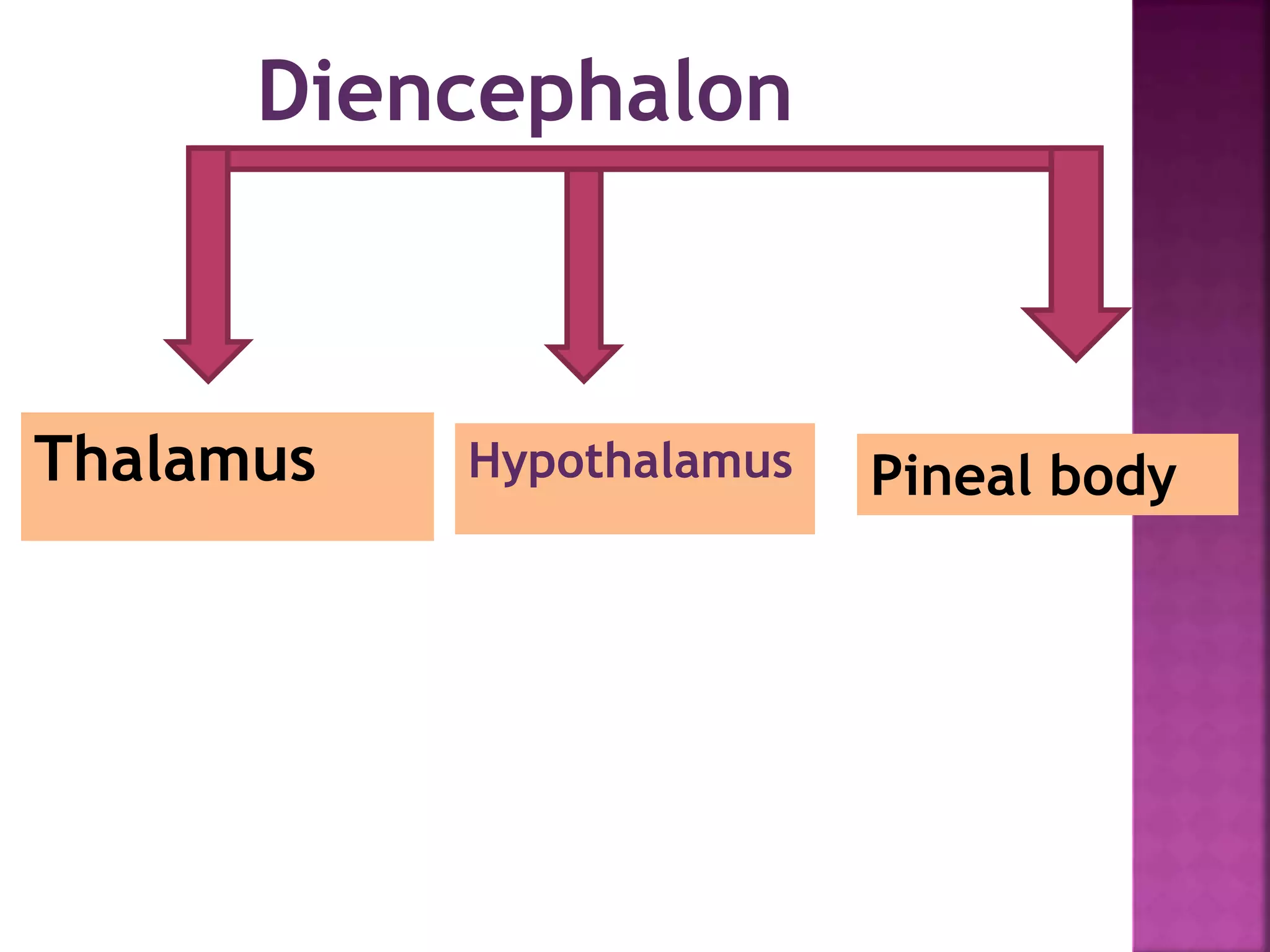
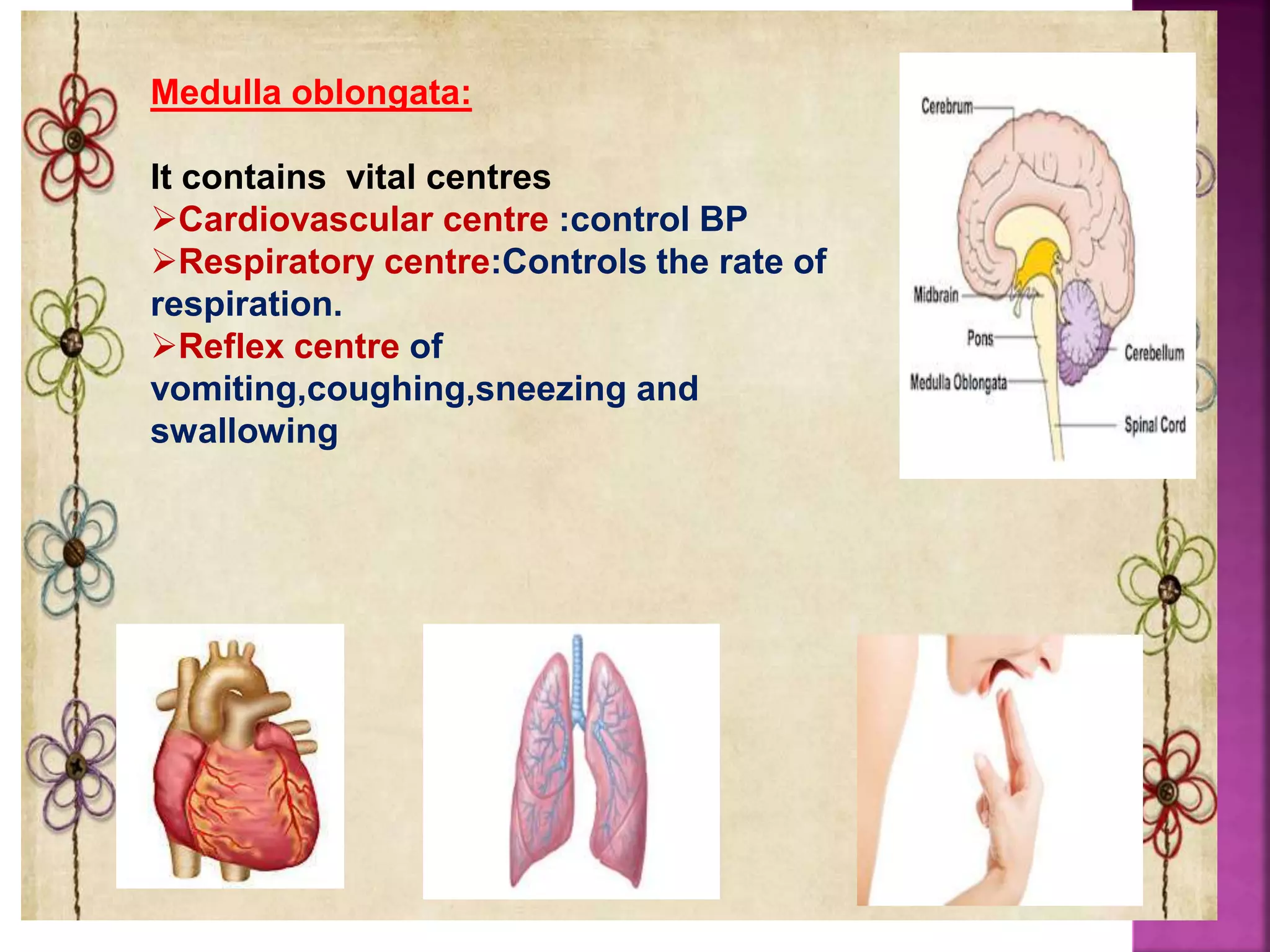
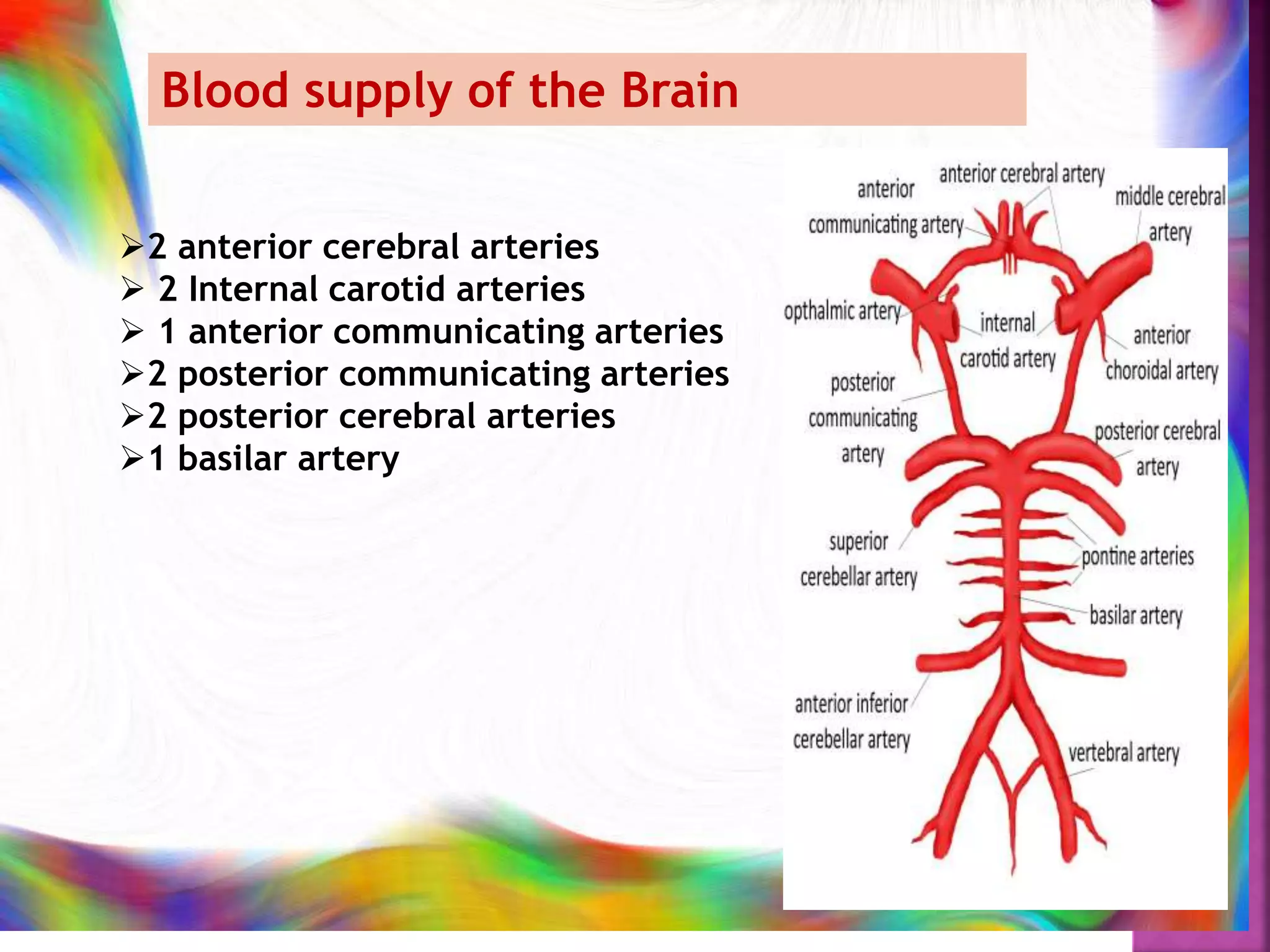
The document provides an overview of the human brain, detailing its structure, functions, and key components such as the cerebrum, diencephalon, brainstem, and cerebellum. It explains the roles of various brain parts in sensory processing, memory, movement, and autonomic functions, as well as the blood supply to the brain. Additionally, it contains bibliographic references for further reading on anatomy and physiology.