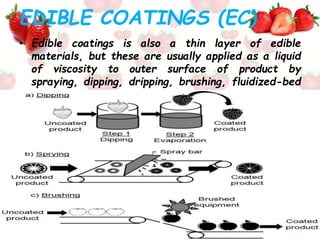
This document discusses edible films and coatings used for food packaging. It begins by introducing common food packaging materials like plastic, paperboard, and metal cans that end up in landfills. It then discusses how edible films and coatings can provide an alternative by acting as the food packaging that can be consumed. Edible films are free-standing sheets that can wrap or separate food layers, while coatings are thin liquid layers applied to food surfaces. Common biopolymers used include polysaccharides like starch, proteins like gelatin and casein, and lipids like wax. Edible packaging can help extend shelf-life by preventing moisture loss and microbial growth while providing a more sustainable alternative to traditional packaging waste.