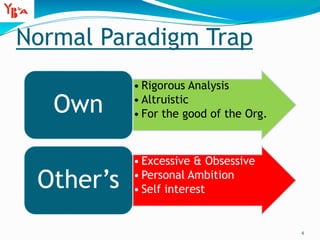
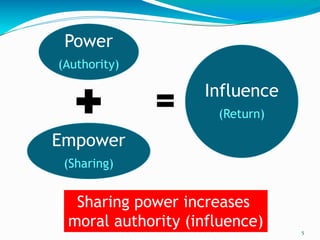
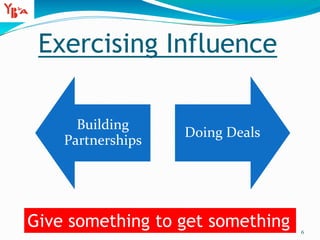
This document discusses sources of power and influence in organizations. It identifies 8 sources of power: positional, relevance, centrality, autonomy, personal characteristics, expertise, charisma, and effort. It also distinguishes between power, which is based on authority, and influence, which involves sharing power to gain influence through moral authority and partnerships. The document provides tips for exercising influence, including giving something to get something and building partnerships. It examines power dynamics and barriers to influence, as well as qualities needed for organizational excellence.