This document provides an overview of polynomials, including:
- Defining polynomials as expressions involving variables and coefficients using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponents.
- Discussing the history of polynomial notation pioneered by Descartes.
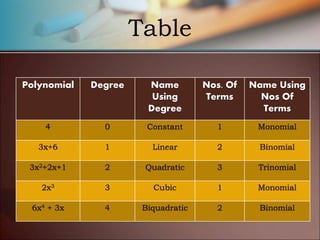
- Explaining the different types of polynomials like monomials, binomials, and trinomials.
- Outlining common uses of polynomials in mathematics, science, and other fields.
- Describing how to find the degree of a polynomial and graph polynomial functions.
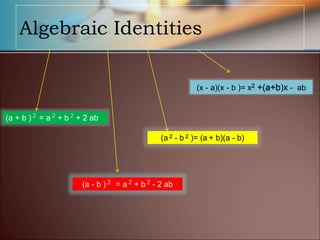
- Explaining arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, and division that can be performed on polynomials.