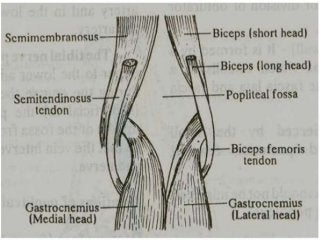
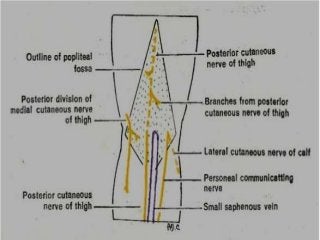
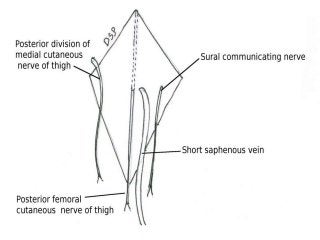
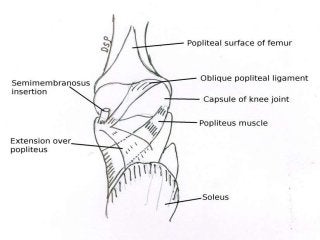
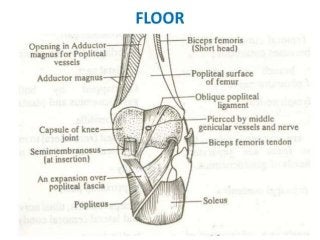
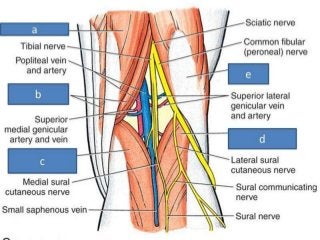
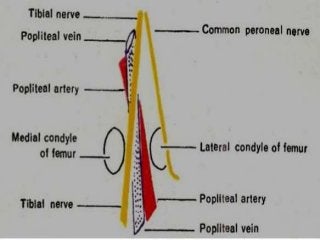
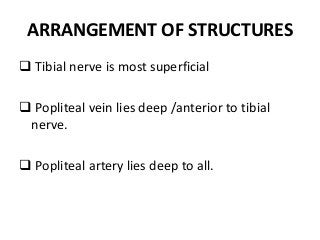
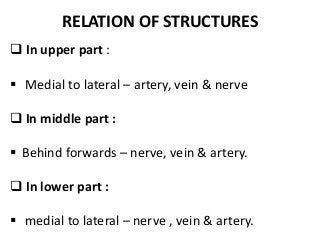
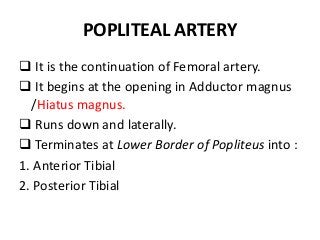
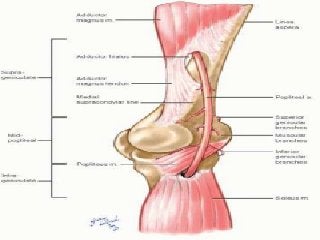
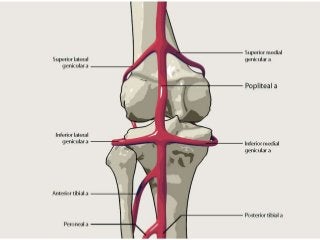
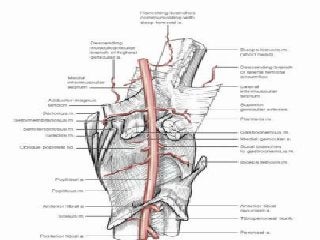
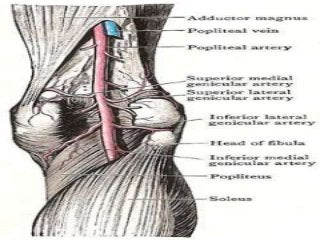
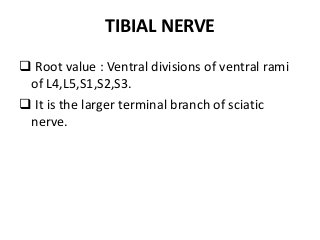
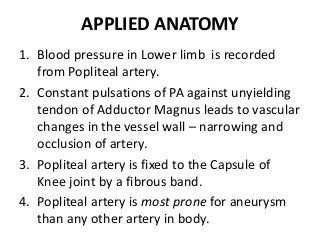
The popliteal fossa is a diamond-shaped depression behind the knee joint containing major neurovascular structures. It is bounded by muscles and contains the popliteal artery, vein and tibial nerve. The popliteal artery is the continuation of the femoral artery, while the popliteal vein forms the continuation of the femoral vein. The tibial nerve provides branch innervation to muscles and skin in the posterior leg. The common peroneal nerve is also present, branching to innervate muscles on the lateral leg. These structures have important relationships that allow blood flow and innervation to the lower limb.