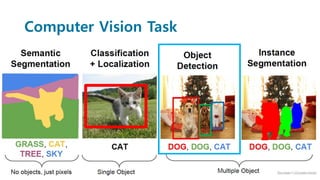
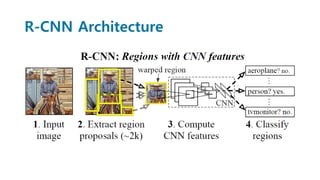
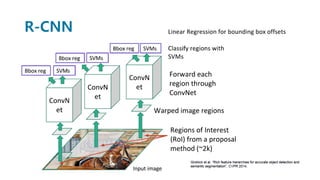
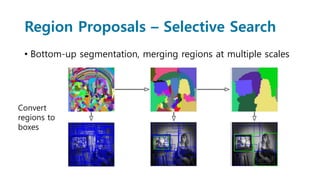
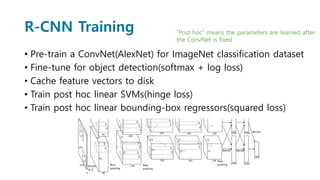
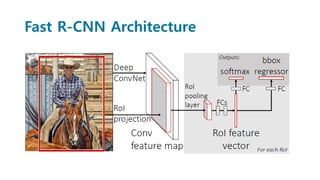
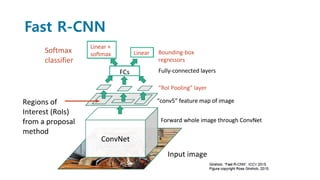
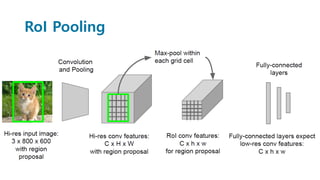
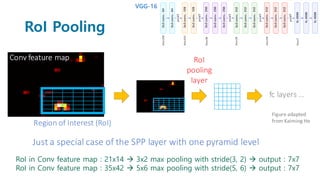
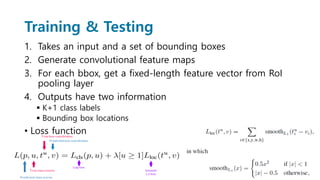
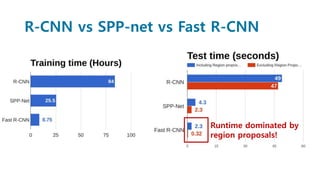
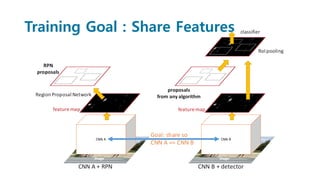
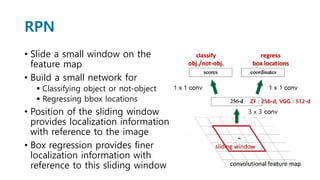
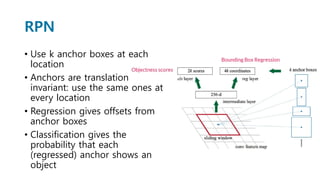
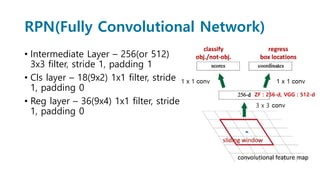
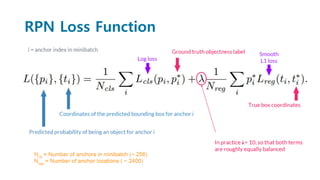
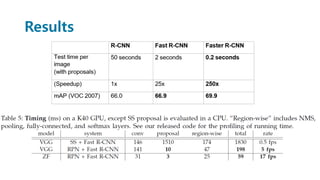
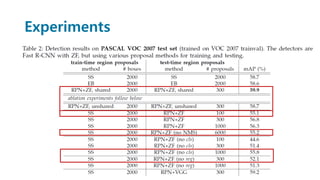
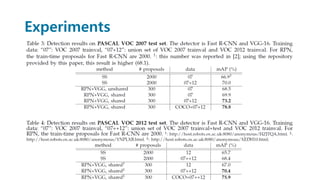
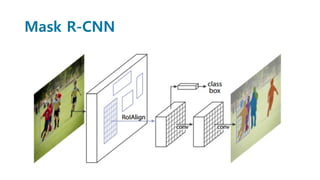
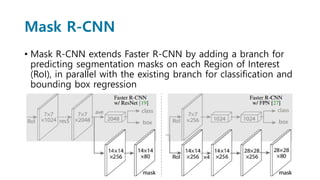
Faster R-CNN improves object detection by introducing a Region Proposal Network (RPN) that shares full-image convolutional features with the detection network, thus enabling nearly cost-free region proposals. The RPN slides over feature maps and predicts object bounds and objectness at each position. During training, anchors are assigned positive or negative labels based on Intersection over Union with ground truth boxes. Faster R-CNN runs the RPN in parallel with Fast R-CNN for detection, end-to-end in a single network and stage. This achieves state-of-the-art object detection speed and accuracy while eliminating computationally expensive selective search for proposals.