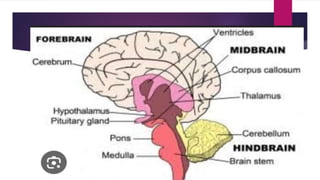
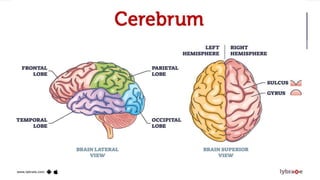
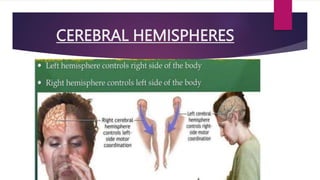
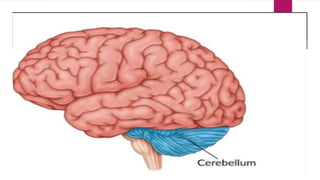
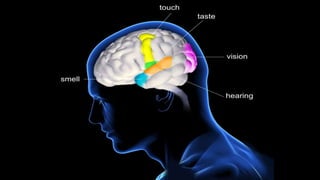
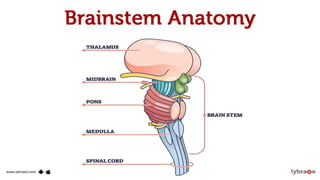
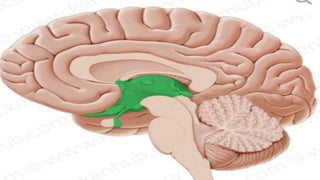
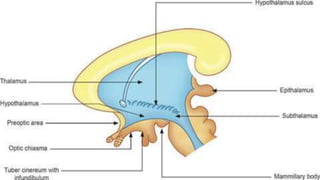
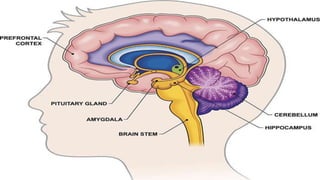
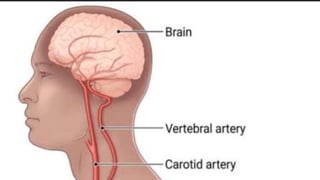
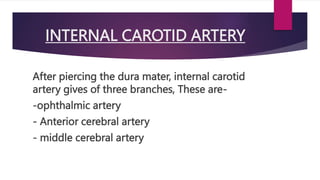
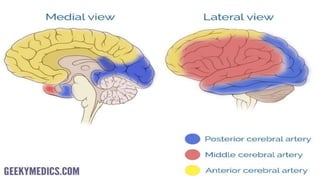
This seminar explores the structure and functions of the brain. It will identify the major regions of the brain - the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem - and describe their specialized roles. The seminar will examine specific functions of each brain lobe and their interconnections, as well as areas responsible for special sensations. It will also investigate specialized structures like the limbic system and explore the brain's blood supply.