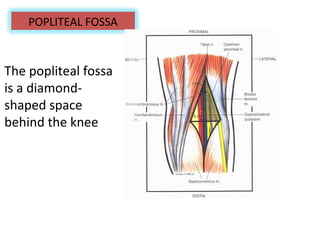
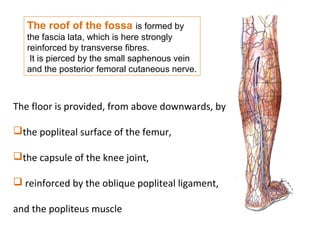
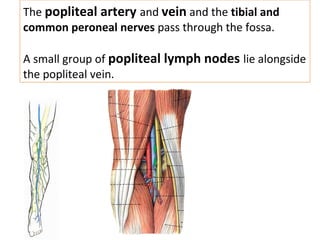
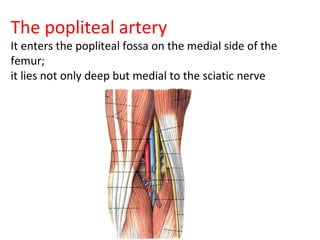
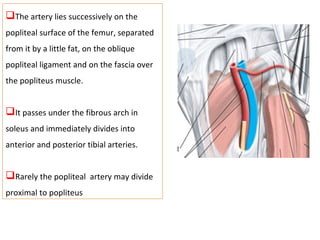
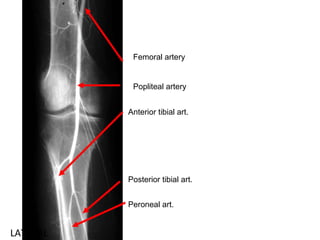
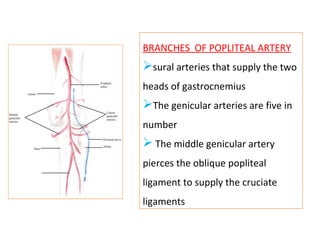
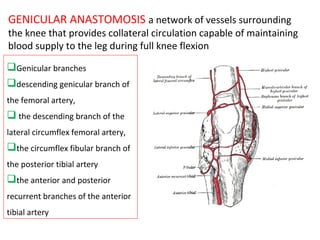
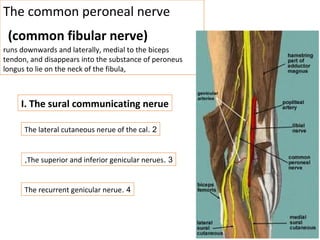
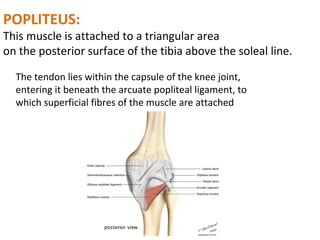
The popliteal fossa is a diamond-shaped space behind the knee where important structures like the popliteal artery, vein and nerves pass through. The roof is formed by fascia and the floor is formed by bones and ligaments. The popliteal artery enters the fossa and divides into anterior and posterior tibial arteries. The common peroneal and tibial nerves also pass through providing sensation and innervation to the leg. The popliteus muscle assists in rotating the femur to unlock the knee during flexion.