1. The document discusses key concepts in statistics including population, sampling, random sampling, standard error, and standard error of the mean.
2. A population is the total set of observations, while a sample is a subset selected from the population. Random sampling selects subjects entirely by chance so each member has an equal chance of being selected.
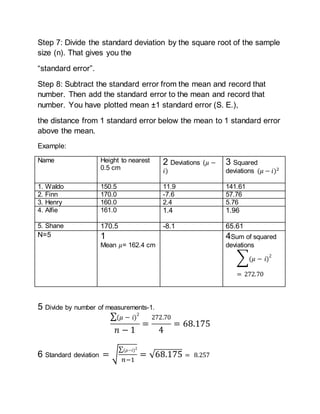
3. The standard error is the standard deviation of a statistic's sampling distribution and indicates how much a statistic may vary between samples. It decreases with larger sample sizes. The standard error of the mean specifically measures how much the sample mean may differ from the population mean.