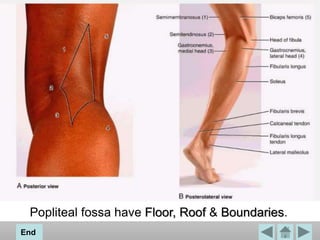
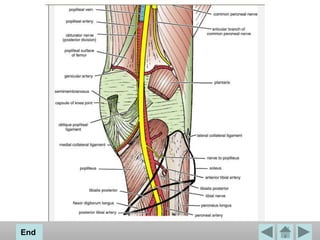
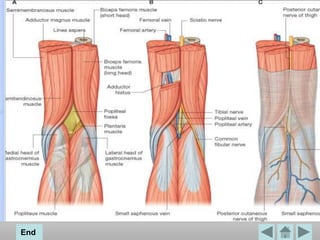
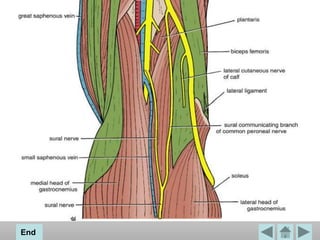
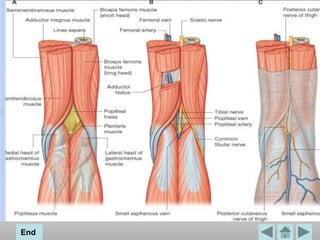
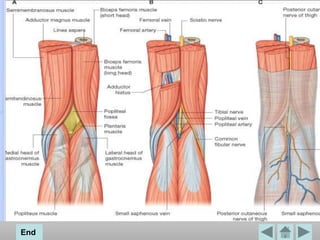
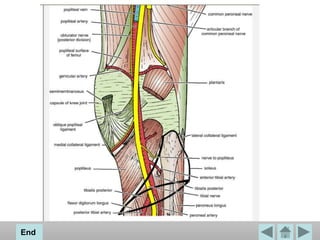
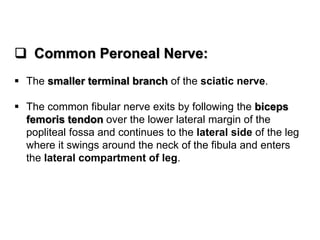
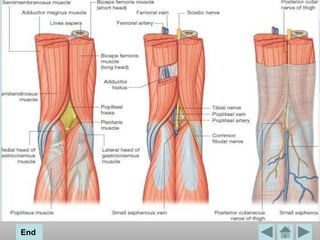
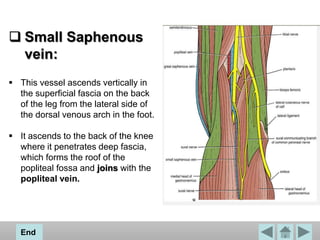
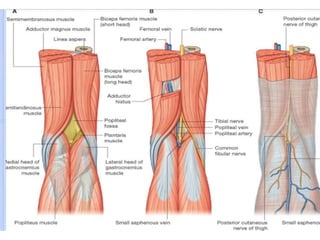
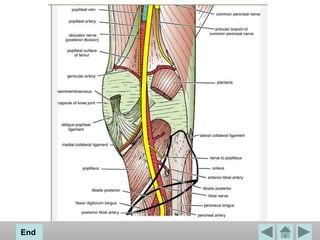
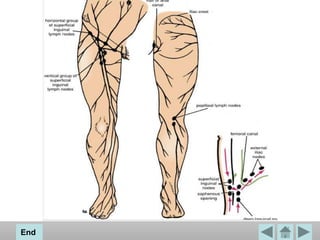
The popliteal fossa is a diamond-shaped space located behind the knee. It contains the popliteal artery and vein, the tibial and common fibular nerves, the small saphenous vein, and popliteal lymph nodes. The popliteal artery continues as the femoral artery passes through the adductor hiatus and descends through the popliteal fossa before dividing into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries. The nerves innervate the muscles and skin of the calf and back of the leg.