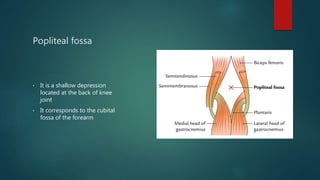
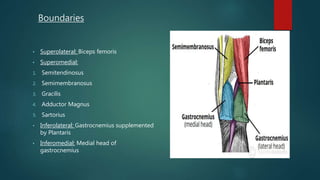
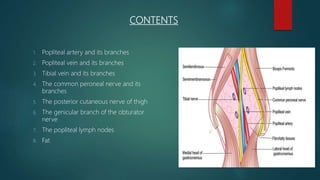
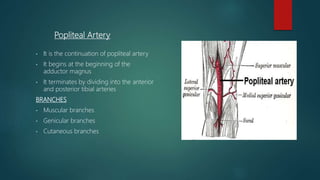
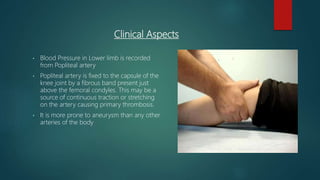
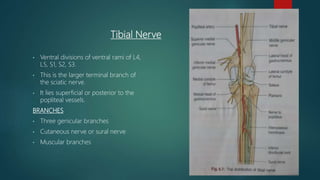
The popliteal fossa is a shallow depression located behind the knee joint. It contains the popliteal artery and its branches, the popliteal vein and its branches, the tibial nerve and its branches, the common peroneal nerve and its branches, the posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh, genicular branches of the obturator nerve, and popliteal lymph nodes. The popliteal artery begins at the beginning of the adductor magnus and terminates by dividing into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries. Damage to structures like the popliteal artery or tibial nerve can cause issues like blood clots, aneurysms, or sensory and motor loss.