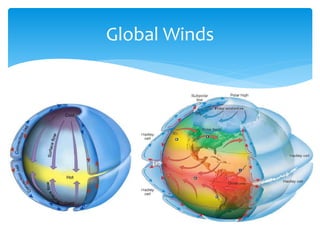
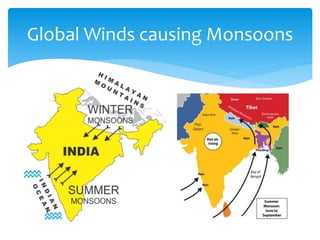
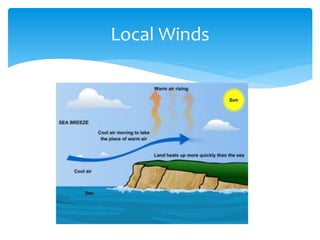
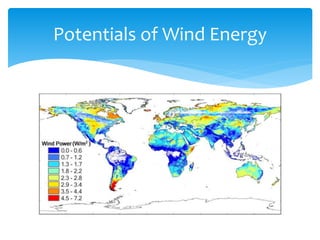
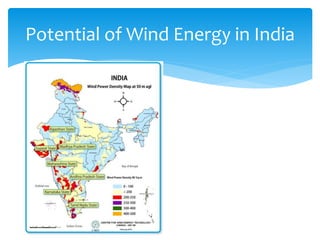
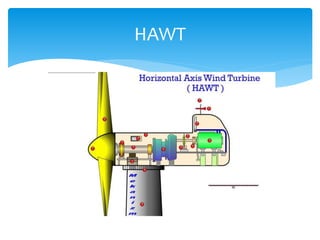
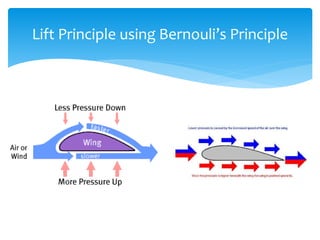
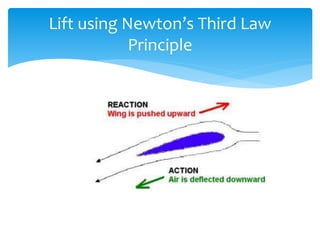
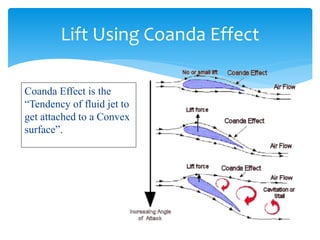
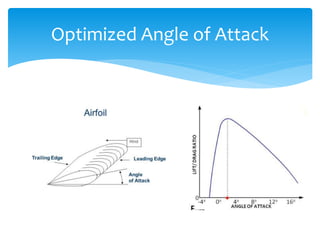
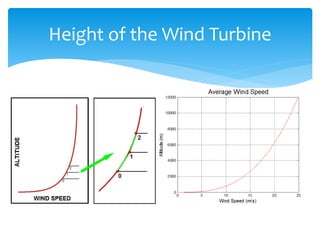
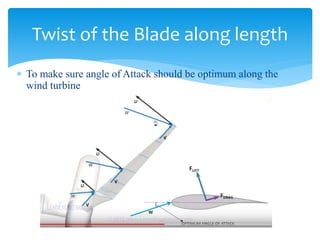
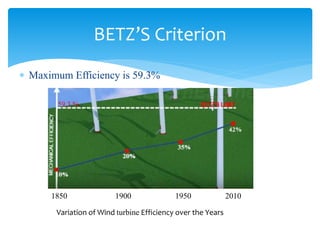
The document discusses various aspects of wind energy, including its potential sources and types of wind turbines such as horizontal and vertical axis windmills. It covers the design considerations, aerodynamics, and efficiency of wind turbines, referencing principles like Bernoulli’s principle and Newton’s third law. Additionally, it highlights the importance of mechanical power transmission, blade design factors, and innovations in wind energy applications.