This document compares the efficiency of four power electronic converters used in grid-connected permanent magnet wind turbine systems: intermediate boost converter, intermediate buck-boost converter, back-to-back converter, and matrix converter. It develops a model to calculate power generation from the wind turbine at different wind speeds. It then establishes a relationship between wind speed and power losses in the semiconductor devices of each converter to evaluate efficiency over the wind speed range. Simulation results show the power loss characteristics with varying wind speed and determine the most efficient converter is the intermediate boost converter for typical wind conditions at the kW level.


![diversity and security. However, the most important aspect for connecting a WECS with the
electric grid requires a power electronic converter (PEC) that allows variable-speed operation,
reduces mechanical stress, and increases efficiency. Among various performances and design
criteria for the converter, the overall efficiency is one of the most significant factors because of
a growing concern regarding the energy savings and cost. However, a considerable lack in
comparison of a series of converters is observed in the previous literatures that practically
discussed with the precise model of semiconductor devices power loss that varies with the
wind speed and finally, the global efficiency of the converters in the wind energy domain.
The PECs are composed of semiconductor devices and indeed, power losses occur during
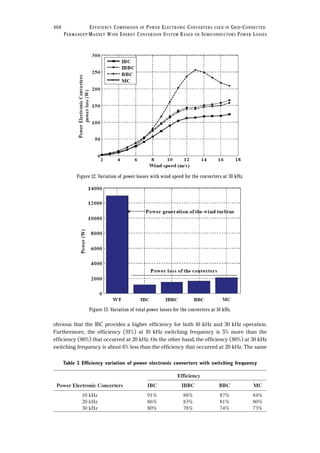
operation. Moreover, as the PECs are connected to a wind turbine; the power losses will vary with
the wind speeds. As a result, while calculating the efficiency of a converter, one should also
consider the variation of the losses for each wind speed to clarify the effectiveness of a specific
converter for the entire wind speed regime. A calculation of converter efficiency for a given
operating condition is performed in [1–19] in terms of the total semiconductor power losses.
However, either calculating converter efficiency or individual semiconductor power loss model
lacks a considerable valid justification. This is because, firstly, a non-linear loss model approach is
unable to reflect the switching losses of the semiconductor devices, which could be a dominant
factorduringthehighswitchingstate[1–8].Secondly,powerlossmodelbasedonthedataprovided
by the manufacturers is ambiguous and pessimistic [9–13]. Thirdly, physics-based simulation
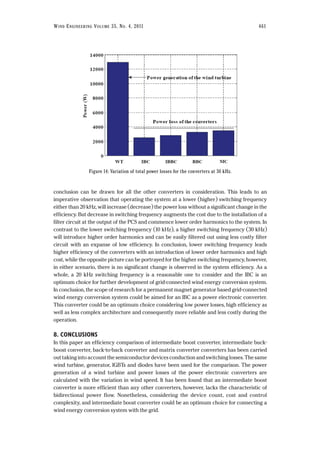
modelsofsemiconductordevicespowerlossesrequiresimplicitintegrationmethods,leadingtoan
increased simulation time. Furthermore, it requires detail knowledge of the dimensions of the
devices [14, 15]. There have been numerous other efforts for modeling the power losses of
converters used in wind turbine systems. In [16–19] presented the concept of maximum device
rating power loss model of the converter, however, switching losses is often ignored.
Based on the above discussions, it can be asserted that most of the attempts for the
converter efficiency calculation in terms of the power loss model have been developed based
on several assumptions and often neglected a fraction of the entire converter power losses.
This discrepancy could affect the preference of an efficient grid-connected WECS that is in a
great need for high penetration of the wind power. As a consequence, this research aims at
advancing the use of grid-connected WECS by modeling the wind turbine (WT) power
generation and power losses of the semiconductor devices for the most useable converters
with the variation in wind speeds. Based on the power generation and loss for individual wind
speed, a global efficiency is calculated for the considered wind speed regime of each
converter and an efficient converter is determined.
This paper is organized as follows: Followed by a detail literature review in the second
section, the selected converter systems are presented in the third section. The fourth section
describes the global efficiency calculation of the converters. The modeling approach to obtain
the power generation of the furled WT along with the operating conditions is described in the
fifth section, while the sixth section contains the mathematical model for power loss
calculations in the semiconductor devices. Simulation results and discussions are presented
and discussed in the seventh section and finally, the findings of the investigations are
highlighted in the conclusions.
3. POWER ELECTRONIC CONVERTERS FOR GRID CONNECTED WIND ENERGY
CONVERSION SYSTEM
The design concept of wind turbine has progressed from induction generator based fixed
speed, flapping/passive pitching-controlled drive train with gearbox to permanent magnet
generator (PMG)-based variable-speed, furling/soft stall-controlled systems with or without
446 EFFICIENCY COMPARISON OF POWER ELECTRONIC CONVERTERS USED IN GRID-CONNECTED
PERMANENT-MAGNET WIND ENERGY CONVERSION SYSTEM BASED ON SEMICONDUCTORS POWER LOSSES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2ce15902-c6ee-4eee-b399-1728a840bc95-150128232617-conversion-gate02/85/Power-Electronics-3-320.jpg)
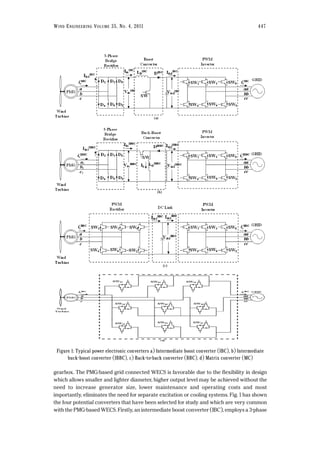
![bridge rectifier, a boost converter and a grid-connected pulse width modulated (PWM)
inverter (Fig. 1a) [10, 20]. Secondly, intermediate buck-boost converter (IBBC), employs a 3-
phase bridge rectifier, a buck-boost converter and a grid-connected PWM inverter (Fig. 1b) [21,
22]. Thirdly, back-to-back converter (BBC), composed of a rectifier, DC link and a PWM
inverter (Fig. 1c) [23, 24]. And lastly, matrix converter (MC), employs 9 bidirectional switches
for three phase input and output connection between the generator and grid (Fig. 1d) [25, 26].
Each of the converters has their own advantages and disadvantages and a brief literature
review can be found in [27].
4. EFFICIENCY CALCULATION
In order to calculate the efficiency of the converters, the relation between the wind speed and
power generation/loss for each wind speed is needed. Once the power generation is known
for discrete wind speed using Section V, the total power generation, Pg is expressed as
(1)
where wi represents a particular wind speed within the wind speed regime and Pg,i (wi) is the
power generation for wi wind speed. . The power loss for the wind speed of each converter can
be found as described in Section VI and the total power loss, Pl is mathematically expressed as
(2)
The global efficiency, η of the converters is then calculated as,
(3)
5. WIND TURBINE MODEL
A wind turbine can be characterized by the non-dimensional curve of power coefficient, Cp as
a function of tip speed ratio, λ, where, λ is given in terms of rotor speed, ωs (rad/s), wind speed,
w (m/s), and rotor radius, Rw (m) as
(4)
The relationship between Cp and λ can be approximated by a quartic equation. In this
research, the curve is obtained from the literature [28]. A model for Cp as a function of λ is
calculated and the curve generated by the approximate model and the actual data are
presented in Fig. 2a. Statistical analysis shows that the R2 value of the model is 99.8% and the
p-value from the chi-square goodness-of-fit test is less than 0.0001, which shows that the
predicted model for Cp with the fitted coefficients is acceptable. The resulting equation is
found to be
(5)
The curve between wind speed and furling angle is derived from published data [29]. An
approximate model is used to determine the relation between wind speeds and furling angle.
It is found that a fifth order model is sufficient to represent the relationship. The R2 value and
the p-value from the chi-square goodness-of-fit test of the expected model are found to be
Cp λ λ λ λ λ( )= − + − +0 00044 0 012 0 097 0 2 0 114 3 2
. . . . .
λ
ω
=
R
w
w s
η =
−
×
P P
P
g l
g
100%
P P wl l i i
i w
wn
= ( )
=
∑ ,
1
P P wg g i i
i w
wn
= ( )
=
∑ ,
1
448 EFFICIENCY COMPARISON OF POWER ELECTRONIC CONVERTERS USED IN GRID-CONNECTED
PERMANENT-MAGNET WIND ENERGY CONVERSION SYSTEM BASED ON SEMICONDUCTORS POWER LOSSES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2ce15902-c6ee-4eee-b399-1728a840bc95-150128232617-conversion-gate02/85/Power-Electronics-5-320.jpg)

![wcosθ [30]. Incorporating the furling action, the theoretical power of the wind turbine can be
written from (7) as
(8)
Equation (8) represents the power for varying wind speed of the wind turbine rotor without
accounting for maximum power production. Maintaining a constant optimum tip speed ratio
can ensure the maximum power production. It should be noted that the value of the optimum
tip speed ratio varies from one turbine to another. The relation between power coefficient and
tip speed ratio used in this study requires to assume an optimum tip speed ratio of 7 for the
wind turbine and thus (8) is expressed in terms of the optimum power coefficient as
(9)
where Cp,OPT(λ) is the optimum value of power co-efficient at the optimum TSR.
The theoretical maximum power of the wind turbine described in (9) serves as the dynamic
power reference for all four converters. In the variable-speed systems the speed increases
linearly with the wind speed up to the rated speed, which in this case is reached at 13 m/s. And
from rated to cut-out wind speed, i.e., 17 m/s the turbine speed is lowered using furling action.
The current at the output of the generator is determined by the power generation by the WT
and the generator voltage.
6. POWER LOSS MODEL
A mathematical model of the power losses in the semiconductor devices (diodes/IGBTs) is
required in order to compare the efficiency of the converters. The losses for the
semiconductor devices are strongly dependent on the voltage and current waveforms.
Simplified analytical derivation of voltage and current equations associated with the
individual semiconductor devices are derived to determine the power losses. The power loss
model presented in this investigation focus on the losses generated during the conduction and
switching states of the semiconductor devices.
6.1. Intermediate Boost Converter (IBC)
For the 3-phase diode bridge rectifier, the losses are calculated for a single diode from the known
voltage and current equations. It is assumed that the current and voltage in the 3-phase diode
bridge rectifier are equally distributed in the diodes. As a consequence, considering each diode
current,Id1
IBC
andforwardvoltage,Vftheconductionlosses,Pc1,d-R
IBC
forthediodeisexpressedas[31]
(10)
Under the assumption of a linear loss model for the diodes, the switching loss in each diode,
Ps1,d-R
IBC
is given by [32]
(11)
where Vdc
IBC
and Idc
IBC
are the output current and voltage of the bridge rectifier.
The total losses of the 3-phase diode bridge rectifier, Pt,d-R
IBC
is expressed as
(12)P P Pt d R
IBC
c d R
IBC
s d R
IBC
, , ,− − −= +( )6 1 1
P f E
V
V
I
I
s d R
IBC
WT SR
dc
IBC
r d
dc
IBC
r d
1,
, ,
. .− =
P V Ic d R
IBC
f d
IBC
1 1, − =
P = 0.5R AC wmax w p,OPT
3
λ θ( )( )cos
P AC waero p= ( )( )0 5
3
. cosρ λ θ
450 EFFICIENCY COMPARISON OF POWER ELECTRONIC CONVERTERS USED IN GRID-CONNECTED
PERMANENT-MAGNET WIND ENERGY CONVERSION SYSTEM BASED ON SEMICONDUCTORS POWER LOSSES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2ce15902-c6ee-4eee-b399-1728a840bc95-150128232617-conversion-gate02/85/Power-Electronics-7-320.jpg)
![The conduction and switching loss of the boost converter is calculated by assuming an ideal
inductor (LD
IBC
) at the input. For a boost converter, the IGBT is turned on for a duration d,
while the diode conducts for the duration (1–d). The on-state current of the IGBT is the input
current, Idc
IBC
, while the inverter input current, Idc2
IBC
is given by [33]
(13)
The conduction loss for the diode, Pc,d-B
IBC and IGBT, Pc,i-B
IBC can be obtained by multiplying
their on-state voltage and current with the respective duty cycle and is given by [33]
(14)
(15)
The actual commutation voltage and current for the boost converter are the DC link voltage,
Vdc2
IBC
and input current to the converter, Idc
IBC
. The switching loss of the diode, Ps,d-B
IBC
and
IGBT, Ps,i-B
IBC
in the boost converter are given by [33]
(16)
(17)
The sum of (14) to (17) gives the total losses, Pt,(d+i)-B
IBC
(18)
With the exclusion of snubber circuit, the PWM inverter consists of 6 IGBTs and 6 anti parallel
diodes. The conduction losses of a diode, Pc1,d-I
IBC
and IGBT, Pc1,i-I
IBC
for the inverter can be
expressed as [34],
(19)
(20)
where Iom
IBC
is the maximum value of the sinusoidal output current, iom
IBC
.
For the inverter, the commutation voltage and current are the DC link voltage and output
current. An approximated solution for the switching loss of a diode, Ps1,d-I
IBC
and IGBT, Ps1,i-I
IBC
is
given by [35]
(21)
(22)
The loss, Pt,(d+i)-I
IBC
of the PWM inverter is obtained as the sum of (19) to (22) and expressed by
(23), while the total loss, Pt
IBC
for the IBC is expressed by (24).
P f E E
V
V
I
I
s i I
IBC
sw ON OFF
dc
IBC
r i
om
IBC
r i
1
21
,
, ,
− = +[ ]π
P f E
V
V
I
I
s d I
IBC
sw SR
dc
IBC
r d
om
IBC
r d
1
21
,
, ,
− =
π
P r I V Ic i I
IBC
ce om
IBC
ce om
IBC
1
2
0
1
8
1
3
1
2
1
8
, − = +
( ) + +
π π
P r I V Ic d I
IBC
d om
IBC
f om
IBC
1
2
0
1
8
1
3
1
2
1
8
, − = −
( ) + −
π π
P P P P Pt d i B
IBC
c d B
IBC
c i B
IBC
s d B
IBC
s i B
IBC
,( ) , , , ,+ − − − − −= + + +
P f E E
V
V
I
I
s i B
IBC
sw ON OFF
dc
IBC
r i
dc
IBC
r i
,
, ,
. .− = +( ) 2
P f E
V
V
I
I
s d B
IBC
sw SR
dc
IBC
r d
dc
IBC
r d
,
, ,
. .− = 2
P I V r I dc i B
IBC
dc
IBC
ce ce dc
IBC
, .− = +( )0
P I V r I dc d B
IBC
dc
IBC
f d dc
IBC
, .− = +( ) −( )0 1
I I ddc
IBC
dc
IBC
2 1= −( )
WIND ENGINEERING VOLUME 35, NO. 4, 2011 451](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2ce15902-c6ee-4eee-b399-1728a840bc95-150128232617-conversion-gate02/85/Power-Electronics-8-320.jpg)

![6.3. Back-to-Back Converter (BBC)
It is well understood that the modulation algorithm is always unique for a specific
conventional PWM converter regardless of DC-AC or AC-DC operation mode, the model of
conduction and switching losses is also unique to a specific conventional PWM converter as
far as the conditions of physical devices keep unchanged. In view of these the PWM rectifier
results (35) and (36) for the conduction, Pcc1,d-R
BBC
and switching loss, Pcc1,i-R
BBC
of the anti
parallel diode respectively. In addition, (37) and (38) presents the conduction, Pss1,d-R
BBC
and
switching, Pss1,i-R
BBC
loss of the IGBT respectively [36].
(35)
(36)
(37)
(38)
where Iam
BBC
is the maximum value of the PMG line current at the input of the PWM rectifier.
The total loss, Ptt(d+i),-R
BBC
for the PWM rectifier is given by
(39)
Assuming the DC link capacitor average voltage is constant and remains in proper
coordination to work the inverter properly. This also implies that the mean capacitor current
is zero so as the power losses of the capacitor. The power loss of the DC link capacitor due to
leakage current is ignored for the time being.
In a similar manner as applied for the PWM inverter power loss calculation of the IBC and
IBBC, (19) to (22) are adapted to calculate the conduction and switching loss for the PWM
inverter of the BBC and the PWM inverter loss, Ptt(d+i),-I
BBC
is expressed by (40), while the total
losses, Pt
BBC
of the BBC is expressed by (41).
(40)
(41)
6.4. Matrix Converter (MC)
Since a suitable bidirectional semiconductor switch can be realized using several ways, this
research considered the back-to-back IGBT arrangement as it allows independent control of
the current in both directions within each switch. In this paper, the control method reported
[37] has been employed because of good input current control characteristics under balanced
input voltage conditions. In this analysis, a 3-phase MC is used and a sinusoidal current output
is assumed. The conduction losses of the diode and IGBT for a single phase are presented by
(42) and (43) respectively.
(42)P V I r Ic d
MC
f om
MC
d om
MC
, = + ( )2 2
0
2
π
P P Pt
IBBC
tt d i R
BBC
t d i I
BBC
= ++( )− +( )−, ,
P P P P Pt d i I
BBC
c d I
BBC
c i I
BBC
s d I
BBC
s i I
BBC
, , , , ,+( )− − − − −= + + +( )6 1 1 1 1
P P P P Ptt d i R
BBC
cc d R
BBC
cc i R
BBC
ss d R
BBC
ss i R
BBC
, , , , ,+( )− − − − −= + + +( )6 1 1 1 1
P f E E
V
V
I
I
ss i R
BBC
sw ON OFF
dc
BBC
r i
am
BBC
r i
1
1
,
, ,
− = +[ ]π
P f E
V
V
I
I
ss d R
BBC
sw SR
dc
BBC
r d
am
BBC
r d
1
1
,
, ,
− =
π
P r I V Icc i R
BBC
ce am
BBC
ce am
BBC
1
2
0
1
8
1
3
1
2
1
8
, − = +
( ) + +
π π
P r I V Icc d R
BBC
d am
BBC
f am
BBC
1
2
0
1
8
1
3
1
2
1
8
, − = −
( ) + −
π π
WIND ENGINEERING VOLUME 35, NO. 4, 2011 453](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2ce15902-c6ee-4eee-b399-1728a840bc95-150128232617-conversion-gate02/85/Power-Electronics-10-320.jpg)
![(43)
where Iom
BBC
is the maximum value of the line current at the output of the MC.
The switching losses when normalized with the reference voltage and current results (44)
and (45) for the diode and IGBT respectively.
(44)
(45)
where Va
BBC
is the maximum value of the line current at the output of the MC.
The total losses of the MC is then found as
(46)
7. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
The analytical calculations illustrated in the above sections were carried out to determine the
total power generation/losses, and afterwards efficiency in four power electronic converters
under varying wind speed conditions. The rated power for the wind turbine is assumed to be
1.5 kW. The inverter switching frequency is considered as 20 kHz and to investigate the worst-
case scenario of the power loss in this numerical simulation study, the modulation index is
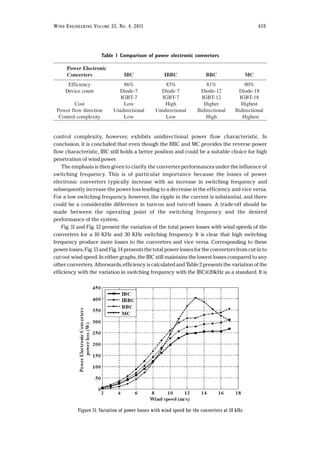
assumed unity and load current is assumed in phase with the output voltage. In addition, the
variation of duty cycle of the IBC and IBBC is considered as the maximum value. This is due to
the fact that the semiconductor devices will transmit the maximum indirect power, i.e.,
maximum stress on the devices thus resembles the worst case scenario [38]. The thermal
model of the converters is neglected provided that the heat sink is adequate enough to
maintain the semiconductors proper working. Power wasted in the power supplies for the
control of the converters is also ignored (It may be between 10–20W). The analytical
calculation is based on the EUPEC IGBT module FP15R12W1T4_B3 [39].
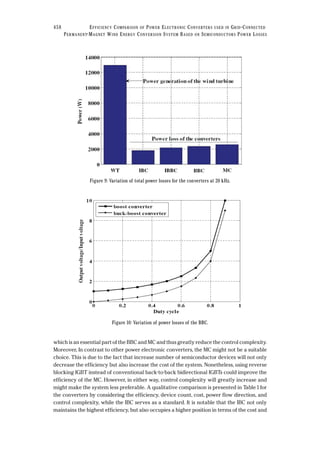
Fig. 3 shows the power generation by the wind turbine based on the modeling equations
described in Section 5 and operating from a wind speed of 2 m/s (cut-in) to 17 m/s (cut-out),
while the rated wind speed is 13 m/s. The furling control has been established through the
furling model (6) and effectively reduces the power above rated wind speed. This power
serves as the dynamic power reference for all power electronic converters and summed up to
calculate the total power generation by the WT for the considered wind speed regime.
The conduction and switching losses for the diodes and IGBTs of the IBC, which composed of
a 3-phase diode bridge rectifier, a boost converter and a PWM inverter is presented in Fig. 4a–c
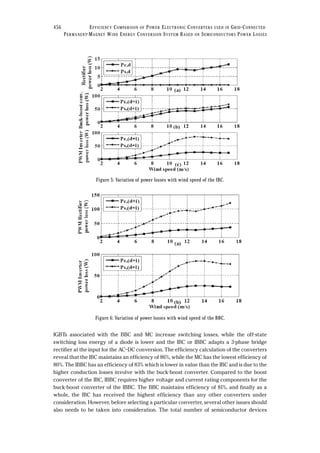
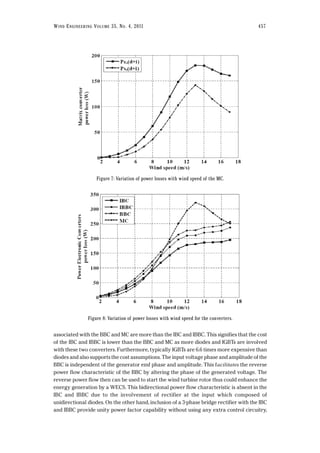
respectively for a similar wind variation. In an analogous fashion, power losses for the IBBC, BBC
and MC are presented through Fig. 5, Fig. 6 and Fig. 7 respectively. The total loss of each
converter is shown in Fig. 8 and can be found by summing up all the losses (conduction and
switching) for each converters. The results of the power losses for the converters show that the
power loss is higher for a low wind speed (12m/s) than for the rated wind speed (13 m/s) except
for the MC and are due to the furling action. The furling angle varies abruptly from 9 m/s to 13
m/s with negligible change close to the maximum speed. Meanwhile, the voltage remains linear
with the wind speed. As a result, the captured aerodynamic power as well as the current are
asymmetrical on either side of the rated wind speed and are reflected on the power loss curve.
P P P P Pt
IBBC
c d
MC
c i
MC
s d
MC
s i
MC
= + + +( )3 , , , ,
P f E E
V
V
I
I
s i
MC
sw ON OFF
a
MC
r d
am
IBBC
r d
,
, ,
. .= +( ) 12
2
π
P f E
V
V
I
I
s d
MC
sw SR
a
MC
r d
am
IBBC
r d
,
, ,
. .=
12
2
π
P V I r Ic i
MC
ce om
MC
ce om
MC
, = + ( )2 2
0
2
π
454 EFFICIENCY COMPARISON OF POWER ELECTRONIC CONVERTERS USED IN GRID-CONNECTED
PERMANENT-MAGNET WIND ENERGY CONVERSION SYSTEM BASED ON SEMICONDUCTORS POWER LOSSES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2ce15902-c6ee-4eee-b399-1728a840bc95-150128232617-conversion-gate02/85/Power-Electronics-11-320.jpg)