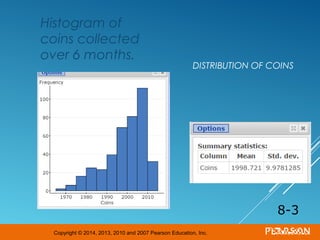
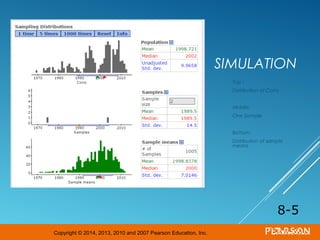
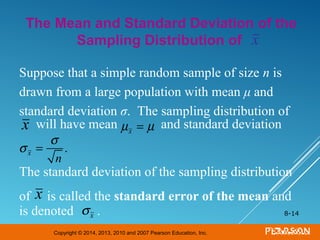
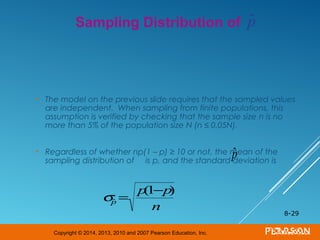
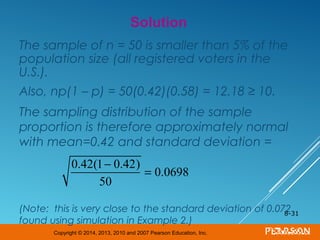
This document discusses sampling distributions and their properties. It begins by describing the distribution of the sample mean for both normal and non-normal populations. As sample size increases, the distribution of the sample mean approaches a normal distribution regardless of the population distribution. The document then discusses the sampling distribution of the sample proportion. For large samples, this distribution is approximately normal with mean equal to the population proportion and standard deviation inversely related to sample size. Examples are provided to illustrate computing sample proportions and probabilities involving sampling distributions.