Embed presentation
Downloaded 780 times

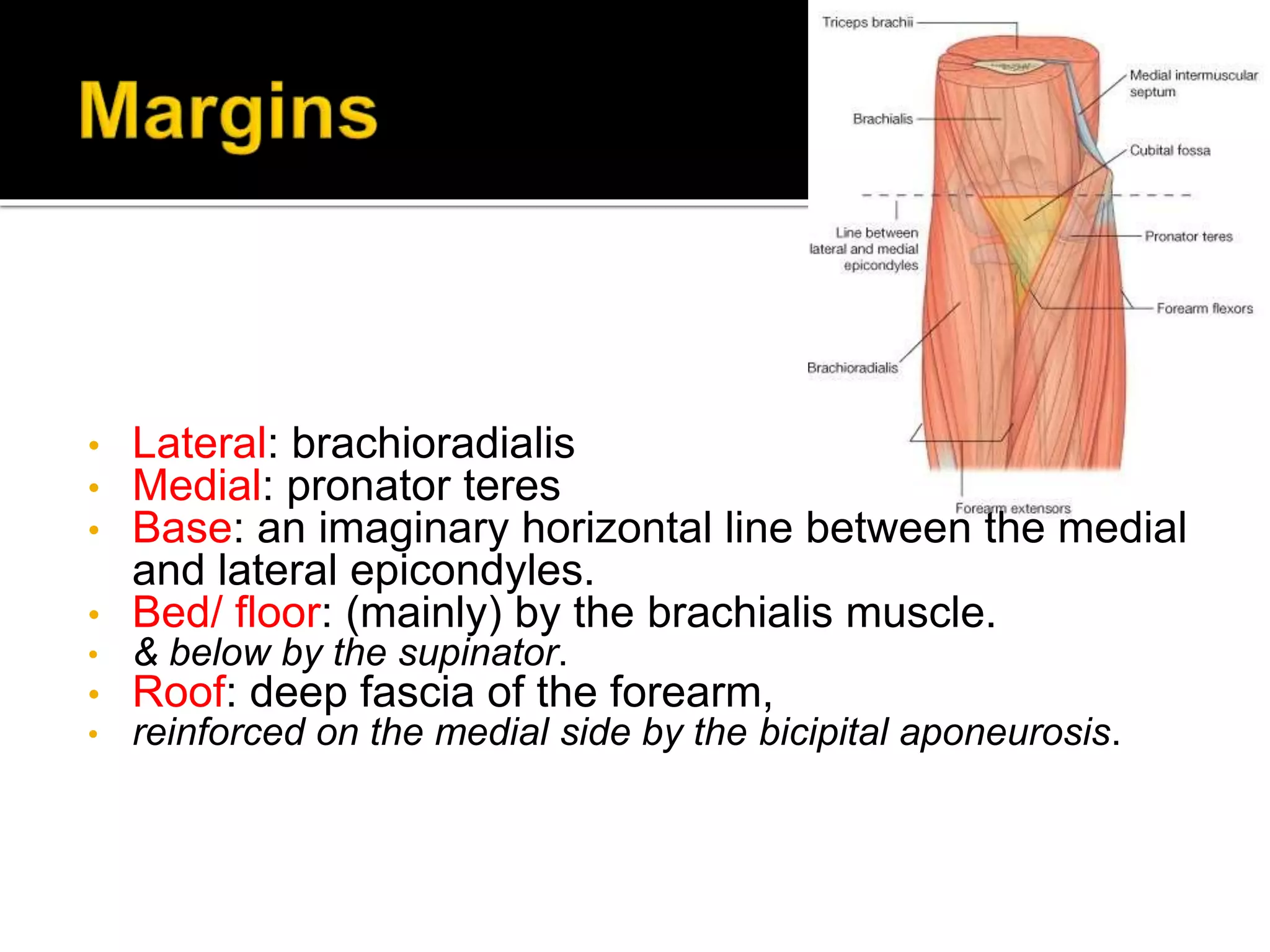
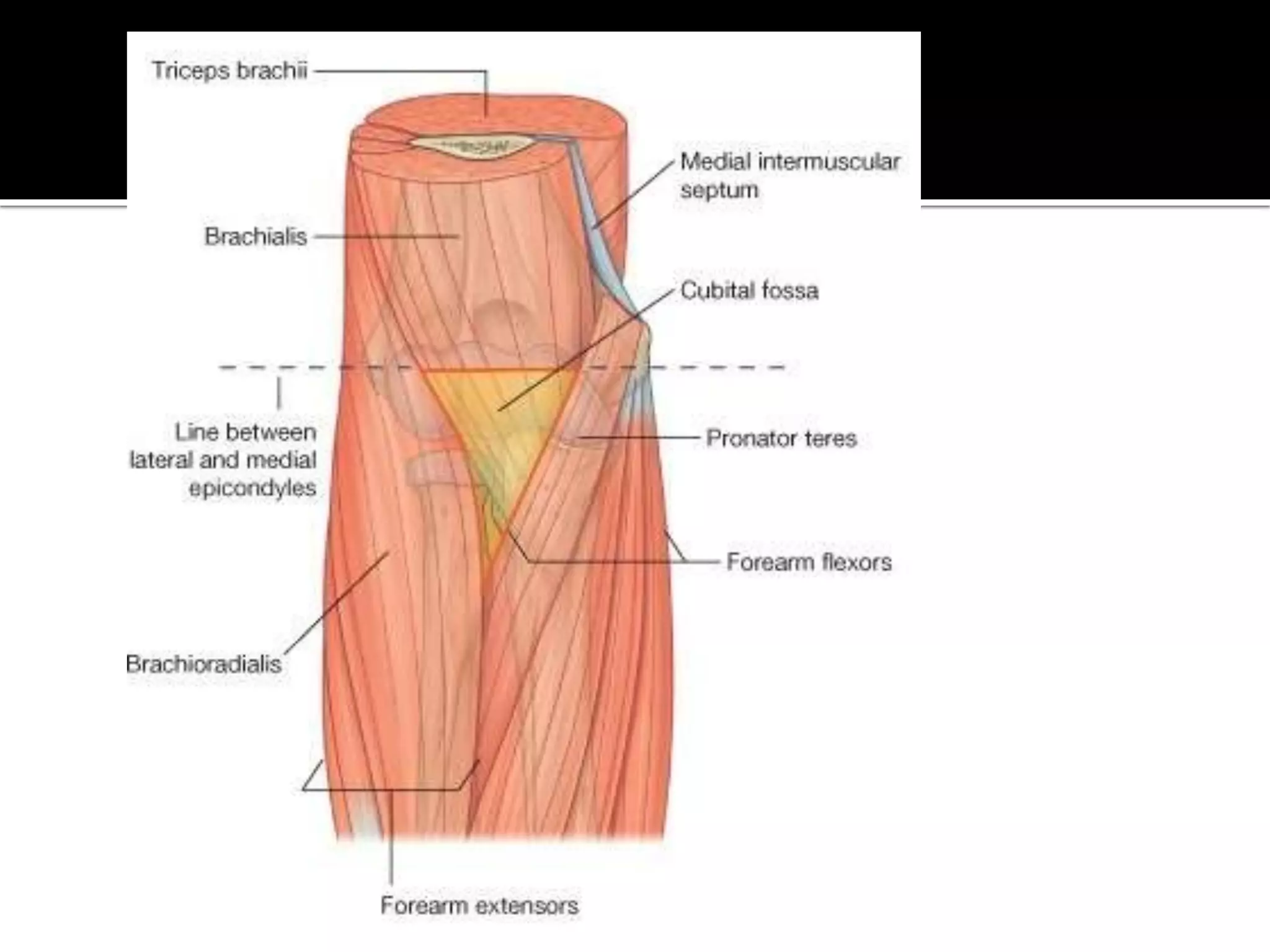
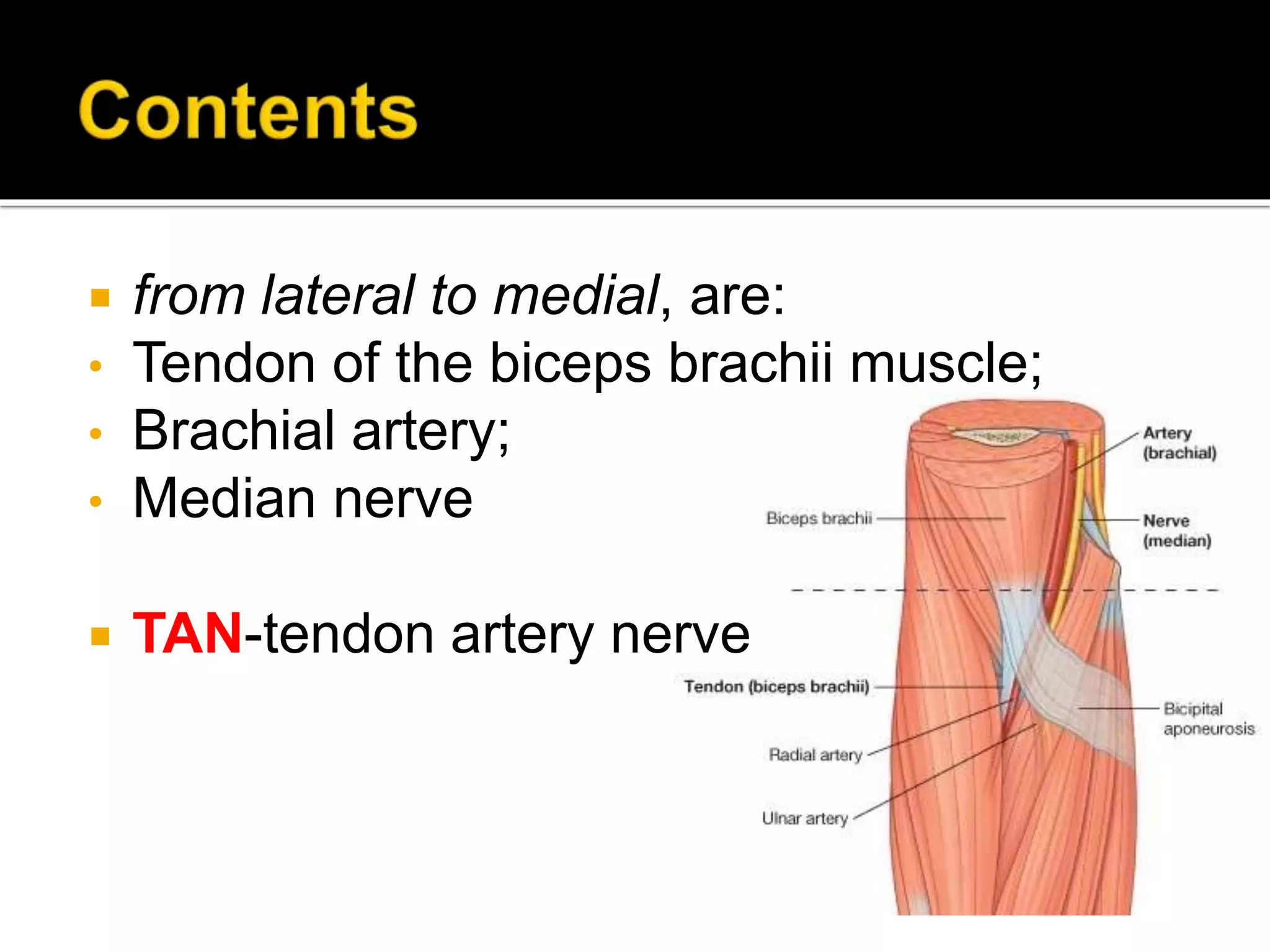

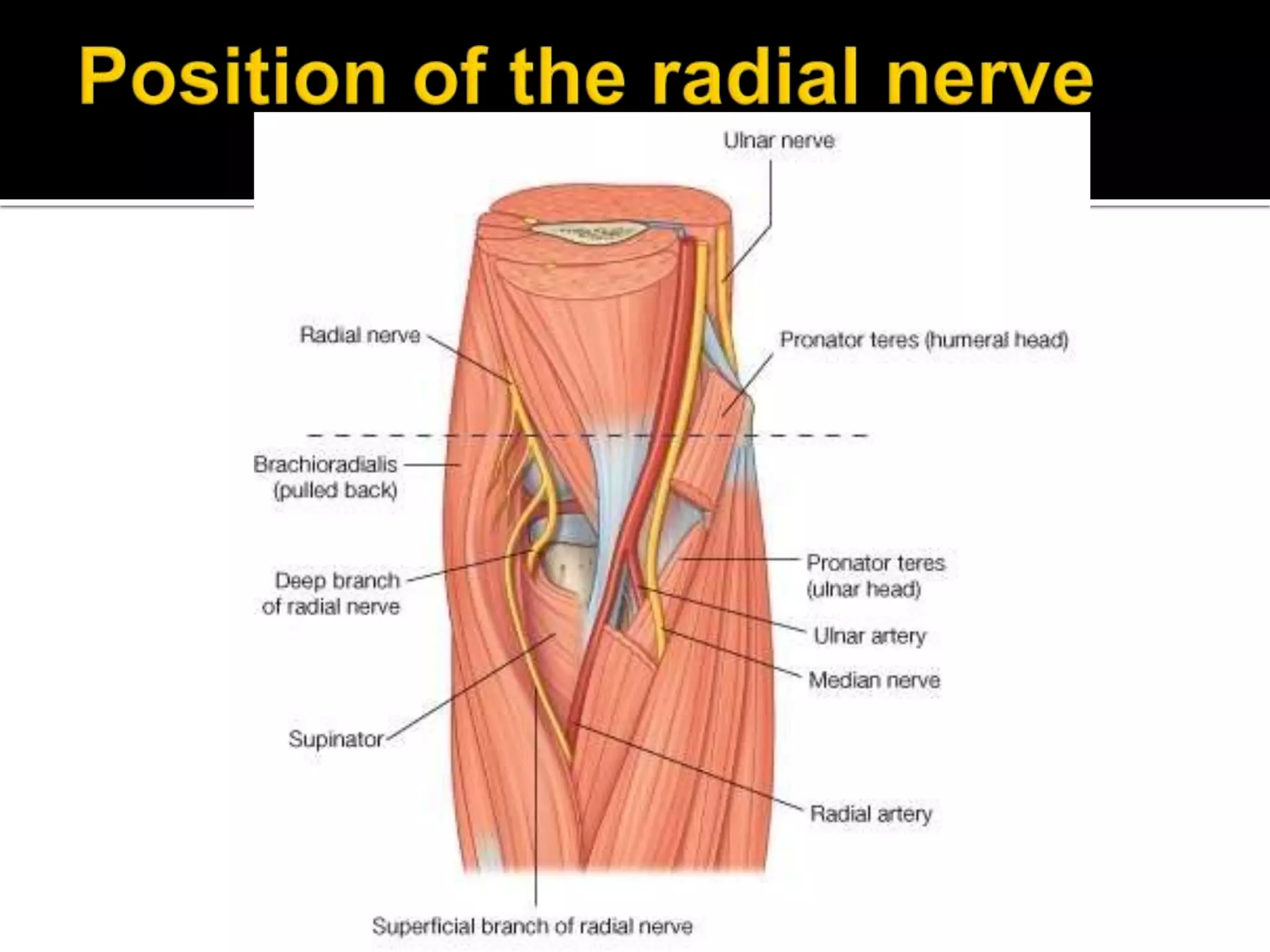
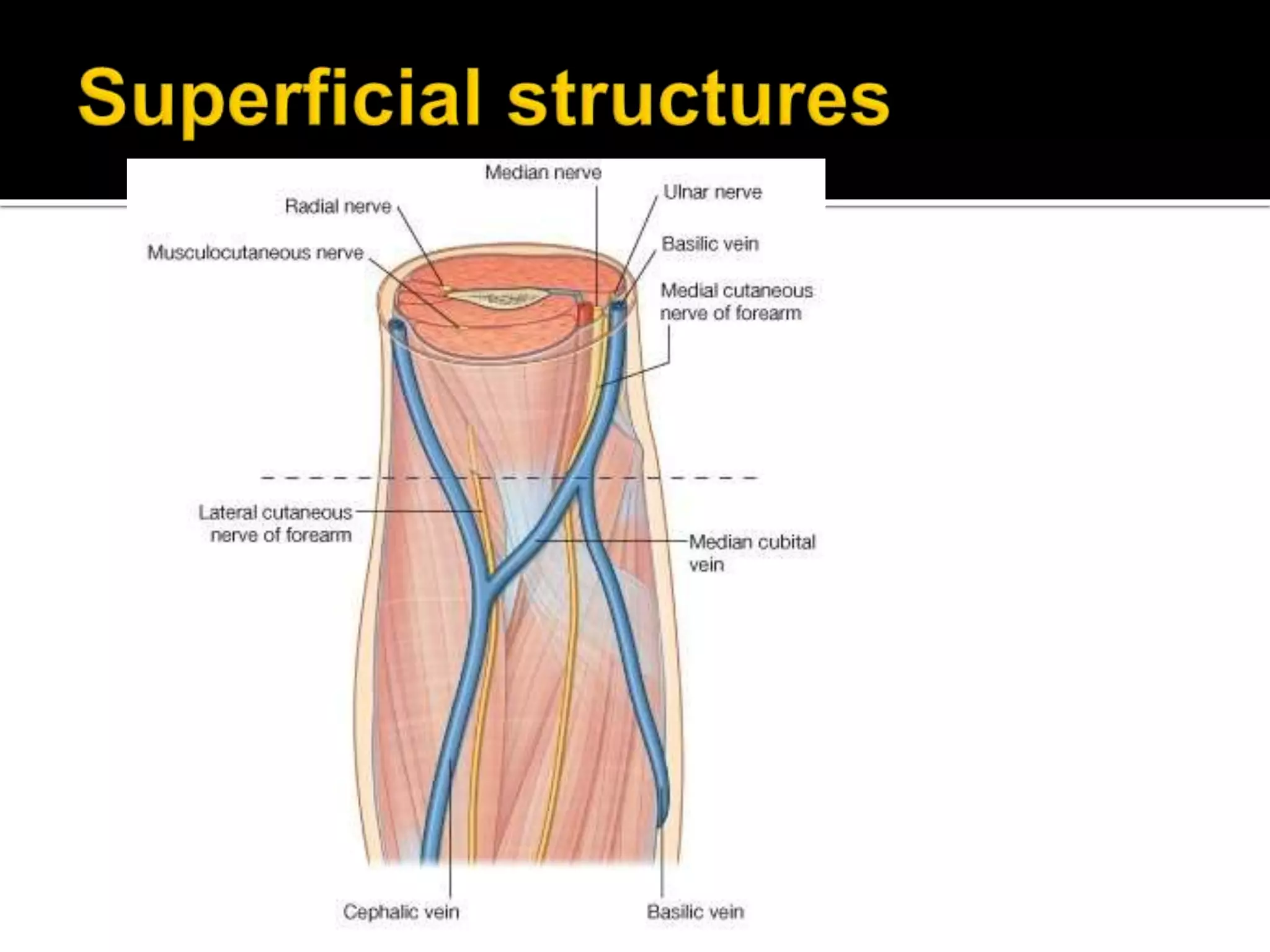
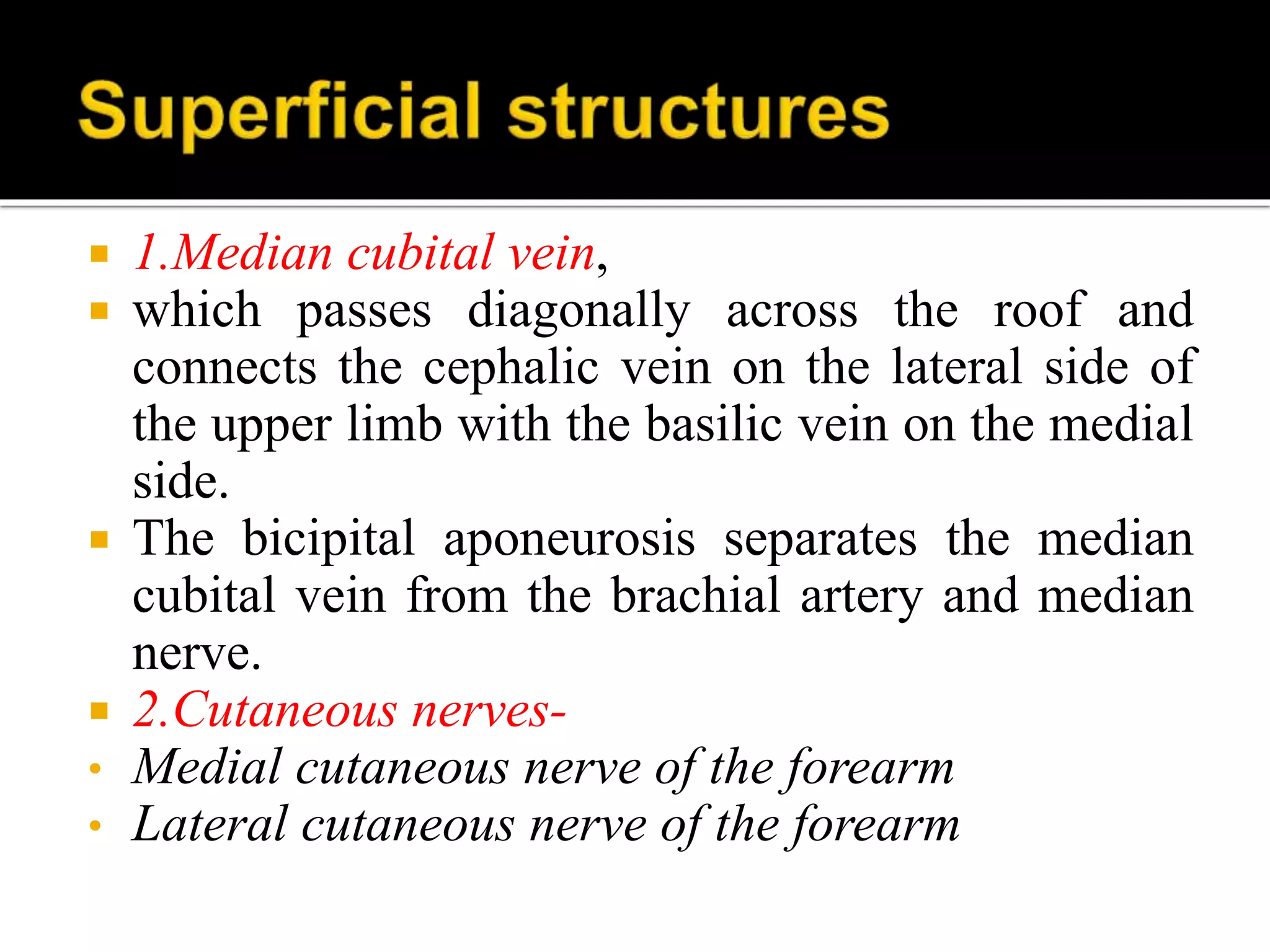

The cubital fossa is located on the anterior surface of the elbow. It is bordered laterally by the brachioradialis muscle, medially by the pronator teres muscle, and its floor is formed mainly by the brachialis muscle. The brachial artery, median nerve, and biceps brachii tendon pass through the cubital fossa from lateral to medial. The radial nerve divides into superficial and deep branches as it passes through the cubital fossa, while the ulnar nerve passes behind the medial epicondyle. Structures passing through or adjacent to the cubital fossa include the median cubital vein and cutaneous nerves of the forearm.







