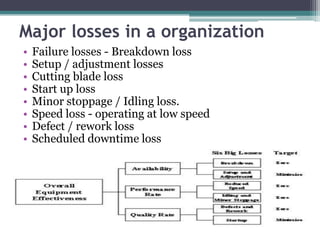
This document provides an introduction to Total Productive Maintenance (TPM). TPM aims to maximize equipment effectiveness and minimize breakdowns through a multifaceted approach involving all employees. It covers safety, quality maintenance and improvement. The origins of TPM can be traced back to 1951 in Japan and focuses on achieving zero defects, breakdowns and accidents. TPM benefits include increased productivity and employee morale, improved quality and safety, and reduced costs.