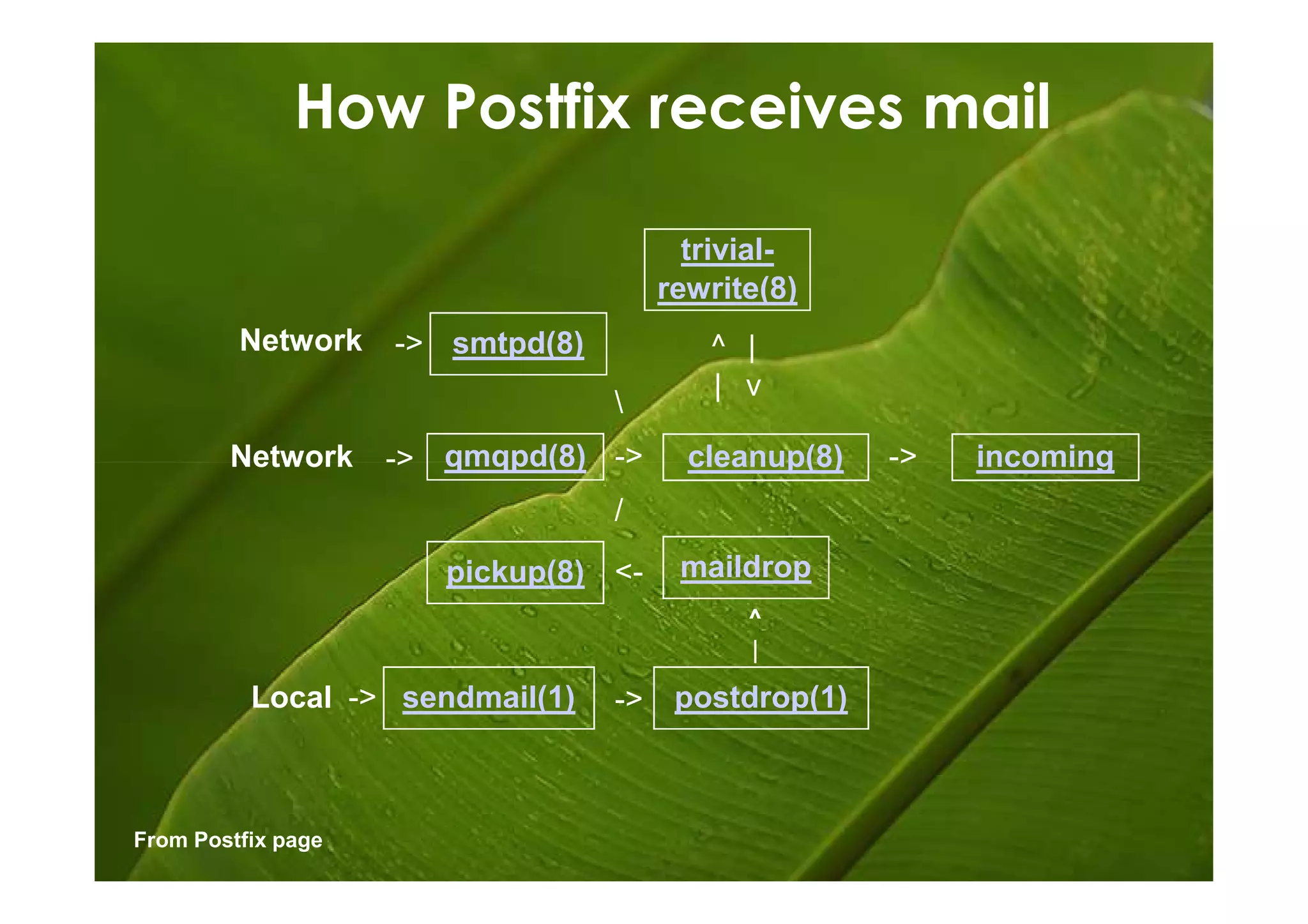
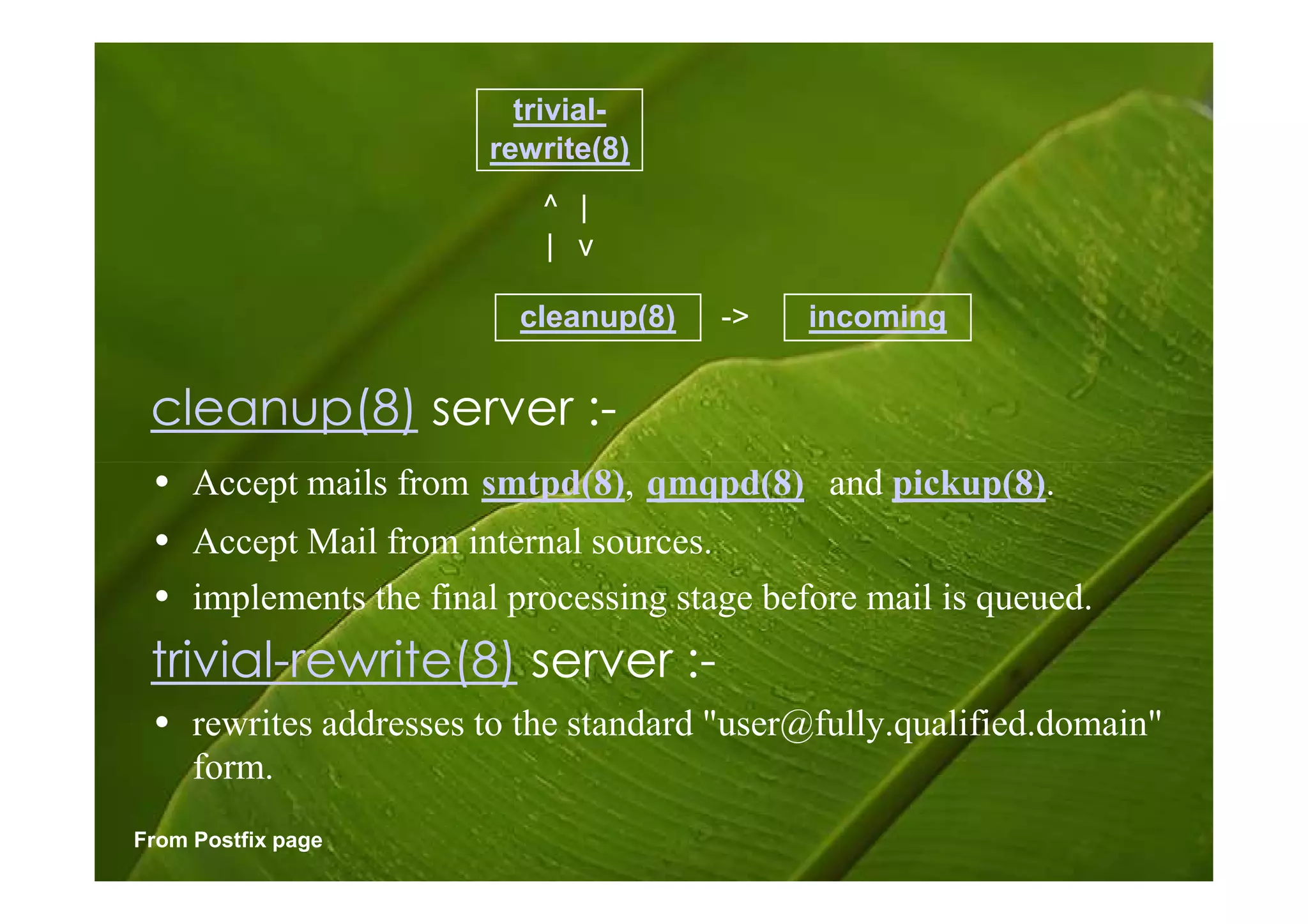
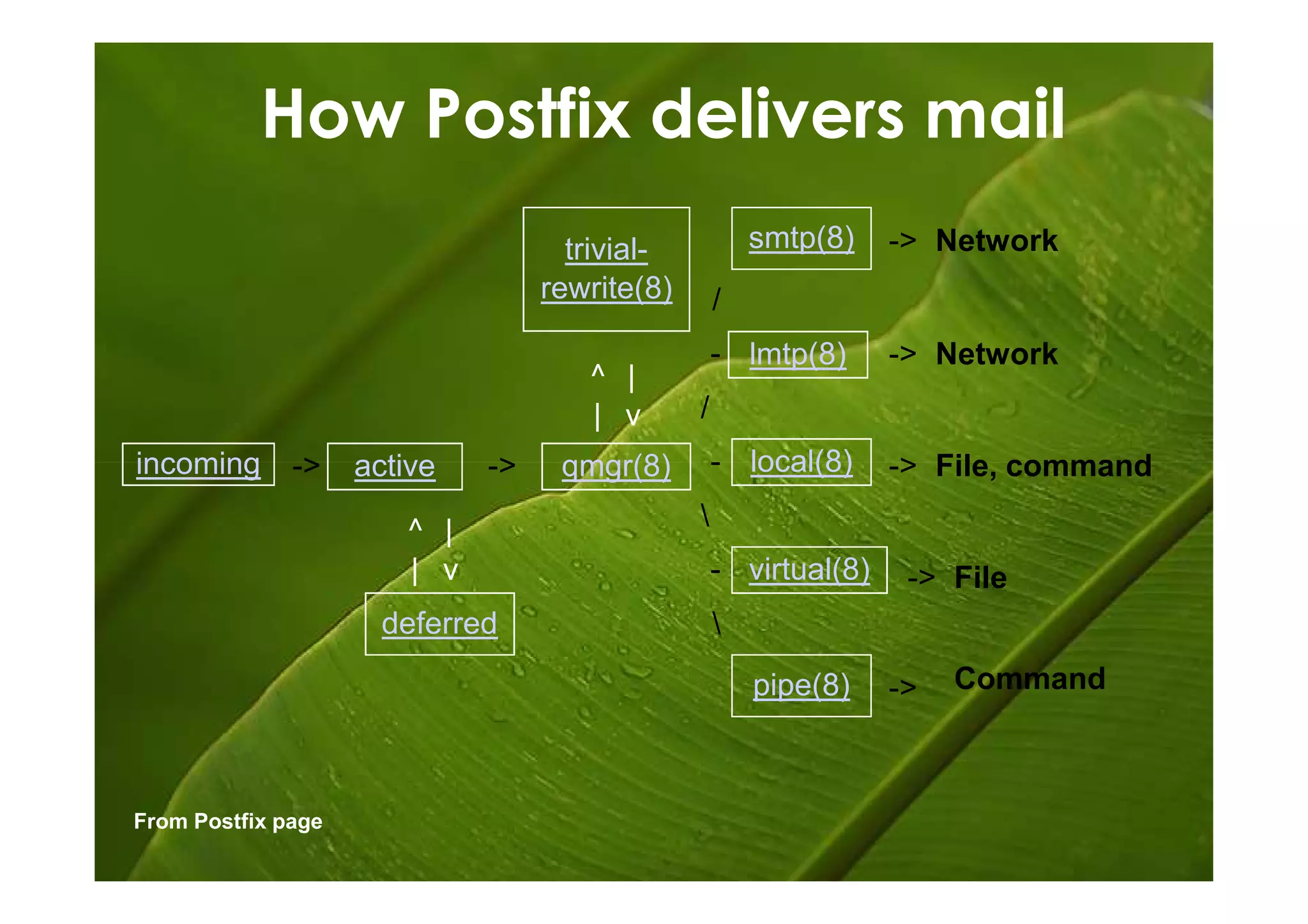
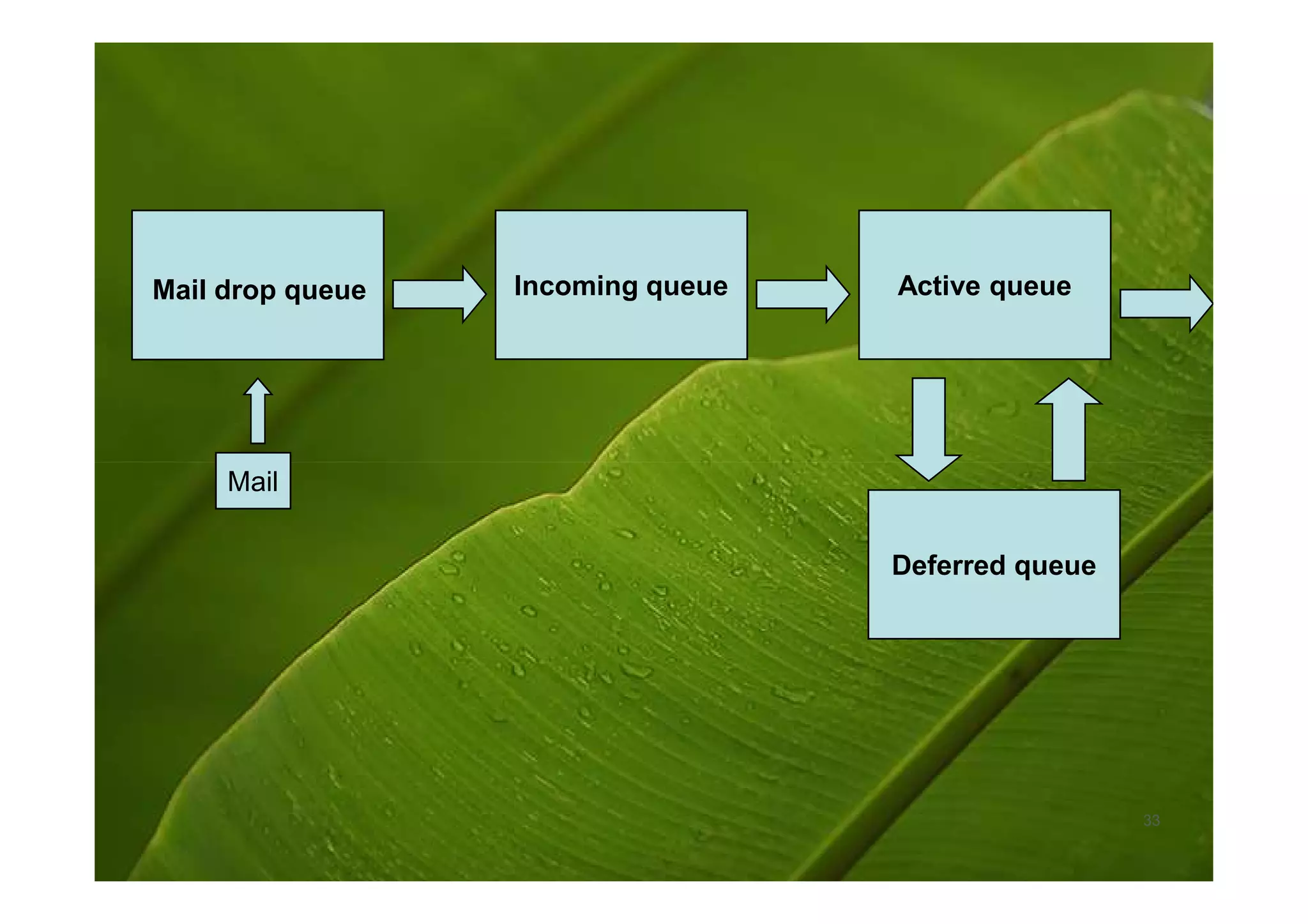
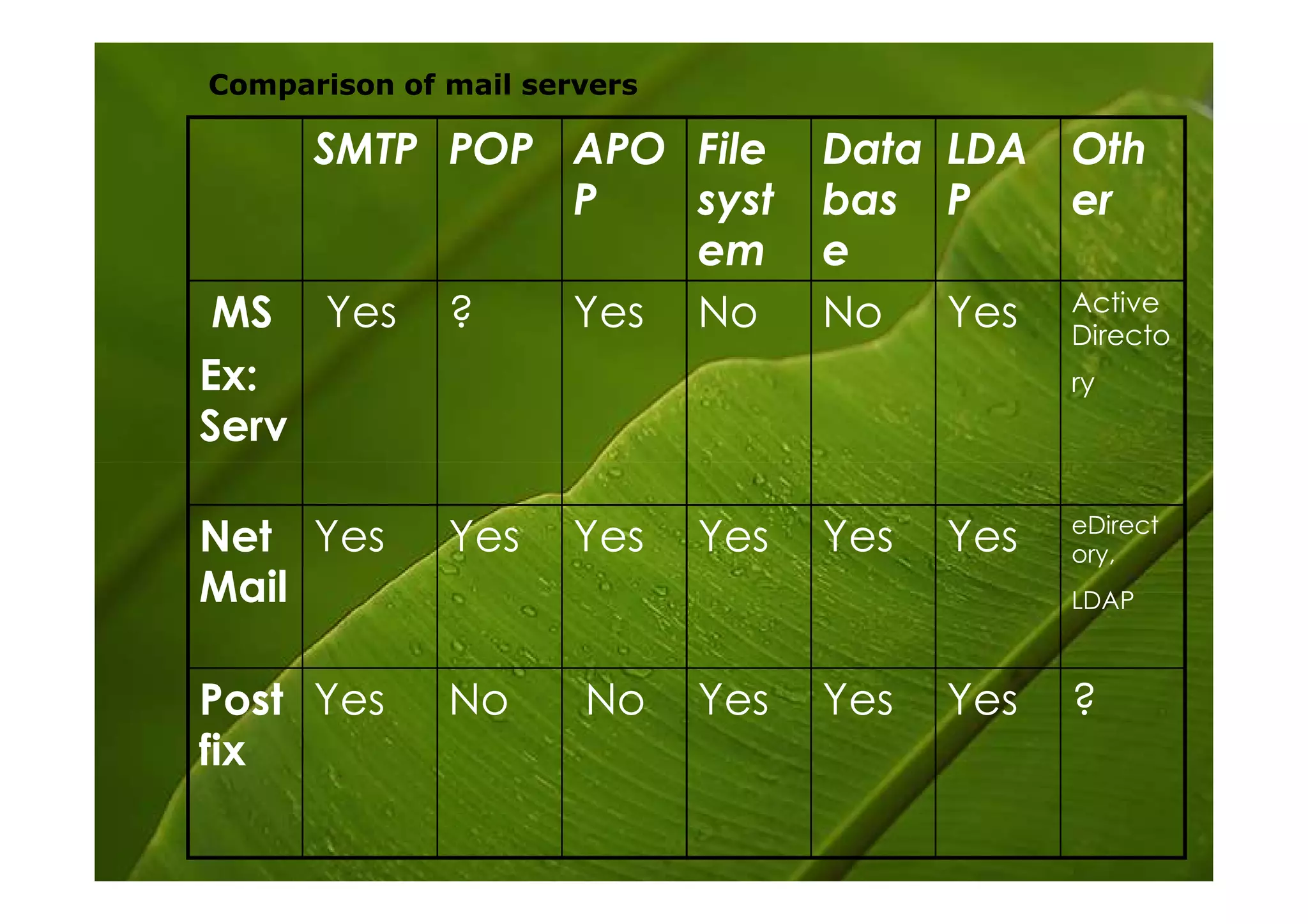
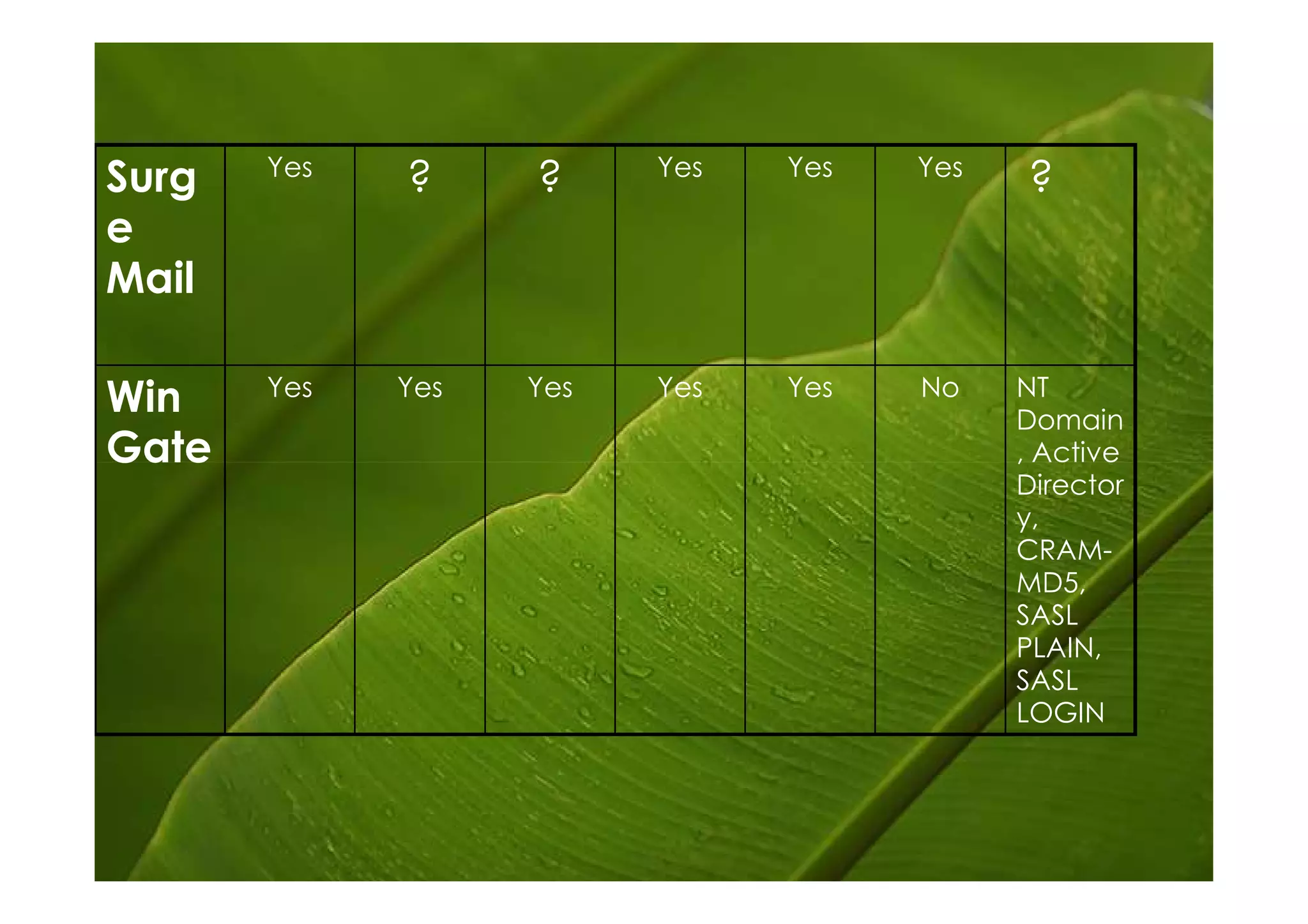
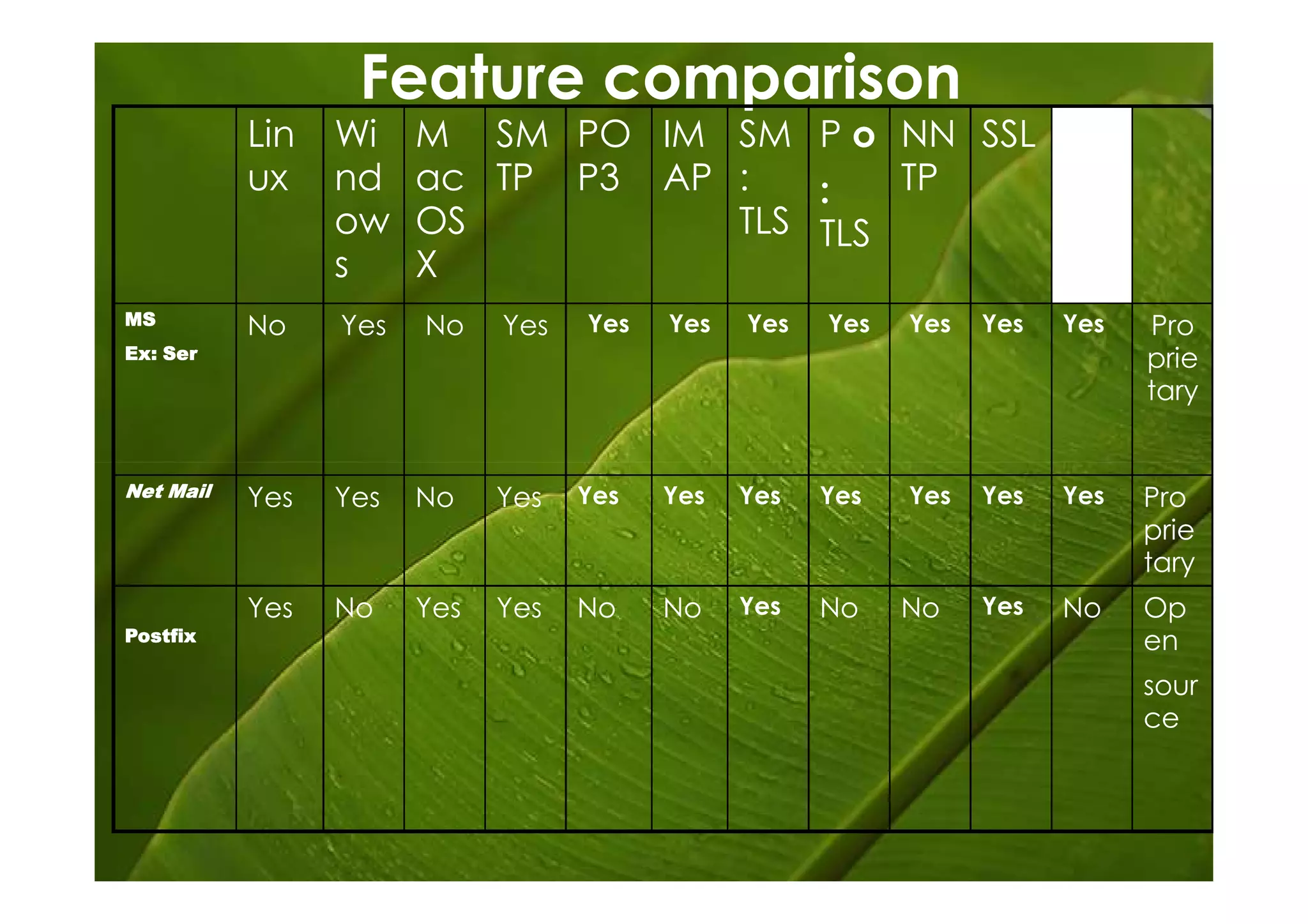
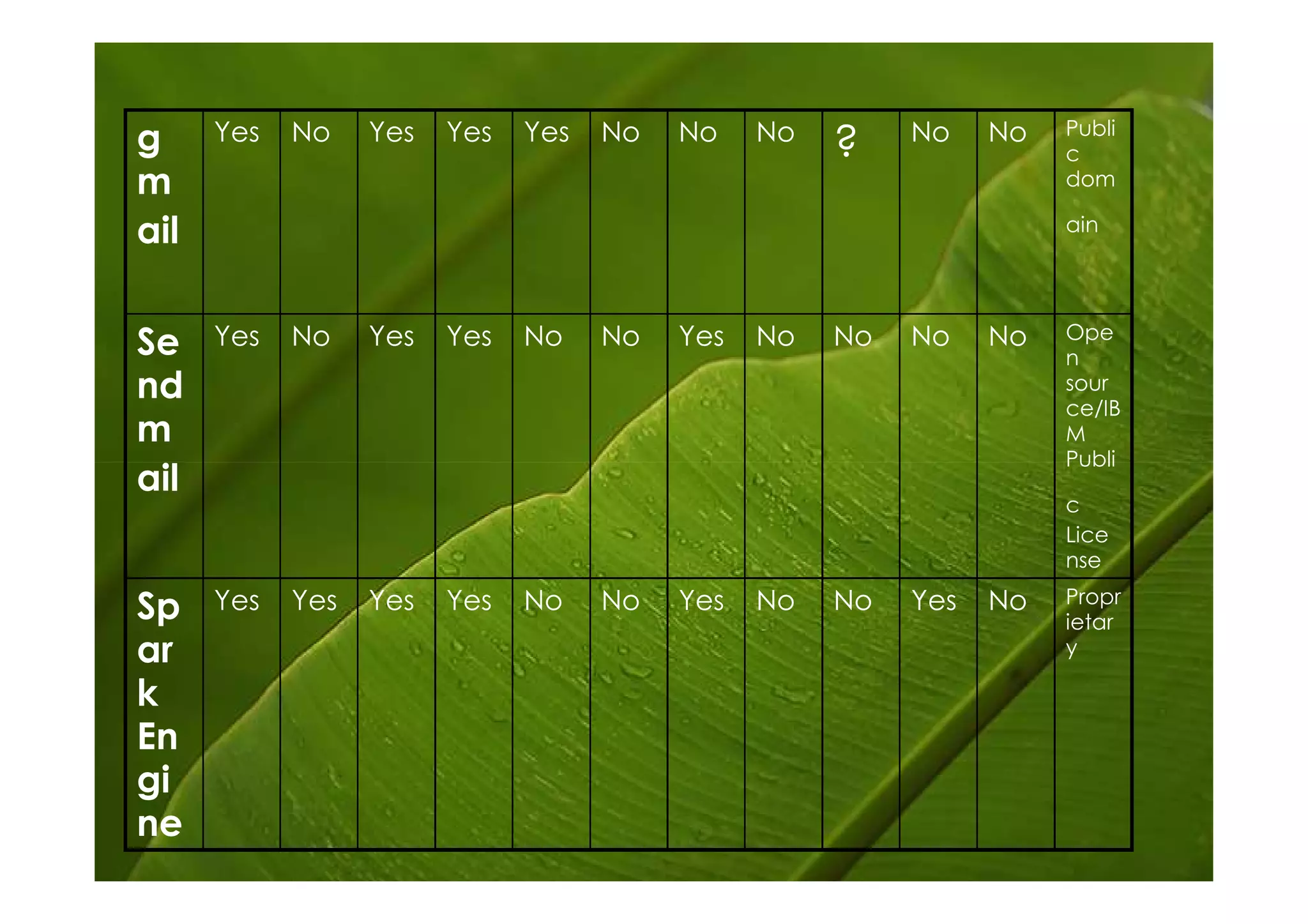
Postfix is a free and open-source mail transfer agent (MTA) that is commonly used on Linux systems. It handles receiving and delivering email by using several server processes and queues. When receiving mail, Postfix uses smtpd, qmqpd, pickup, and cleanup servers to validate messages and add them to the incoming queue. For delivery, it uses qmgr to route messages from the incoming queue through active delivery agents like smtp, lmtp, local, and virtual to recipients or deferred queue if delivery fails. Postfix prioritizes stability, scalability and security in its flexible and modular design.