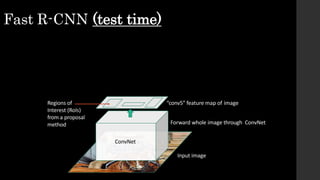
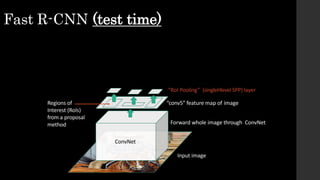
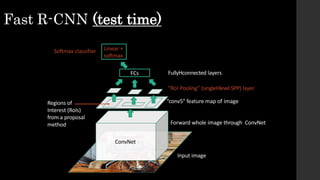
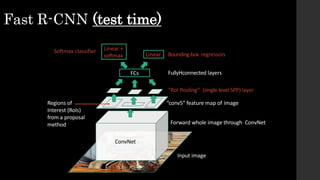
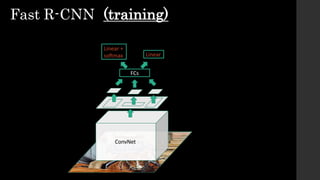
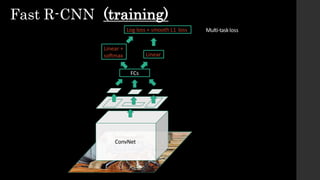
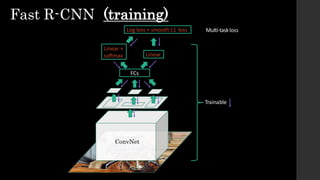
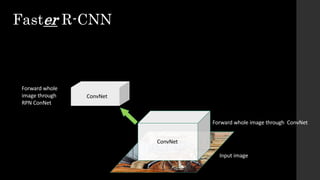
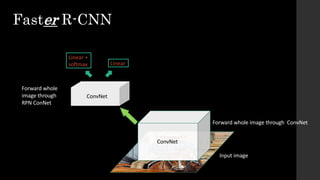
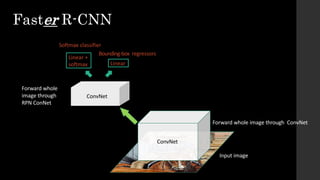
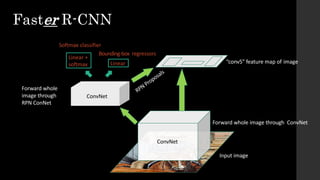
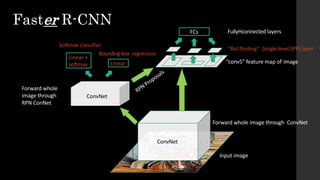
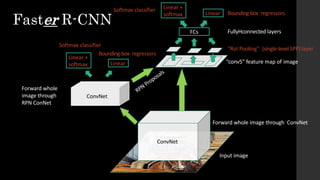
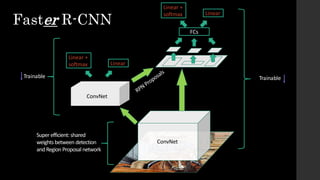
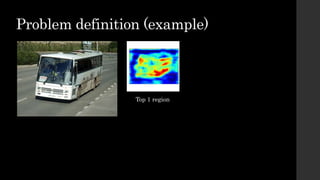
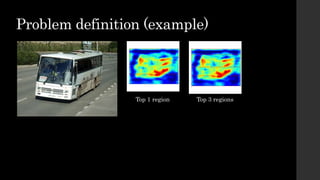
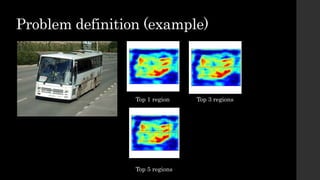
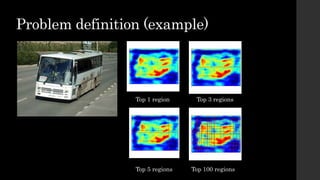
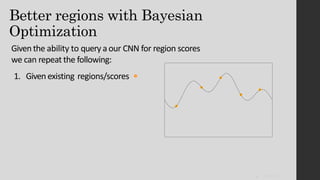
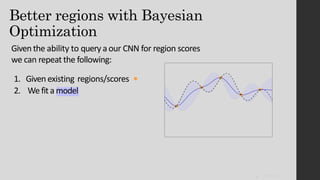
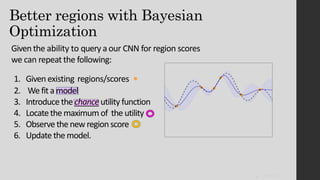
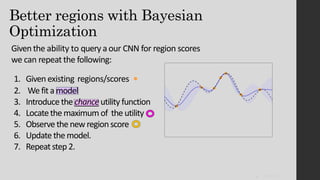
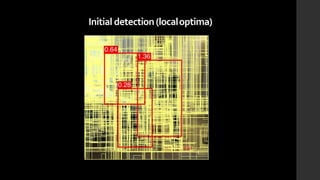
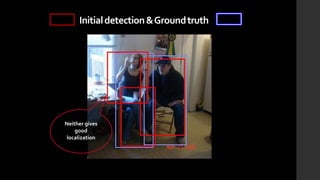
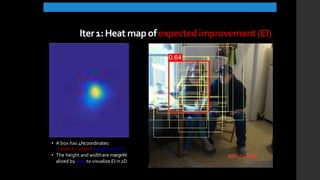
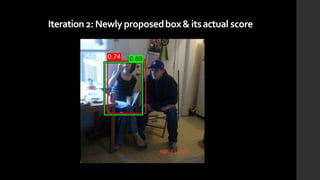
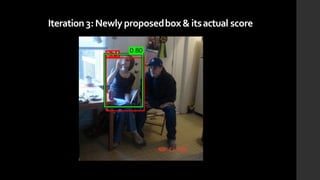
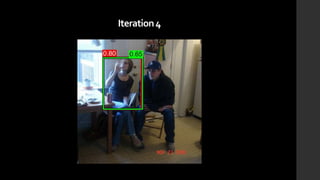
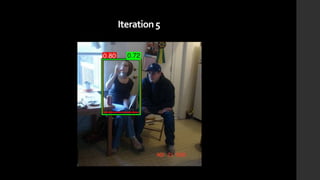
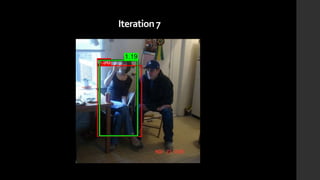
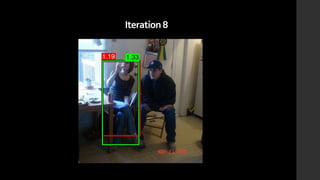
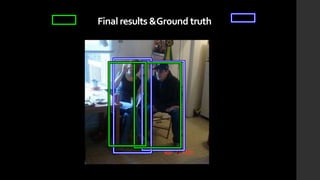
The document discusses the evolution of region-based CNN object detectors, highlighting the limitations of previous models like R-CNN, SPP-Net, and Fast R-CNN, particularly in terms of training time and reliance on external region proposal algorithms. It proposes a solution utilizing Bayesian optimization to improve the quality of region proposals in object detection by iteratively refining the locations of proposed regions for better localization. The methodology involves querying the CNN for region scores, fitting a model, and optimizing a utility function to effectively sample new regions that maximize detection accuracy.






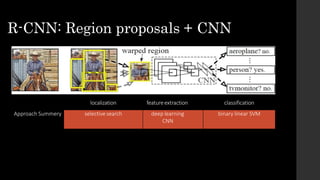


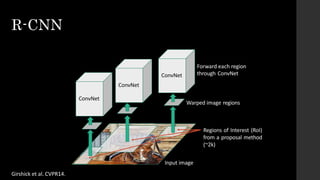
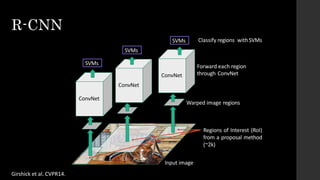
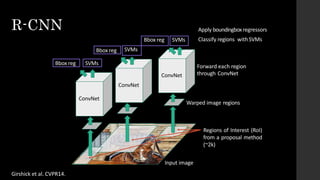



![• Ad hoc training objectives
• FineHtune network with softmax classifier (log loss)
• Train postHhoclinear SVMs (hingeloss)
• Train postHhocboundingHboxregressions (least squares)
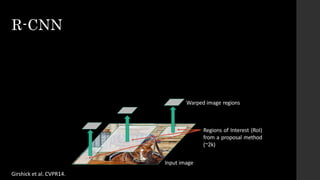
• Training is slow (84h), takes a lot of disk space
• Inference (detection) is slow
• 47s / image with VGG16 [Simonyan & Zisserman. ICLR15]
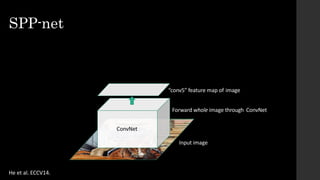
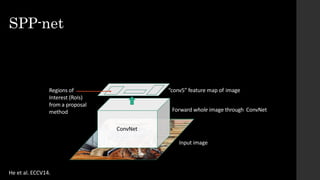
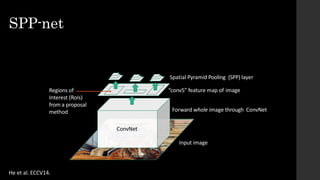
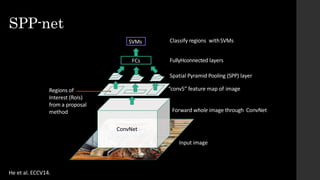
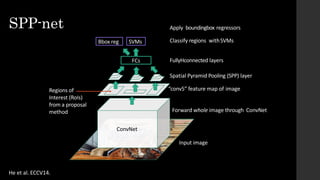
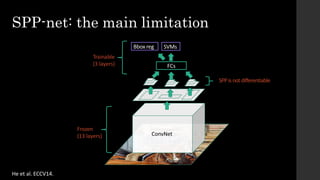
• Fixed by SPP-net[He et al. ECCV14]
~2000 ConvNet forward passes per image
What’s wrong with R-CNN?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/proposal-170807144522/85/Improving-region-based-CNN-object-detector-using-bayesian-optimization-17-320.jpg)