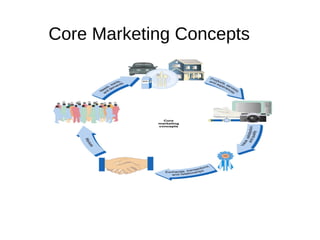
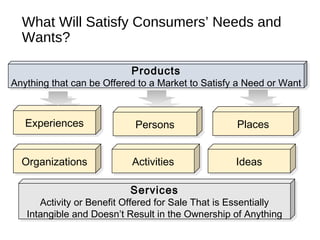
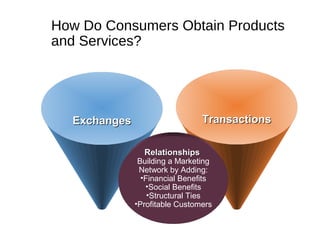
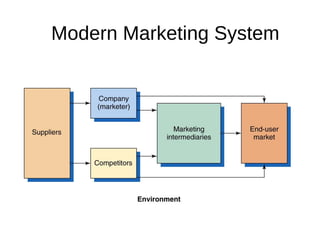
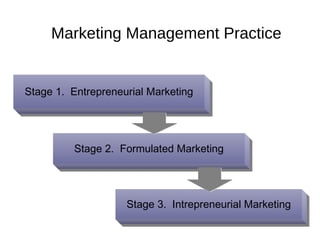
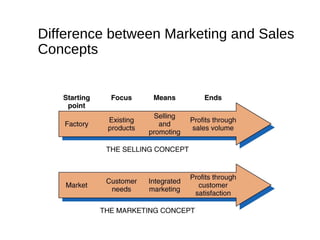
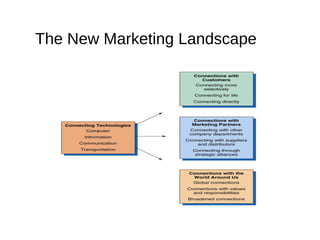
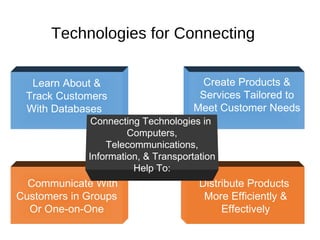
The document provides an overview of key concepts in marketing and marketing management. It defines marketing as managing profitable customer relationships by attracting new customers and retaining current ones. The goals of marketing are to promise superior value to attract customers and deliver satisfaction to keep them. Marketing is further defined as a social and managerial process where individuals obtain what they need through creating and exchanging products of value with others. The document then discusses marketing management philosophies from production to societal concepts and how new technologies enable connecting with customers, partners, and the world to build relationships.