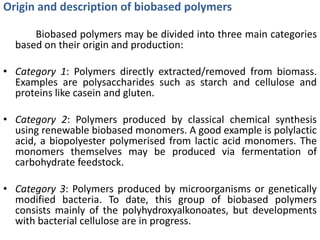
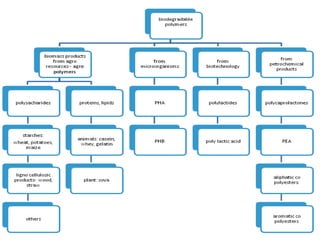
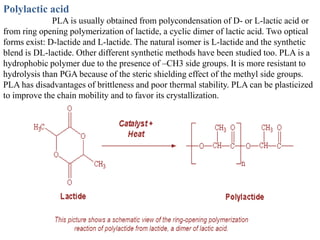
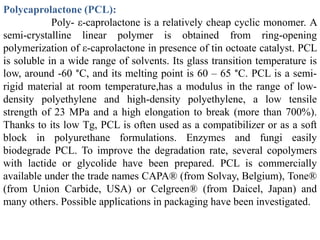
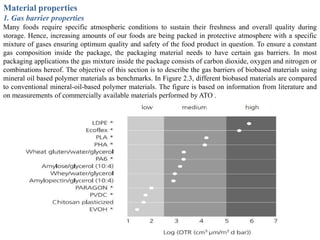
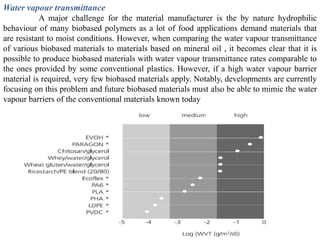
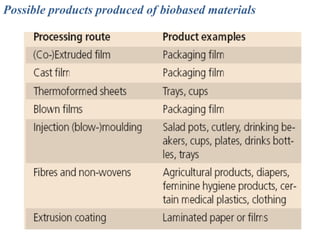
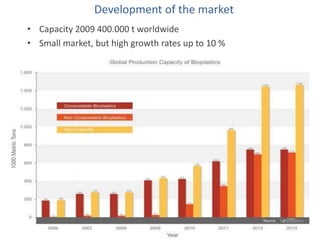
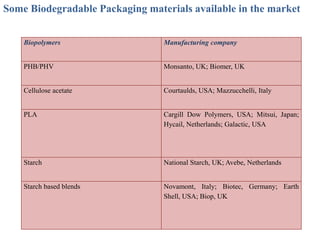
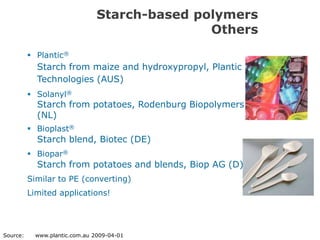
Biopolymers can be divided into three categories based on their origin and production:
1) Polymers directly extracted from biomass like starch and cellulose
2) Polymers produced from biobased monomers through chemical synthesis like polylactic acid
3) Polymers produced by microorganisms or genetically modified bacteria like polyhydroxyalkanoates
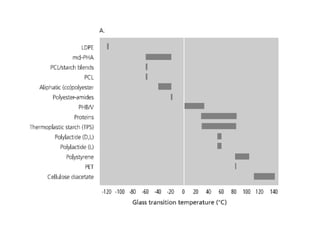
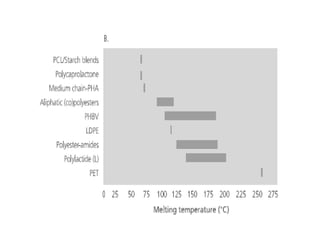
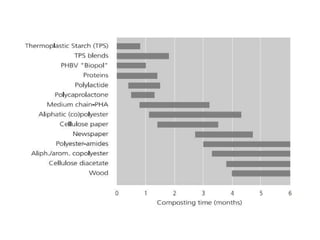
Common biopolymers include starch, polylactic acid, polyhydroxyalkanoates, and polycaprolactone. These materials have properties similar to conventional plastics but are biodegradable. Their gas barrier and thermal properties depend on material and humidity conditions. Biopolymers can be composted within weeks to months depending on