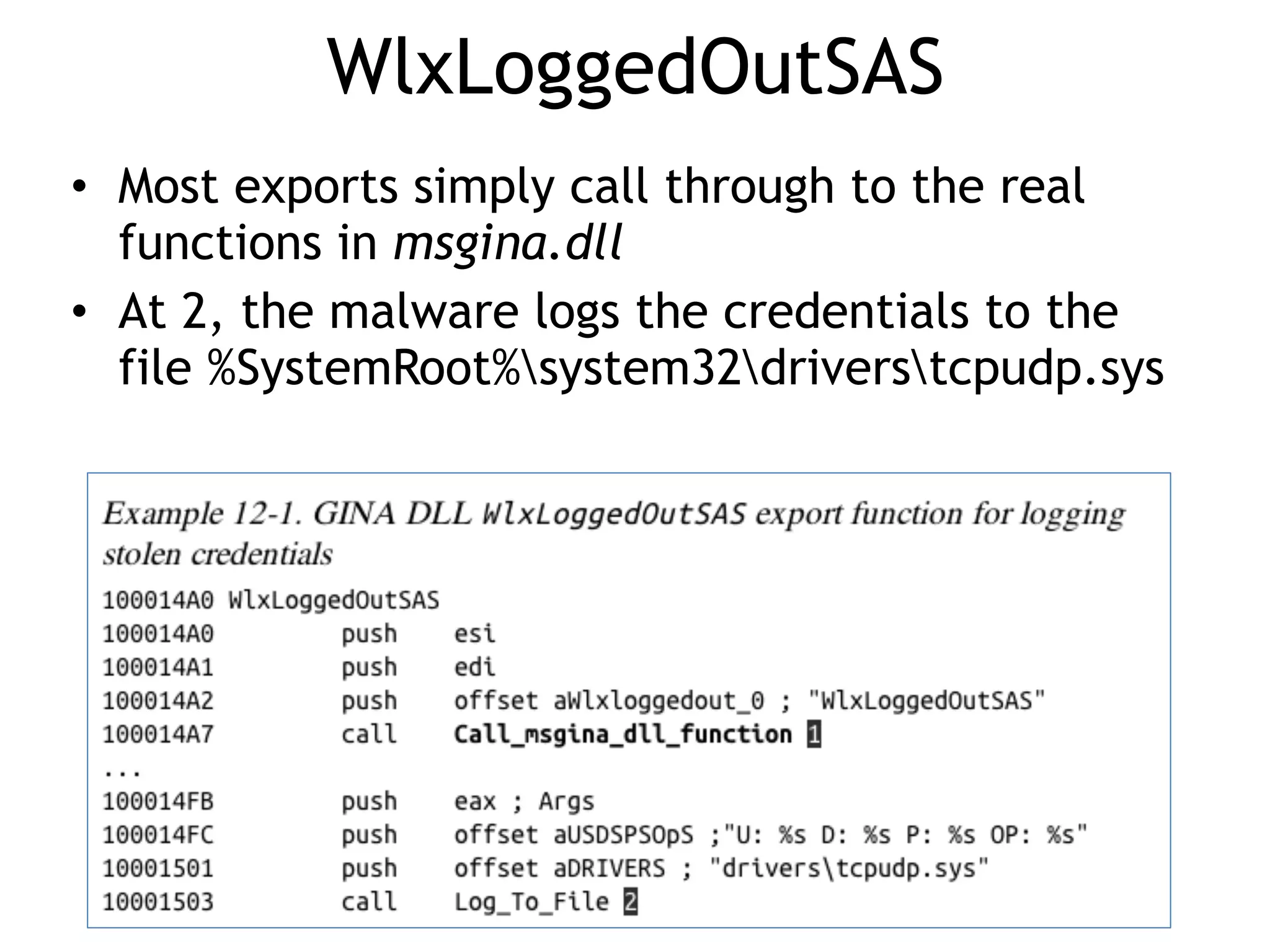
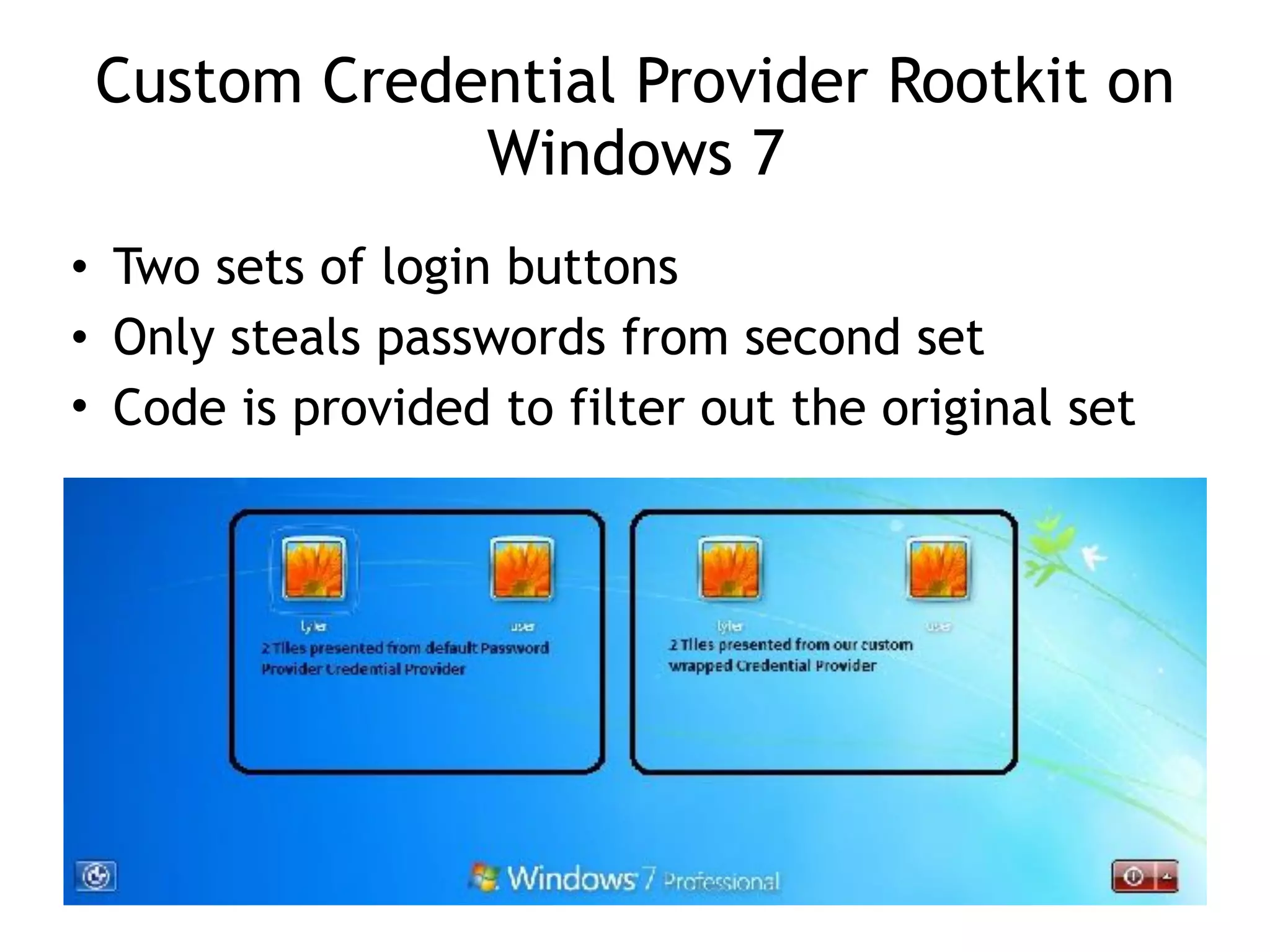
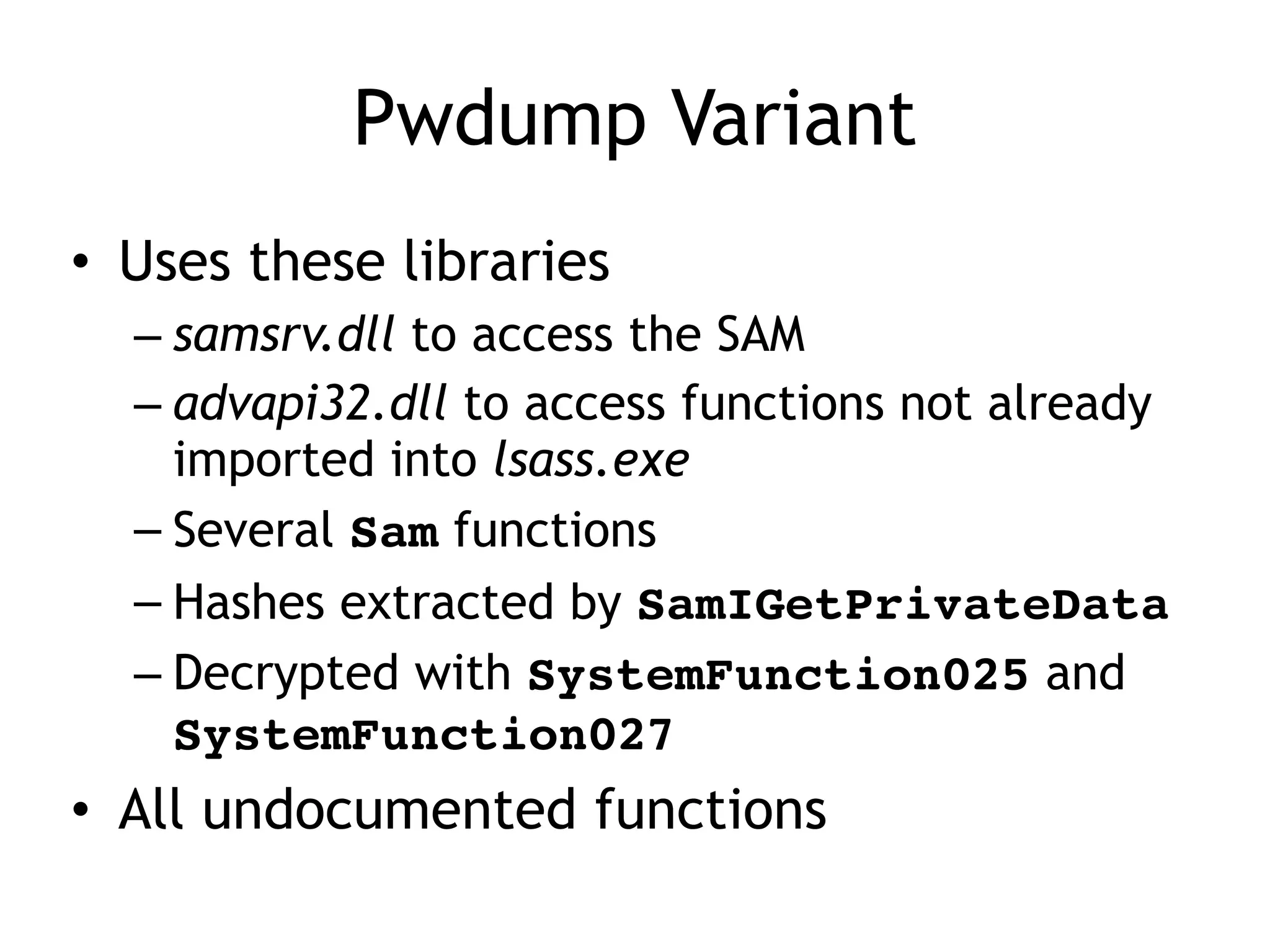
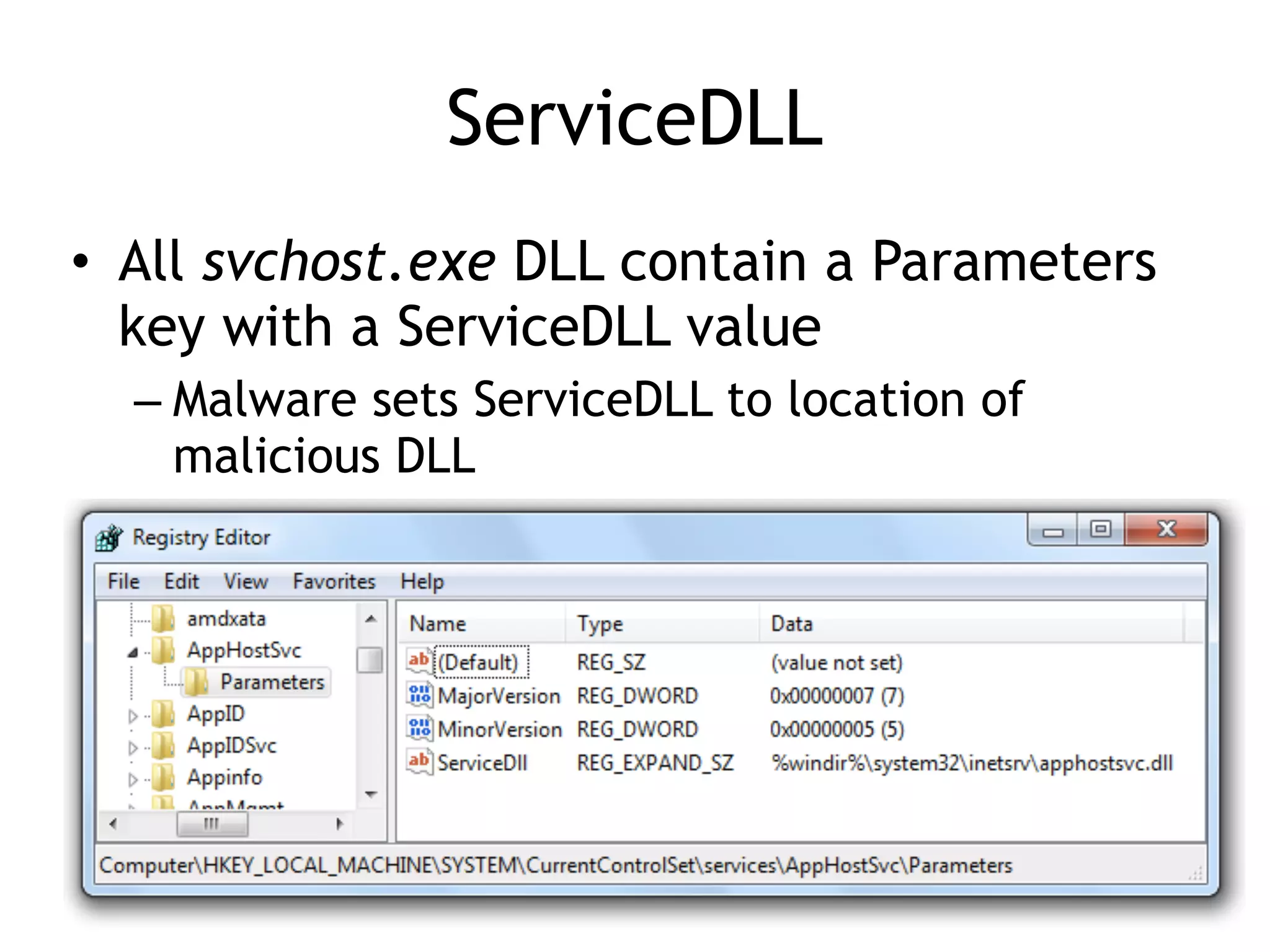
This document summarizes various types of malware behaviors including downloaders and launchers, backdoors, credential stealers, keyloggers, and techniques for persistence and privilege escalation. Downloaders download and execute other malware while launchers prepare other malware for execution. Backdoors provide remote access to infected machines. Credential stealers steal login credentials in various ways. Keyloggers log keystrokes through hooking or polling methods. Malware uses techniques like registry modifications, trojanizing binaries, and DLL load hijacking for persistence. It may also exploit privileges like SeDebugPrivilege for privilege escalation. User-mode rootkits modify OS functionality to hide malware by techniques like IAT and inline hooking.